Key takeaways:
~ Brown fat is rich in mitochondria which use a lot of energy and produce heat through non-shivering thermogenesis.
~ UCP1 is an uncoupling protein that helps mitochondria produce heat and use up fatty acids to be dissipated as heat.
~ Genetic variants that decrease UPC1 are linked to weight gain.
Brown Fat and UCP1: Burning More Energy
The dream of overweight people everywhere: Just turn up the internal heat and naturally burn off the extra fat.
It turns out that genetically some people do have more active ‘internal heat’, and they actually are burning off more energy all the time.
The basis for weight loss, to some degree, hinges on:
- reduce the consumption of stored energy via reducing appetite – and –
- increase the amount of energy used
This is classically thought of as “calories in, calories out”, but it is more complex than research shows. We all know that some people just seem to be able to eat what they want and exercise a little while maintaining a lean physique. Genetics at work…
What is brown fat?
Brown fat is one of the factors that come into play for people who are naturally lean.
There are three kinds of adipose (fat) tissue:
- White adipose (fat) tissue is what we normally think of as fat.
- Brown adipose tissue, on the other hand, is a highly thermally-active tissue that generates a lot of body heat.
- Beige (or brite) adipose tissue is something in between – perhaps a transition between white and brown.
Babies are born with up to 5% of their body mass as brown fat. This thermally-active fat helps to keep the newborn warm since they are unable to shiver.
Adults have relatively little brown fat. What little brown fat adults do have is usually located around the collar bone and across the upper back.
If comparing lean adults to overweight adults, lean adults have a greater percentage of brown fat.
Mammals that hibernate usually have larger amounts of brown fat to keep them warm in the winter.
There has been a lot of interest in activating brown adipose tissue in order to induce weight loss and protect against heart disease and diabetic retinopathy. This seems like an ideal weight loss scheme: simply cause the body to increase the amount of heat produced (calories out) by naturally burning fatty acids.
Mitochondria (energy producers) packed into fat cells
So what makes brown fat ‘brown’? It looks brown under a microscope because it has a lot more mitochondria, which contain iron. The UCPI gene codes for Uncoupling Protein 1 found in these mitochondria. As an example, some studies refer to the UCPI gene as ‘thermogenin’.
Normally, mitochondria produce a little heat as a byproduct of energy production (ATP creation), but the mitochondria in brown adipose tissue that have UCP1 produce quite a bit of heat. Within the mitochondria, UCP1 uncouples the energy generation from ATP and instead uses it to produce the extra heat.[ref]
You can find UCP1 in brown fat and in the retina of the eye. UCP1 is activated by fatty acids and inhibited by purine nucleotides (ADP and GDP).
Let me break that down a little more and add in some details:
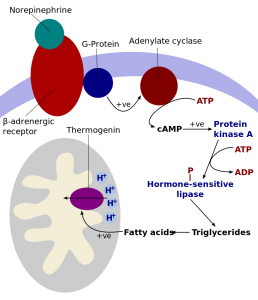
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) signals through a beta-3 adrenergic receptor.
This receptor then activates UCP1 through a series of steps that involve fatty acids.
Activating and Inhibiting UCP1:
You may be wondering: What initiates norepinephrine signaling?
Brown adipose tissue activity increases through the induction of UCP1 by cold temperatures and thyroid hormones. Also, bile acids can increase thyroid activity through the induction of UCP1.[ref]
Other inducers of brown fat include fish oil and iron (only in those that are iron deficient).[ref]
Inhibitors of the UCP1 gene include beta-blockers. Looking at the pathway description above, beta-blockers block the beta-3 adrenergic receptors. Iron deficiency also inhibits brown fat activation.[ref]
Mouse studies show that the deletion of the UCP1 gene causes obesity under normal feeding conditions only if the mice were kept in a ‘thermoneutral’ temperature that was the same as their normal body temperature.
When mice were kept at what we would consider normal room temperatures (18–22°C), they shivered to make up for the lack of UCP1. But when kept at a neutral temperature of 30°C, mice without UPC1 would get fat on a normal diet with the same number of calories.[ref]
Genetic variants in UCP1:
Several polymorphisms in the UCP1 gene decrease its activity. The most studied UCP1 gene variant is -3826A/G (rs1800592) which has been linked in several studies to obesity and diabetic retinopathy risk. A 2013 study found that the variant (C/C genotype*) accelerated an age-related decrease in brown fat activity.[ref] Another study showed that the variant was only significant in women.[ref] A 2011 study of young women showed that those with the C allele had less weight loss on a low-calorie diet than those without the polymorphism.[ref] Other studies have found that the C/C genotype increases the risk of diabetic retinopathy in those with Type I diabetes.[ref][ref]
Note that not all studies link the UCP1 gene to increased BMI – age and ethnicity may play a role.[ref] Interestingly, some researchers have tied the rs1800592 variant to human adaptation to colder climates.
Genetic variants that increase UCP1 activity are associated with a decreased risk of obesity.[ref][ref]
UCP1 Genotype Report
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Lifehacks for activating UPC1, brown fat:
Cold exposure:
One way to stimulate brown fat is by exposing yourself to the cold. This is the most obvious way and possibly the best way. Things to try:
- Try a cold shower or just a shower that ends with 30 seconds of cold water.
- Turn down the heat in the winter (and also save on your energy costs!).
- There are ice vests made to induce cold thermogenesis. (Or you could try just putting an ice pack, wrapped in a thin towel, around your neck as a much cheaper option.)
Caveat: Being cold activates brown fat through norepinephrine release from the adrenal glands. Therefore, if you are already stressed out, have poor thyroid function, or have adrenal fatigue, using cold to induce brown fat may be adding stress to your already stressed system. Use your common sense here, and don’t stress your body out too much.
Taking cold to more of an extreme: Wim Hof on the benefits of cold therapy
Activating cold receptors without cold exposure:
One way that the body senses cold is through the TRPM8 channel. It is activated when the temperature drops to a certain level.
The TRPM8 channel is also activated by menthol (yep, active component in mint) and ilicin (a research chemical). Animal studies with ilicin, which is a more potent activator of TRPM8 than menthol, show that it protects against diet-induced obesity. The animals are fed a diet that is really fattening (think donuts and pizza), but when exposed to the TRPM8 agonist, they don’t get fat due to increased activation of UPC1 and brown fat.[ref]
Sufficient iron (but not too much):
Since iron comes into play with UCP1, making sure that you have sufficient iron is important. Before you supplement, always make sure your iron levels are checked. Seriously. (Also, check to see if you carry the genetic variants for hemochromatosis– iron overload – before supplementing.)
If you are looking for an inexpensive and easy way to get your ferritin, iron, and TIBC levels checked, UltaLabs has an inexpensive test you can order yourself.
Supplements that impact UPC1:
Access this content:
An active subscription is required to access this content.
Related Articles and Topics:
Thyroid Hormones: Genes, Hypothyroidism, and T4/T3 Conversion
References: