will see their genotype report below and the solutions in the Lifehacks section.
A mother’s diet during pregnancy is fundamental to the development of her baby. During pregnancy, there is an increased need for vitamins, choline, folate, DHA, and overall nutrients.[ref]
This article covers some of the known genetic interactions between the mother’s genetic variants and her diet, and shows the effects on the child. You can use this information to understand which nutrients are most important for you to ensure that you have adequate coverage.
However, it is also important to know that excessive supplementation, even of water-soluble vitamins, could have negative effects on the developing fetus.
Pregnancy is not the time to go overboard with supplements or major dietary changes. Talk with your doctor for any medical advice, and please take into consideration the RDA for pregnant women when considering supplements in addition to your dietary intake.
Below you will find seven sections that explain specific nutrient and toxin interactions with genetic variants. I’ll close with some interesting studies on environmental factors in pregnancy.
Choline is an essential nutrient for the developing fetus, used for the development of cell membranes and neurons, and as an alternative source of methyl groups to folate. Interestingly, the placenta stores a large amount of choline so that it can be easily delivered to the growing baby.[ref]
A US national survey showed that over 90% of the adult population doesn’t meet the Adequate Intake (AI) recommendations for choline. The AI is 550 mg/day for men and 425 mg/day for women who aren’t pregnant. During pregnancy and lactation, the AI increases to 550 mg of choline per day.[ref].
Abeywickrama, Halinne Lokuge Thilakshi Chamanika, et al. “TMPRSS6 Rs855791 Polymorphism Is Associated with Iron Deficiency in a Cohort of Sri Lankan Pregnant Women.” Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, vol. 23, no. 1, Dec. 2022, p. 164. Springer Link, https://doi.org/10.1186/s43042-022-00377-8.
Aneji, Chiamaka N., et al. “Deep Sequencing Study of the MTHFR Gene to Identify Variants Associated with Myelomeningocele.” Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology, vol. 94, no. 2, Feb. 2012, pp. 84–90. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1002/bdra.22884.
Asadi-Tarani, Mina, et al. “Maternal and Placental ANRIL Polymorphisms and Preeclampsia Susceptibility.” Personalized Medicine, vol. 20, no. 5, Sept. 2023, pp. 445–52. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.2217/pme-2023-0073.
Azimi-Nezhad, Mohsen, et al. “Association of CYP11B2 Gene Polymorphism with Preeclampsia in North East of Iran (Khorasan Province).” Gene, vol. 733, Apr. 2020, p. 144358. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144358.
Bulloch, Rhodi E., et al. “The Effect of Interactions between Folic Acid Supplementation and One Carbon Metabolism Gene Variants on Small-for-Gestational-Age Births in the Screening for Pregnancy Endpoints (SCOPE) Cohort Study.” Nutrients, vol. 12, no. 6, June 2020, p. 1677. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061677.
Cabezas-Cruz, Alejandro, et al. “Environmental and Molecular Drivers of the α-Gal Syndrome.” Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 10, May 2019, p. 1210. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01210.
Cao, Lirong, et al. “Association of Neural Tube Defects with Gene Polymorphisms in One-Carbon Metabolic Pathway.” Child’s Nervous System: ChNS: Official Journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery, vol. 34, no. 2, Feb. 2018, pp. 277–84. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3558-z.
Cavalli, Pietro. “Prevention of Neural Tube Defects and Proper Folate Periconceptional Supplementation.” Journal of Prenatal Medicine, vol. 2, no. 4, 2008, pp. 40–41. PubMed Central, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3279093/.
Chmurzynska, Agata, et al. “PEMT Rs12325817 and PCYT1A Rs7639752 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Betaine but Not Choline Concentrations in Pregnant Women.” Nutrition Research (New York, N.Y.), vol. 56, Aug. 2018, pp. 61–70. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2018.04.018.
Christensen, Karen E., et al. “The MTHFD1 p.Arg653Gln Variant Alters Enzyme Function and Increases Risk for Congenital Heart Defects.” Human Mutation, vol. 30, no. 2, Feb. 2009, pp. 212–20. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20830.
Claus Henn, Birgit, et al. “Associations of Iron Metabolism Genes with Blood Manganese Levels: A Population-Based Study with Validation Data from Animal Models.” Environmental Health, vol. 10, Nov. 2011, p. 97. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-10-97.
———. “Associations of Iron Metabolism Genes with Blood Manganese Levels: A Population-Based Study with Validation Data from Animal Models.” Environmental Health, vol. 10, Nov. 2011, p. 97. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-10-97.
