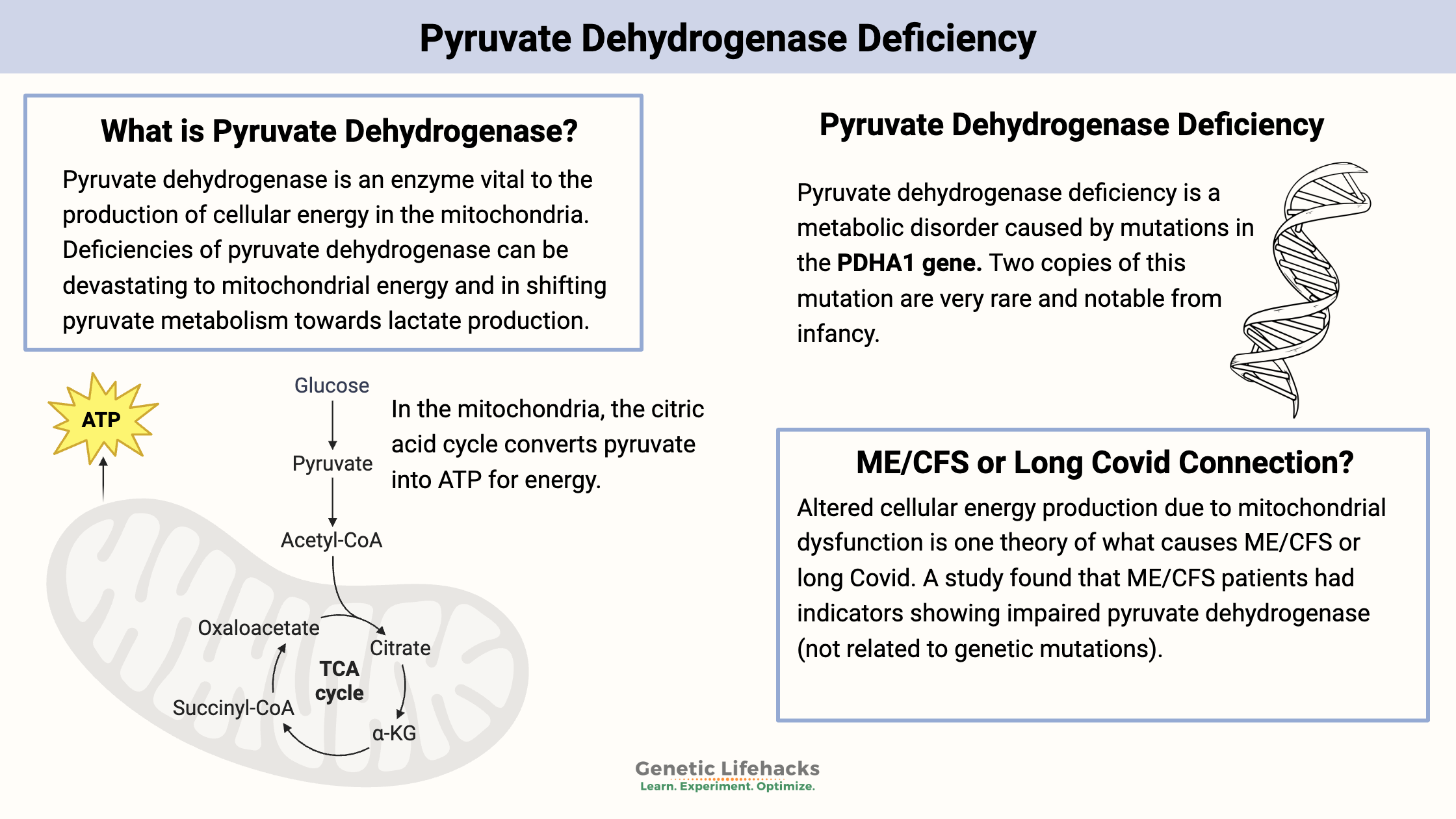
