BH4: Tetrahydrobiopterin Synthesis, Recycling, and Genetic SNPs
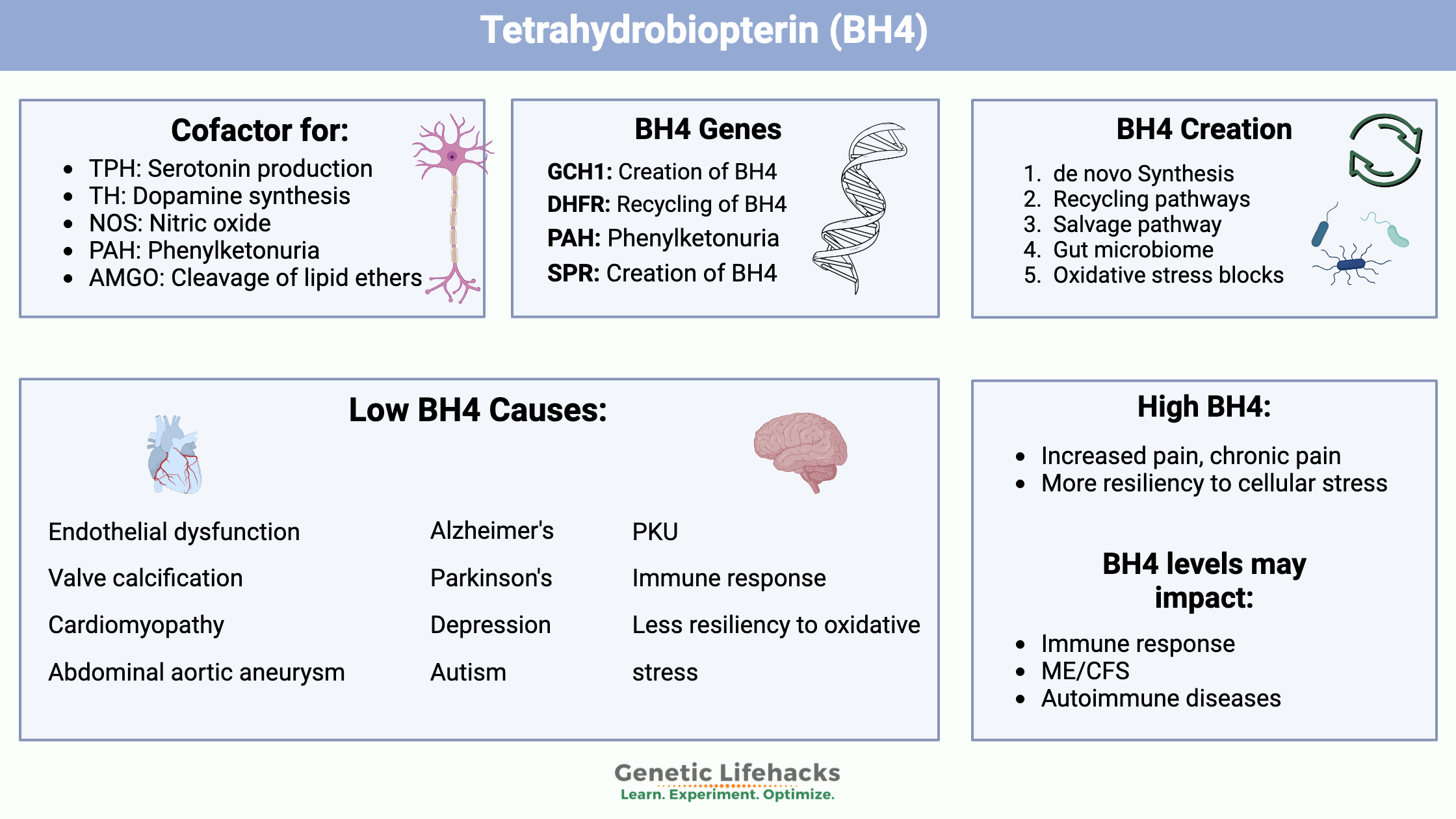
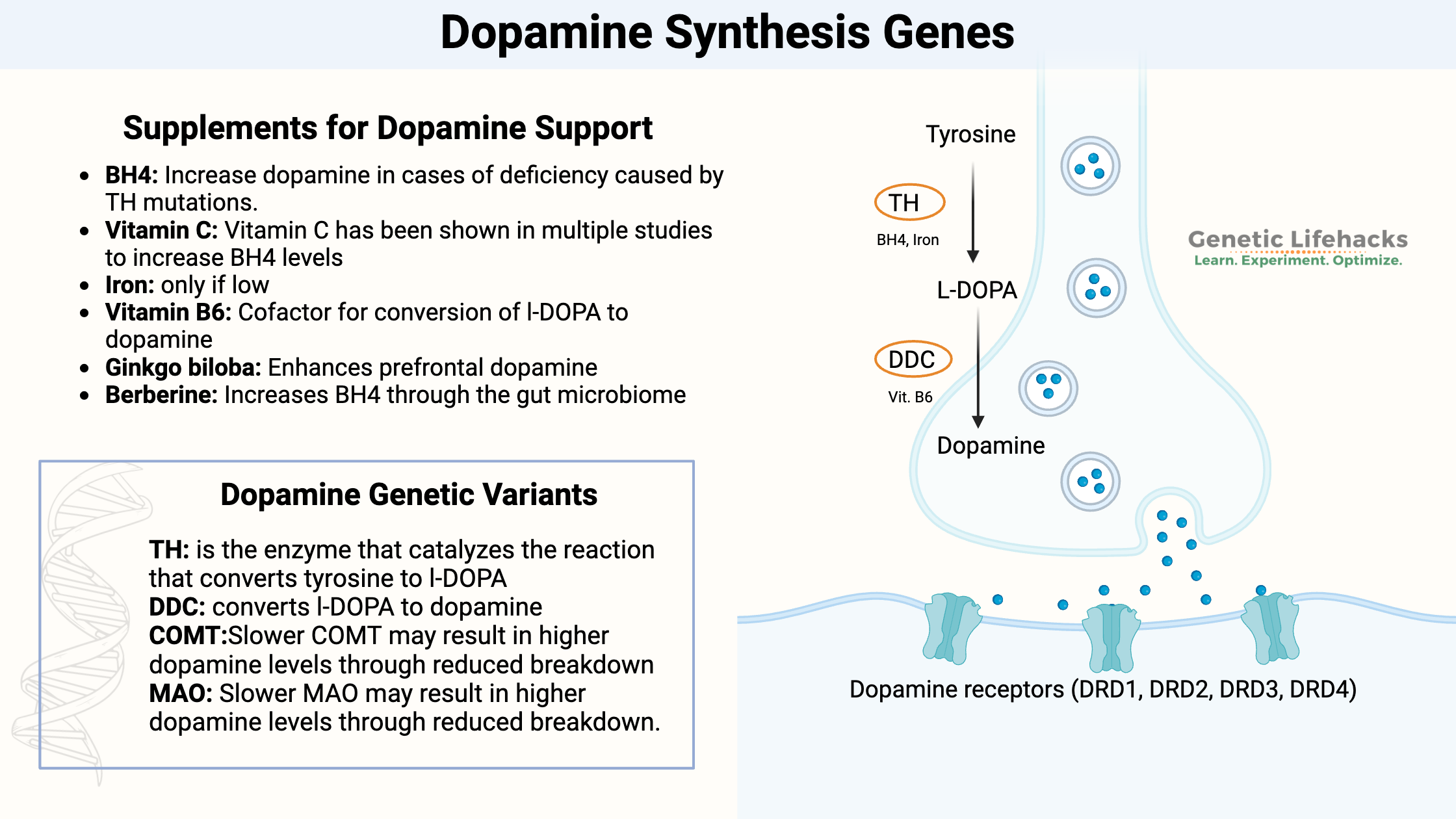