Conway, Marie C, et al. “Influence of Fatty Acid Desaturase (FADS) Genotype on Maternal and Child Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) Status and Child Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review.” Nutrition Reviews, vol. 78, no. 8, Jan. 2020, pp. 627–46. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuz086.
da Costa, Kerry-Ann, Olga G. Kozyreva, et al. “Common Genetic Polymorphisms Affect the Human Requirement for the Nutrient Choline.” The FASEB Journal : Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, vol. 20, no. 9, July 2006, pp. 1336–44. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-5734com.
da Costa, Kerry-Ann, Karen D. Corbin, et al. “Identification of New Genetic Polymorphisms That Alter the Dietary Requirement for Choline and Vary in Their Distribution across Ethnic and Racial Groups.” The FASEB Journal, vol. 28, no. 7, July 2014, pp. 2970–78. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-249557.
Derakhshan, Arash, et al. “Association of Phthalate Exposure with Thyroid Function during Pregnancy.” Environment International, vol. 157, Dec. 2021, p. 106795. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106795.
Dragovic, Sanja, et al. “Effect of Human Glutathione S-Transferase hGSTP1-1 Polymorphism on the Detoxification of Reactive Metabolites of Clozapine, Diclofenac and Acetaminophen.” Toxicology Letters, vol. 224, no. 2, Jan. 2014, pp. 272–81. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.10.023.
Ganz, Ariel B., et al. “Genetic Variation in Choline-Metabolizing Enzymes Alters Choline Metabolism in Young Women Consuming Choline Intakes Meeting Current Recommendations.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 18, no. 2, Jan. 2017, p. 252. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020252.
Grada, Sebastian, et al. “Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Toxoplasma Gondii in Patients Diagnosed with Schizophrenia: A Case-Control Cross Sectional Study.” Biomedicines, vol. 12, no. 5, May 2024, p. 998. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050998.
Hu, Ying, et al. “BHMT Gene Polymorphisms as Risk Factors for Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate in a Chinese Population.” Biomedical and Environmental Sciences: BES, vol. 24, no. 2, Apr. 2011, pp. 89–93. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3967/0895-3988.2011.02.001.
Ji, Yuelong, et al. “Association of Cord Plasma Biomarkers of In Utero Acetaminophen Exposure With Risk of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Childhood.” JAMA Psychiatry, vol. 77, no. 2, Feb. 2020, pp. 180–89. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3259.
Jia, En-Zhi, et al. “Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Gene Polymorphisms and Coronary Artery Disease: Detection of Gene-Gene and Gene-Environment Interactions.” Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry: International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology, vol. 29, nos. 3–4, 2012, pp. 443–52. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1159/000338498.
Klatt, Kevin C., et al. “Prenatal Choline Supplementation Improves Biomarkers of Maternal Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Status among Pregnant Participants Consuming Supplemental DHA: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 116, no. 3, Sept. 2022, pp. 820–32. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac147.
Kohlmeier, Martin, et al. “Genetic Variation of Folate-Mediated One-Carbon Transfer Pathway Predicts Susceptibility to Choline Deficiency in Humans.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 102, no. 44, Nov. 2005, pp. 16025–30. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504285102.
Lemaitre, Rozenn N., et al. “Genetic Loci Associated with Plasma Phospholipid N-3 Fatty Acids: A Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies from the CHARGE Consortium.” PLoS Genetics, vol. 7, no. 7, July 2011, p. e1002193. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002193.
Li, Liuxuan, et al. “Association of Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation and Offspring MTRR Gene Polymorphism with Congenital Heart Disease: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study in Han Population.” Journal of Health, Population, and Nutrition, vol. 43, no. 1, Dec. 2024, p. 220. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-024-00699-w.
Li, Xinghui, et al. “CYP11B2 Gene Polymorphism and Essential Hypertension among Tibetan, Dongxiang and Han Populations from Northwest of China.” Clinical and Experimental Hypertension (New York, N.Y.: 1993), vol. 38, no. 4, 2016, pp. 375–80. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2015.1131287.
Li, Yihuan, et al. “Association of Maternal Dietary Intakes and CBS Gene Polymorphisms with Congenital Heart Disease in Offspring.” International Journal of Cardiology, vol. 322, Jan. 2021, pp. 121–28. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.08.018.
———. “Association of Maternal Dietary Intakes and CBS Gene Polymorphisms with Congenital Heart Disease in Offspring.” International Journal of Cardiology, vol. 322, Jan. 2021, pp. 121–28. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.08.018.