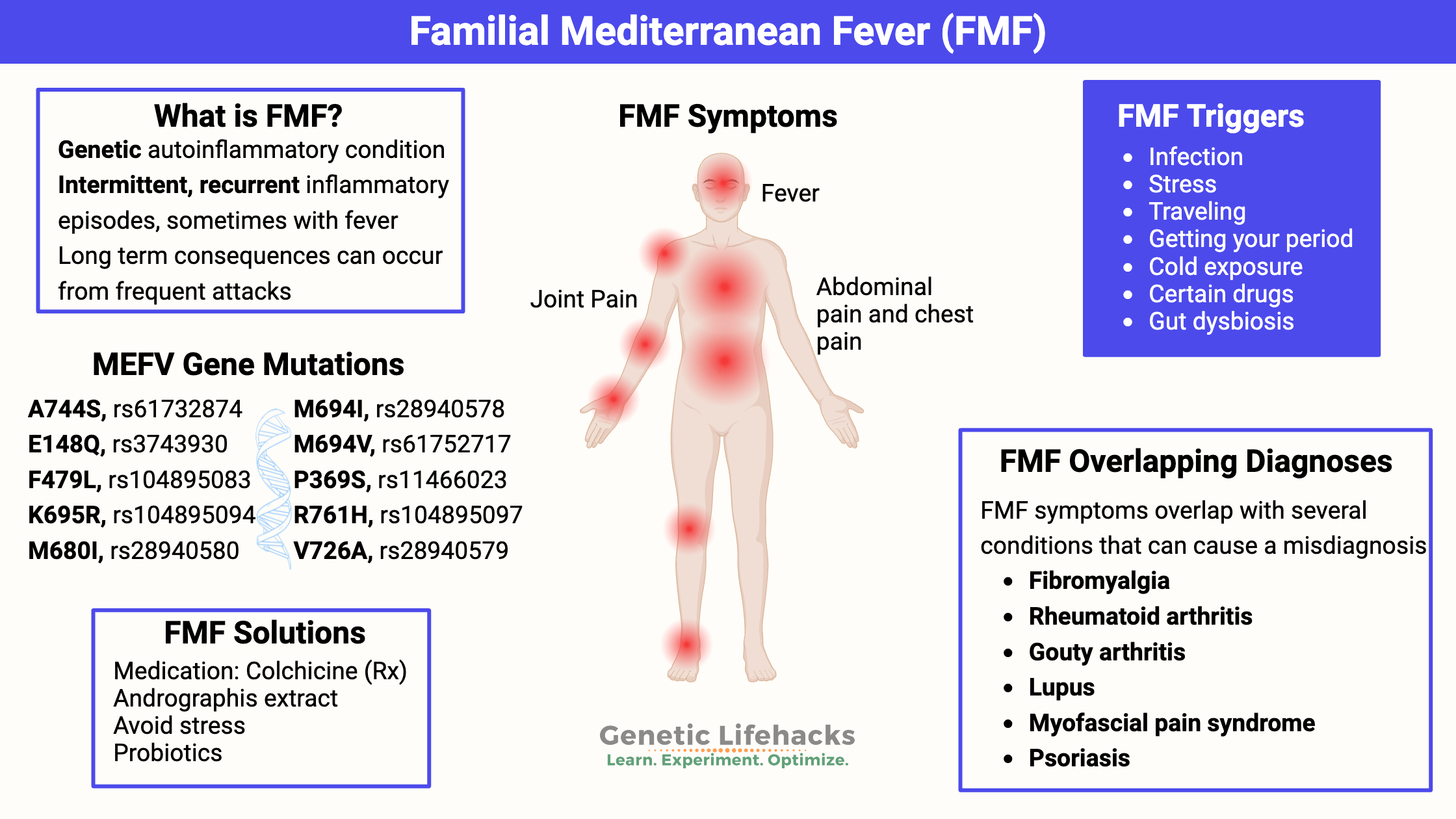
