Celiac Genes: How to Check Your Raw Data
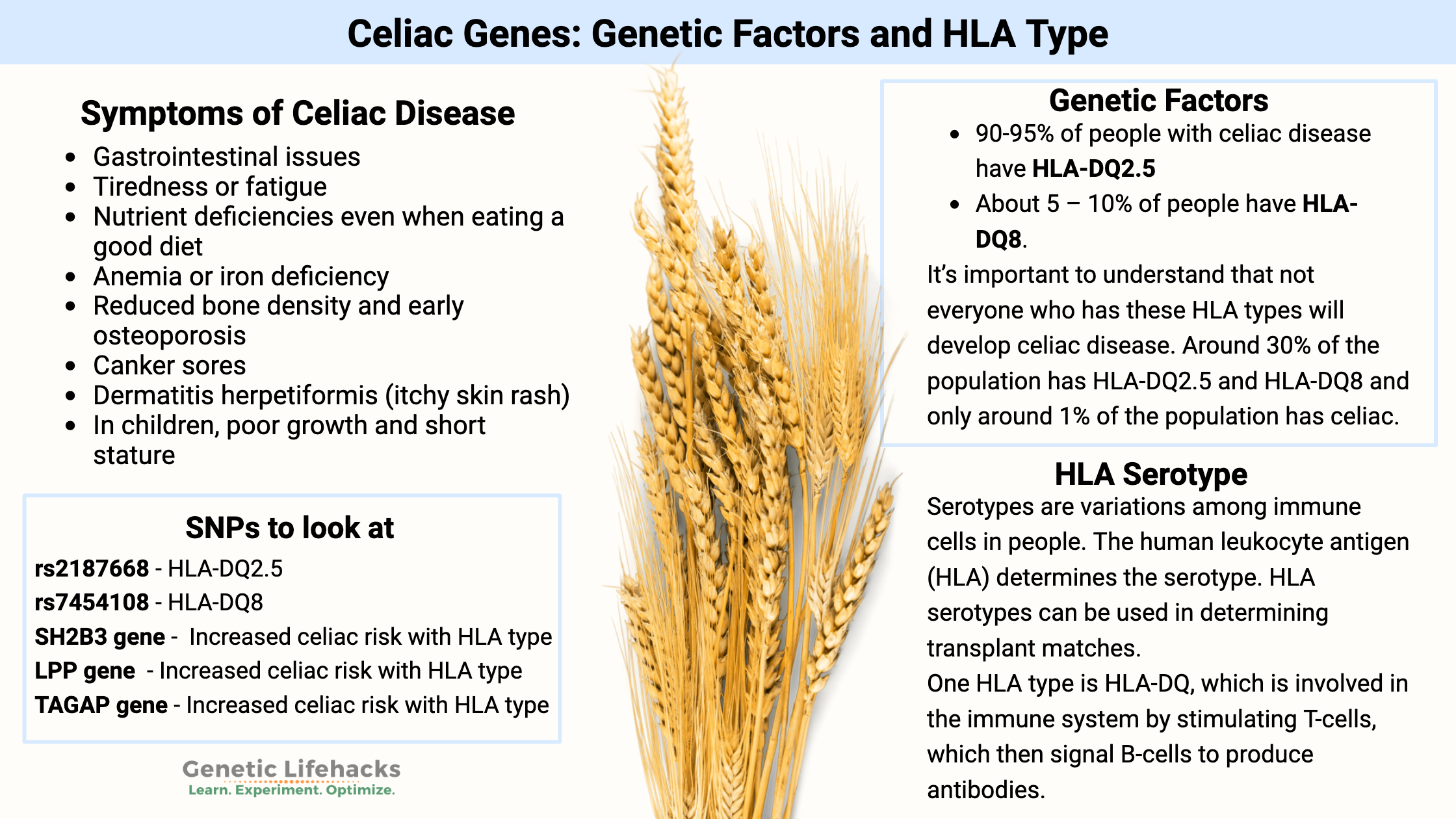
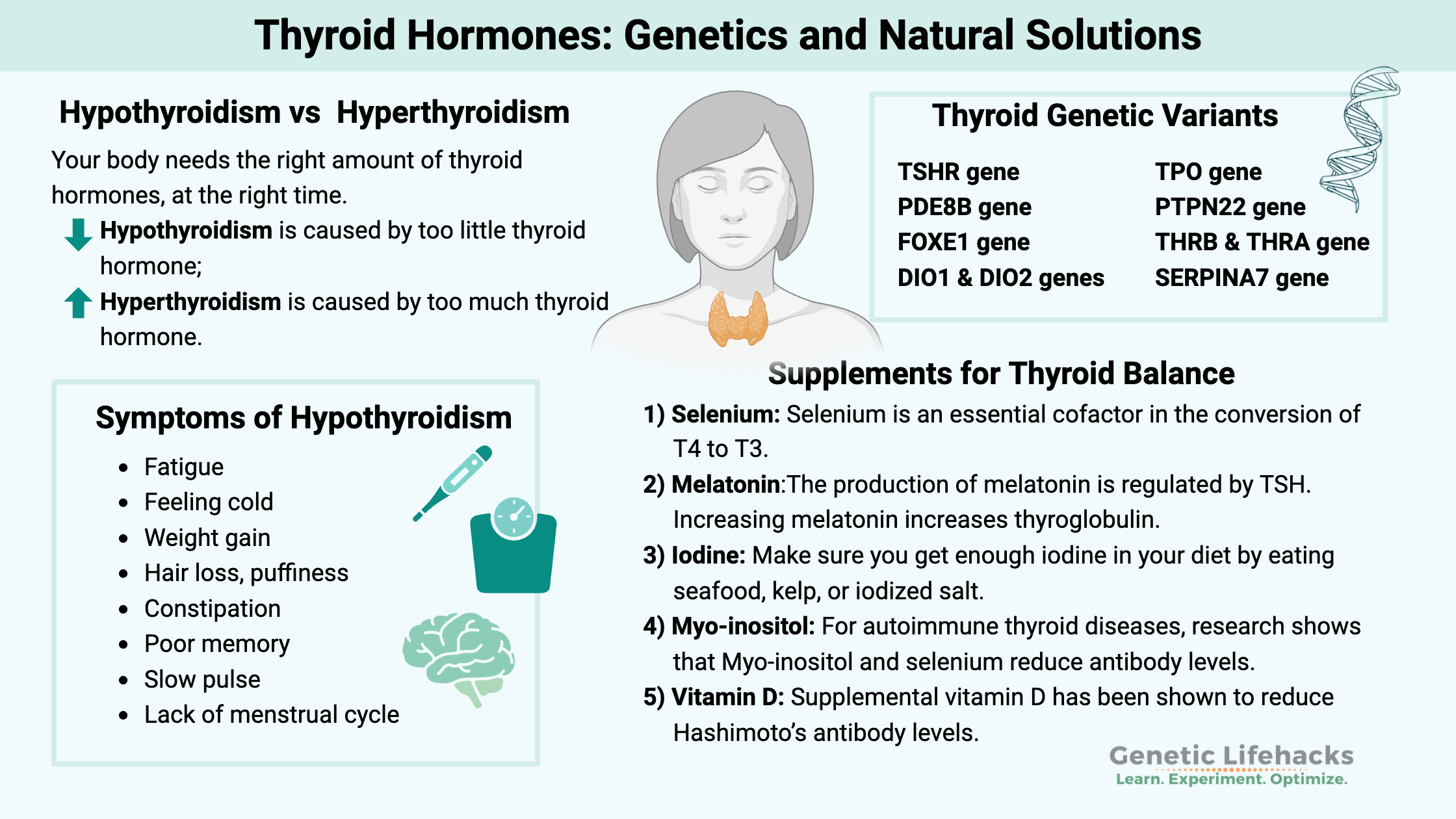