Liu, Taixiu, et al. “Association between Toxoplasma Gondii Infection and Psychiatric Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study in China.” Scientific Reports, vol. 12, Sept. 2022, p. 15092. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16420-y.
Moksnes, Marta R., et al. “A Genome-Wide Association Study Provides Insights into the Genetic Etiology of 57 Essential and Non-Essential Trace Elements in Humans.” Communications Biology, vol. 7, Apr. 2024, p. 432. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06101-z.
Mulatero, Paolo, et al. “CYP11B2 -344T/C Gene Polymorphism and Blood Pressure in Patients with Acromegaly.” The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, vol. 91, no. 12, Dec. 2006, pp. 5008–12. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-0049.
Nauman, Nuzhat, et al. “Low Maternal Folate Concentrations and Maternal MTHFR C677T Polymorphism Are Associated with an Increased Risk for Neural Tube Defects in Offspring: A Case-Control Study among Pakistani Case and Control Mothers.” Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 27, no. 1, 2018, pp. 253–60. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.6133/apjcn.032017.10.
Office of Dietary Supplements – Choline. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 19 Jan. 2026.
Office of Dietary Supplements – Folate. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-Consumer/. Accessed 19 Jan. 2026.
Office of Dietary Supplements – Folate. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 19 Jan. 2026.
Petersen, Julie M., et al. “Periconceptional Intakes of Methyl Donors and Other Micronutrients Involved in One-Carbon Metabolism May Further Reduce the Risk of Neural Tube Defects in Offspring: A United States Population–Based Case-Control Study of Women Meeting the Folic Acid Recommendations.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 118, no. 3, Sept. 2023, pp. 720–28. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.05.034.
“Pregnancy and Fish: What’s Safe to Eat?” Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy-and-fish/art-20044185. Accessed 19 Jan. 2026.
Qiu, Juanjuan, et al. “Association between Polymorphisms in Estrogen Metabolism Genes and Breast Cancer Development in Chinese Women.” Medicine, vol. 97, no. 47, Nov. 2018, p. e13337. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013337.
Reuben, Alexandre, et al. “The Hemochromatosis Protein HFE 20 Years Later: An Emerging Role in Antigen Presentation and in the Immune System.” Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, vol. 5, no. 3, Apr. 2017, pp. 218–32. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1002/iid3.158.
Saraswathy, Kallur Nava, et al. “Spectrum of MTHFR Gene SNPs C677T and A1298C: A Study among 23 Population Groups of India.” Molecular Biology Reports, vol. 39, no. 4, Apr. 2012, pp. 5025–31. Springer Link, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1299-8.
Singh, Prakruti R., et al. “Gene Polymorphisms and Low Dietary Intake of Micronutrients in Coronary Artery Disease.” Journal of Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics, vol. 4, no. 4, 2011, pp. 203–09. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1159/000330229.
Skolmowska, Dominika, et al. “Effectiveness of Dietary Interventions in Prevention and Treatment of Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 15, July 2022, p. 3023. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153023.
Socha, Maciej W., et al. “Epigenetic Genome Modifications during Pregnancy: The Impact of Essential Nutritional Supplements on DNA Methylation.” Nutrients, vol. 16, no. 5, Feb. 2024, p. 678. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050678.
Taesuwan, Siraphat, et al. “Choline Metabolome Response to Prenatal Choline Supplementation across Pregnancy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” FASEB Journal : Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, vol. 35, no. 12, Dec. 2021, p. e22063. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202101401RR.
Thomsen, Liv Cecilie V., et al. “The Antihypertensive MTHFR Gene Polymorphism Rs17367504-G Is a Possible Novel Protective Locus for Preeclampsia.” Journal of Hypertension, vol. 35, no. 1, Jan. 2017, pp. 132–39. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001131.
Turbiville, Donald, et al. “Iron Overload in an HFE Heterozygous Carrier: A Case Report and Literature Review.” Laboratory Medicine, vol. 50, no. 2, Apr. 2019, pp. 212–17. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1093/labmed/lmy065.
Wahlberg, Karin, et al. “Maternal Polymorphisms in Glutathione-Related Genes Are Associated with Maternal Mercury Concentrations and Early Child Neurodevelopment in a Population with a Fish-Rich Diet.” Environment International, vol. 115, June 2018, pp. 142–49. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.015.
Wallace, Taylor C., and Victor L. Fulgoni. “Assessment of Total Choline Intakes in the United States.” Journal of the American College of Nutrition, vol. 35, no. 2, 2016, pp. 108–12. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2015.1080127.
