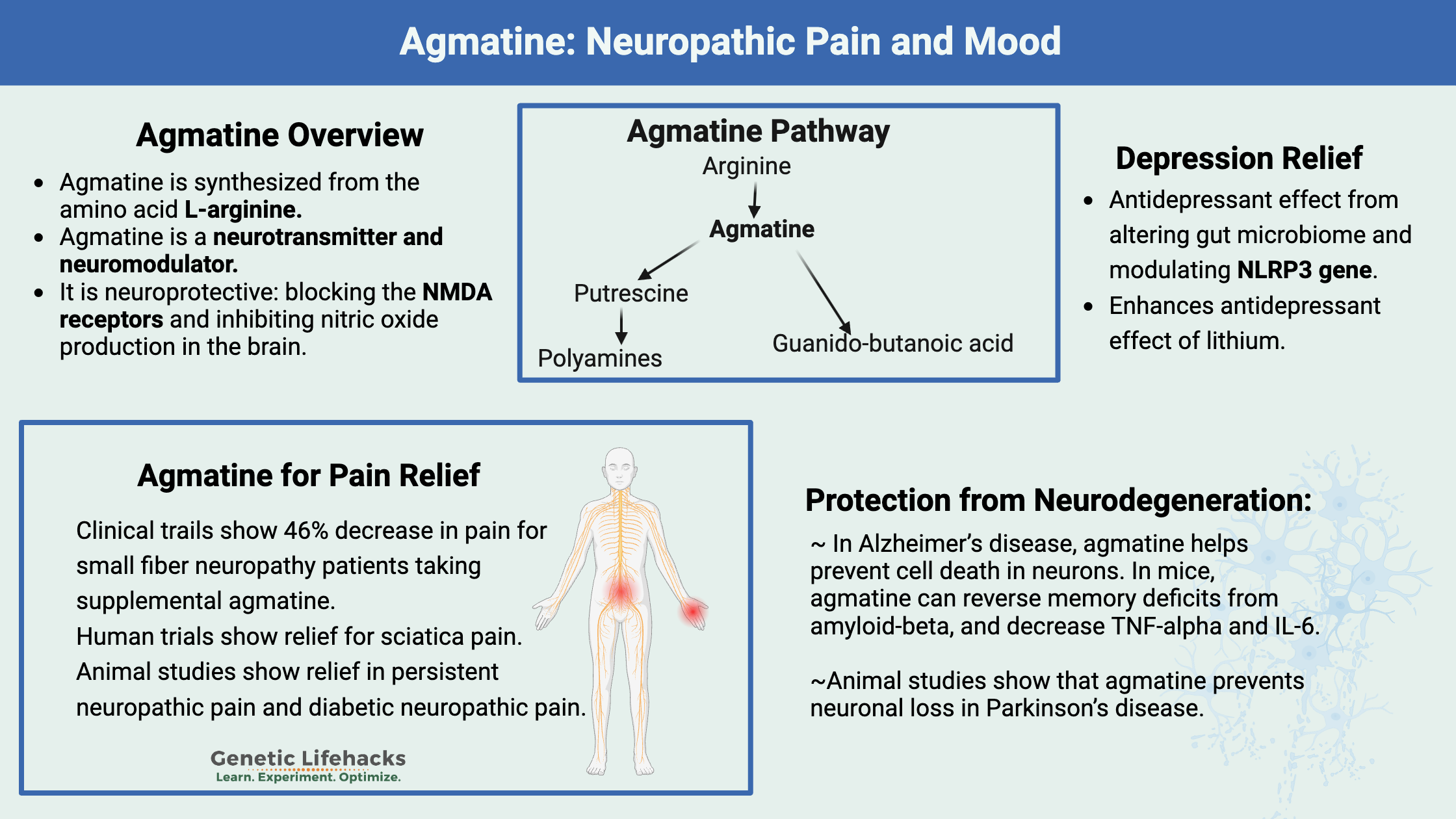
In the brain, agmatine has neuroprotective effects by protecting against excitotoxicity. Some research points to it blocking the NMDA receptors and also inhibiting nitric oxide production in the brain. Protecting the brain against excess excitation may be beneficial in dementia, depression, and schizophrenia.[ref]
El-Sayed, Ek, et al. “Neuroprotective Effect of Agmatine (Decarboxylated l -Arginine) against Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease.” Human & Experimental Toxicology, vol. 38, no. 2, Feb. 2019, pp. 173–84. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327118788139.
Giusepponi, Maria Elena, et al. “Combined Interactions with I1-, I2-Imidazoline Binding Sites and Α2-Adrenoceptors To Manage Opioid Addiction.” ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, vol. 7, no. 10, Oct. 2016, pp. 956–61. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00290.
Izadi, Sadegh, et al. “Agmatine Prevents the Memory Impairment and the Dysfunction of Hippocampal GSK-3β and ERK Signaling Induced by Aluminum Nanoparticle in Mice.” Behavioural Pharmacology, vol. 34, no. 5, Aug. 2023, pp. 299–305. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0000000000000735.
Kotagale, Nandkishor, Rupali Deshmukh, et al. “Agmatine Ameliorates Manifestation of Depression-like Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease.” Brain Research Bulletin, vol. 160, July 2020, pp. 56–64. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.04.013.
Kotagale, Nandkishor, Madhura Dixit, et al. “Agmatine Reverses Memory Deficits Induced by Aβ1-42 Peptide in Mice: A Key Role of Imidazoline Receptors.” Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, vol. 196, Sept. 2020, p. 172976. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172976.
Kralj Cigić, Irena, et al. “Accumulation of Agmatine, Spermidine, and Spermine in Sprouts and Microgreens of Alfalfa, Fenugreek, Lentil, and Daikon Radish.” Foods (Basel, Switzerland), vol. 9, no. 5, May 2020, p. 547. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050547.
“L-Arginine Benefits, Uses & Side Effects.” Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/22536-l-arginine. Accessed 16 Feb. 2026.
Li, Xueying, et al. “Agmatine Alleviates Epileptic Seizures and Hippocampal Neuronal Damage by Inhibiting Gasdermin D-Mediated Pyroptosis.” Frontiers in Pharmacology, vol. 12, Aug. 2021, p. 627557. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.627557.
Lopez, Marcelo F., et al. “Agmatine Reduces Alcohol Drinking and Produces Antinociceptive Effects in Rodent Models of Alcohol Use Disorder.” Alcohol (Fayetteville, N.Y.), vol. 109, June 2023, pp. 23–33. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2023.01.003.
Taksande, Brijesh G., et al. “Agmatine Reverses Ethanol Consumption in Rats: Evidences for an Interaction with Imidazoline Receptors.” Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, vol. 186, Nov. 2019, p. 172779. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2019.172779.
Uzbay, Tayfun I. “The Pharmacological Importance of Agmatine in the Brain.” Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, vol. 36, no. 1, Jan. 2012, pp. 502–19. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.08.006.
Valverde, Ana Paula, et al. “Agmatine as a Novel Candidate for Rapid-Onset Antidepressant Response.” World Journal of Psychiatry, vol. 11, no. 11, Nov. 2021, pp. 981–96. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.981.
Wang, Xiao-Fei, et al. “Agmatine Prevents Adaptation of the Hippocampal Glutamate System in Chronic Morphine-Treated Rats.” Neuroscience Bulletin, vol. 32, no. 6, Dec. 2016, pp. 523–30. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0031-z.
Xu, Weilin, et al. “Neuroprotective Role of Agmatine in Neurological Diseases.” Current Neuropharmacology, vol. 16, no. 9, Nov. 2018, pp. 1296–305. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170808120633.