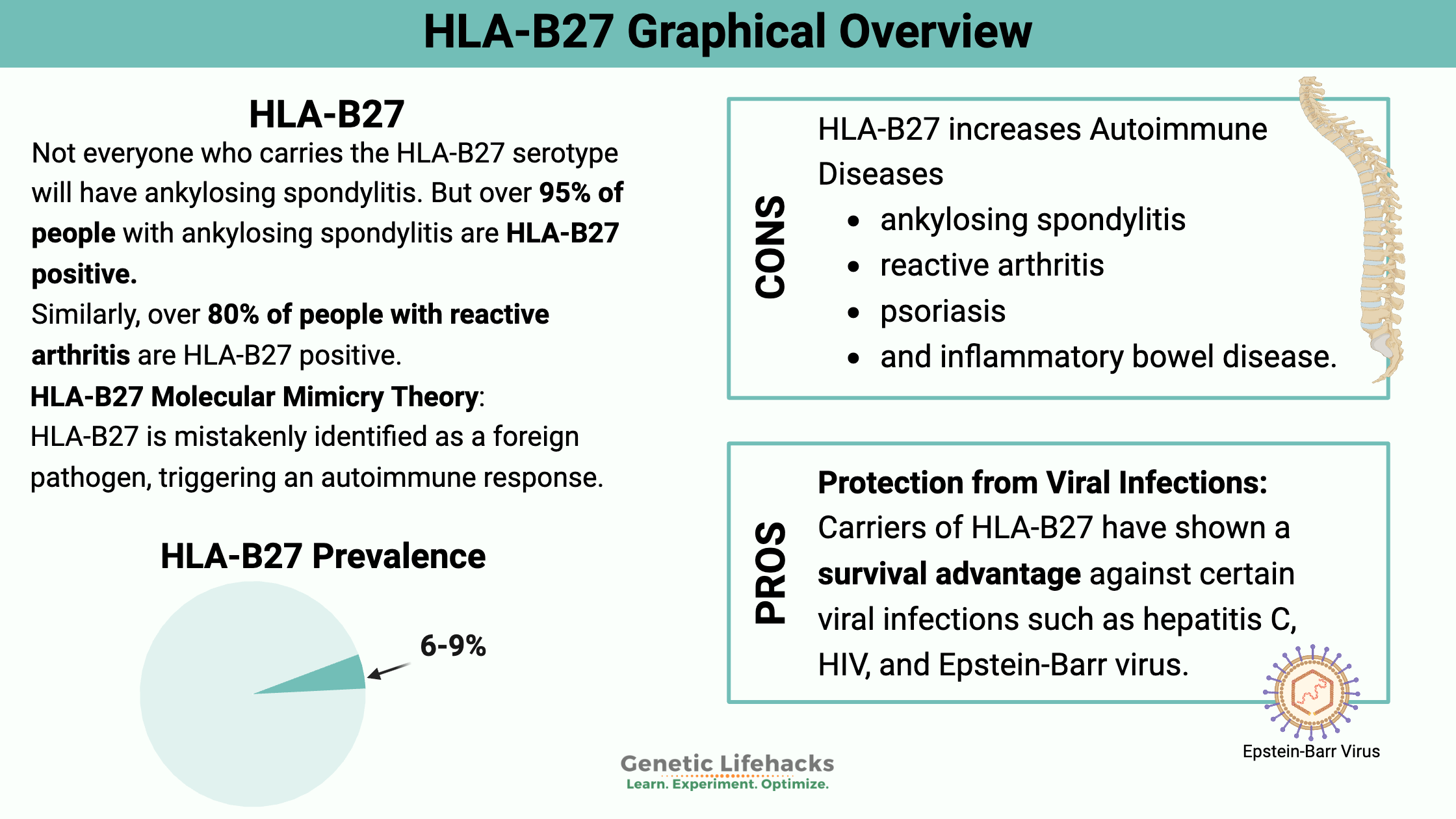
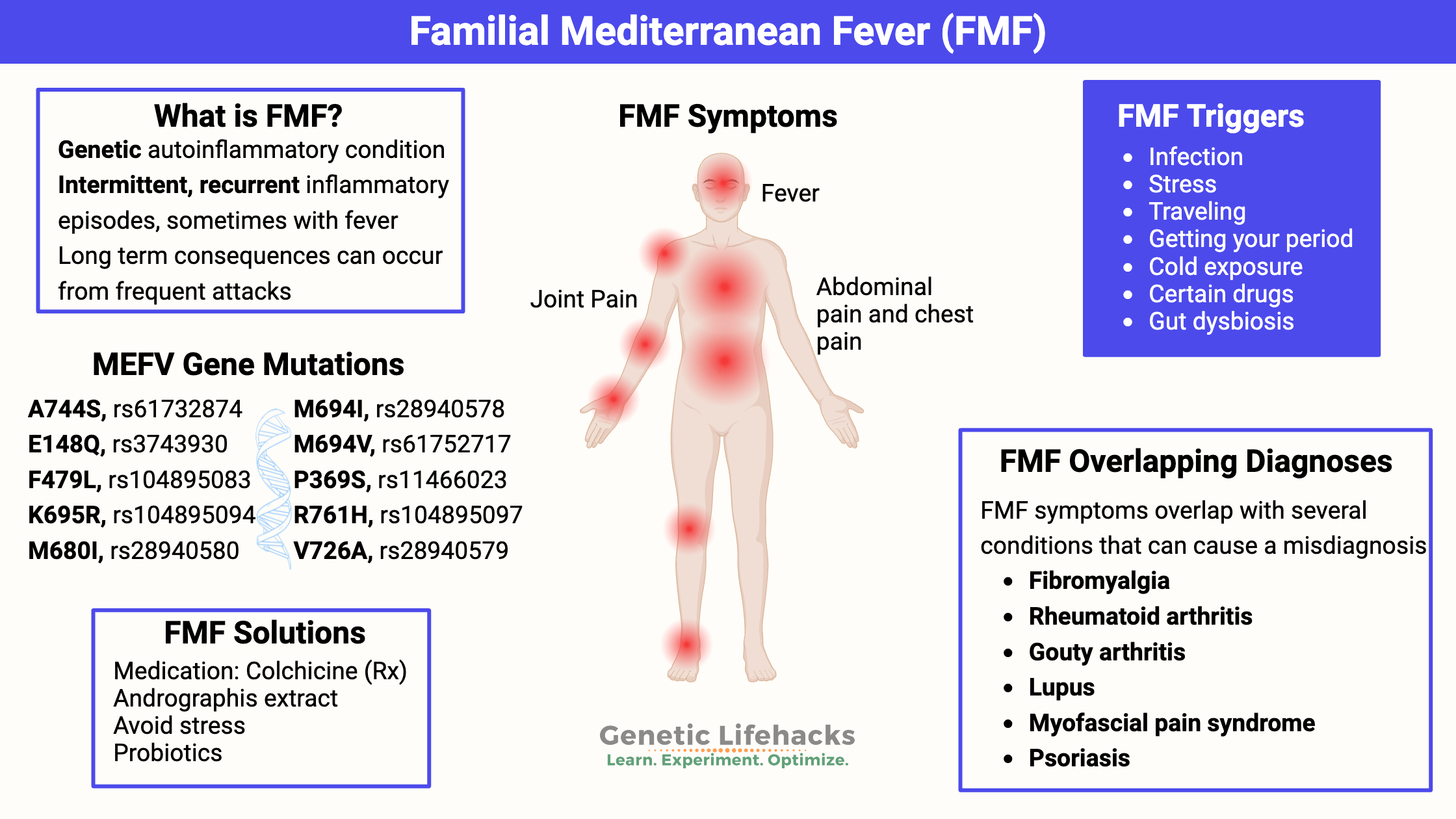
Celiac disease is caused by a combination of environmental factors (eating gluten, other factors) and having the genetic variants that cause susceptibility to the disease. Without the genetic susceptibility, you won’t have celiac.