Wang, Lijuan, et al. “Association between Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Six Hypertensive Candidate Genes and Hypertension among Northern Han Chinese Individuals.” Hypertension Research: Official Journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension, vol. 37, no. 12, Dec. 2014, pp. 1068–74. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2014.124.
Wang, Lin, et al. “Polymorphism in Maternal LRP8 Gene Is Associated with Fetal Growth.” American Journal of Human Genetics, vol. 78, no. 5, May 2006, pp. 770–77. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1086/503712.
Wang, Shuxia, et al. “Relationships between Maternal Gene Polymorphisms in One Carbon Metabolism and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: A Prospective Mother and Child Cohort Study in China.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 10, May 2022, p. 2108. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102108.
“What Does It Mean When Your Baby’s Born With a Heart Problem?” Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21674-congenital-heart-disease. Accessed 19 Jan. 2026.
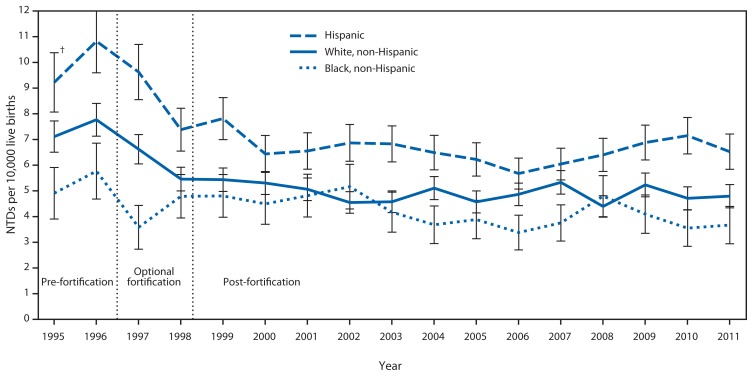
Williams, Jennifer, et al. “Updated Estimates of Neural Tube Defects Prevented by Mandatory Folic Acid Fortification — United States, 1995–2011.” Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, vol. 64, no. 1, Jan. 2015, pp. 1–5. PubMed Central, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4584791/.
Wu, Han, et al. “Genetic Polymorphism of MTHFR C677T with Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis.” Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, vol. 295, no. 5, May 2017, pp. 1105–18. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4322-z.
Wu, Xiaoming, et al. “Folate Metabolism Gene Polymorphisms MTHFR C677T and A1298C and Risk for Preeclampsia: A Meta-Analysis.” Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, vol. 32, no. 5, May 2015, pp. 797–805. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0408-8.
Yang, Boyi, et al. “Associations of MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms with Hypertension and Hypertension in Pregnancy: A Meta-Analysis from 114 Studies with 15411 Cases and 21970 Controls.” PLoS ONE, vol. 9, no. 2, Feb. 2014, p. e87497. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087497.
Yang, Fushuang, et al. “Relationship between Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation during Pregnancy and Risk of Childhood Asthma: Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.” Frontiers in Pediatrics, vol. 10, Nov. 2022, p. 1000532. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2022.1000532.
Yang, Lili, et al. “Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Positively Associated with Schizophrenia: Evidences from UK Biobank Cohort and Case-Controlled Studies.” Journal of Psychiatric Research, vol. 175, July 2024, pp. 243–50. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.025.
Yavin, E., et al. “Delayed Cell Migration in the Developing Rat Brain Following Maternal Omega 3 Alpha Linolenic Acid Dietary Deficiency.” Neuroscience, vol. 162, no. 4, Sept. 2009, pp. 1011–22. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.012.
Yi, Kang, et al. “Association of MTHFD1 G1958A (Rs2236225) Gene Polymorphism with the Risk of Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” BMC Medical Genomics, vol. 18, Jan. 2025, p. 20. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-024-02052-w.
Zeisel, Steven H. “Choline: Critical Role during Fetal Development and Dietary Requirements in Adults.” Annual Review of Nutrition, vol. 26, 2006, pp. 229–50. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.26.061505.111156.
Zhang, Donghong, et al. “Elevated Homocysteine Level and Folate Deficiency Associated with Increased Overall Risk of Carcinogenesis: Meta-Analysis of 83 Case-Control Studies Involving 35,758 Individuals.” PloS One, vol. 10, no. 5, 2015, p. e0123423. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123423.
Zhu, Jie, et al. “Dietary Choline Intake during Pregnancy and PEMT Rs7946 Polymorphism on Risk of Preterm Birth: A Case-Control Study.” Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism, vol. 76, no. 6, 2020, pp. 431–40. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1159/000507472.