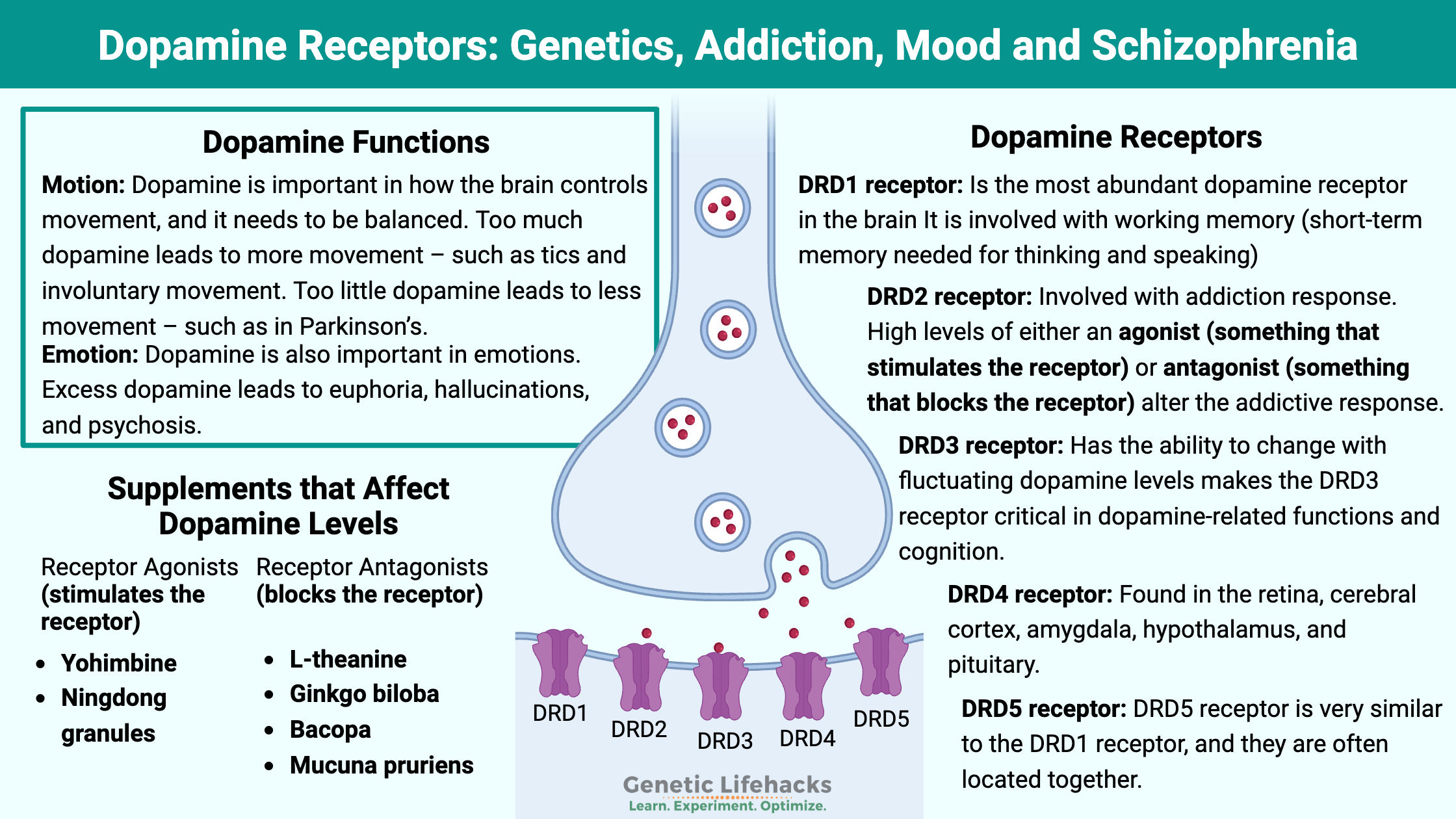
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is an essential cofactor in the production of neurotransmitters and nitric oxide. Genetic variants impact BH4 levels which can affect heart disease, cognitive function, and immune response.