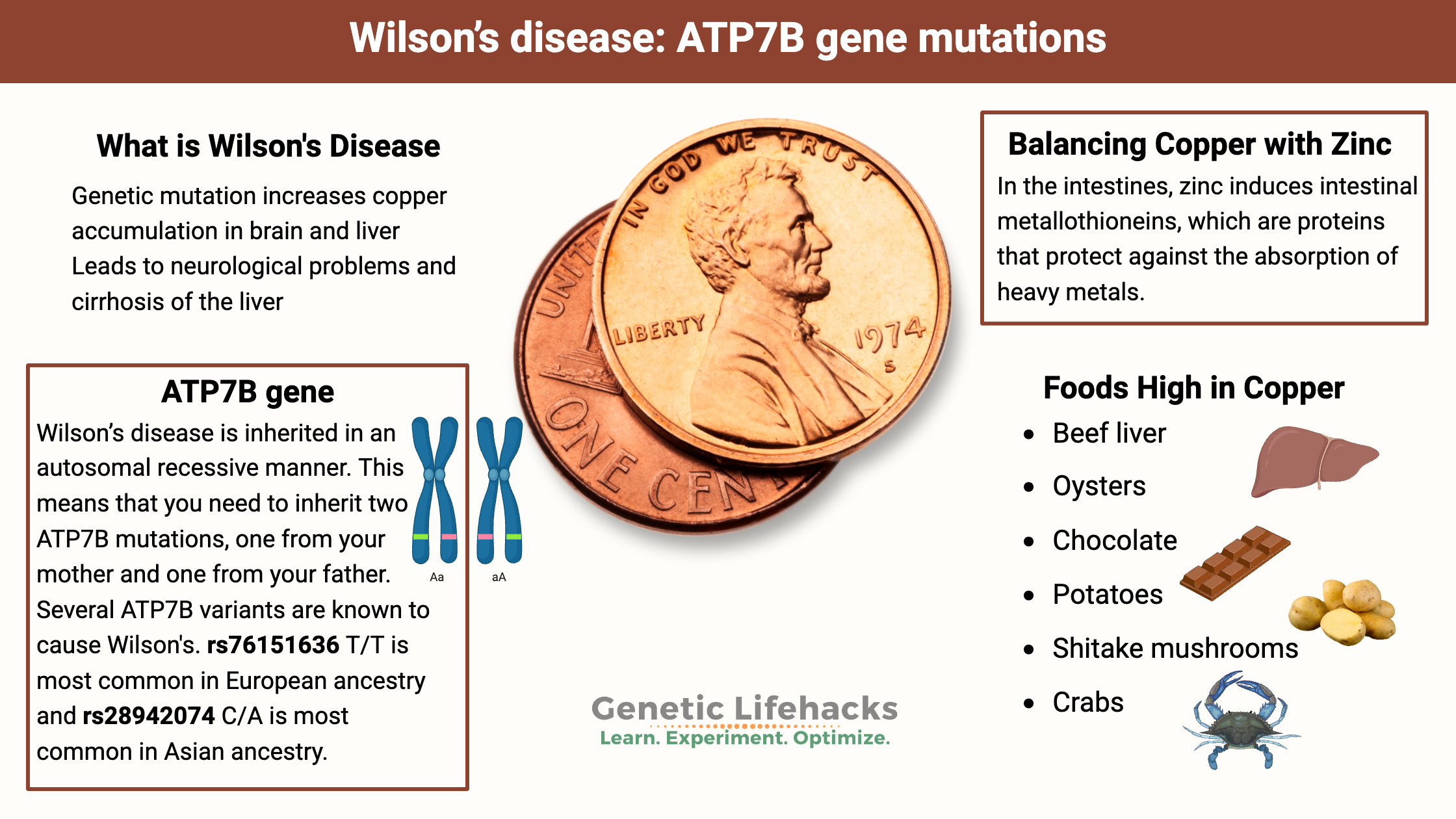
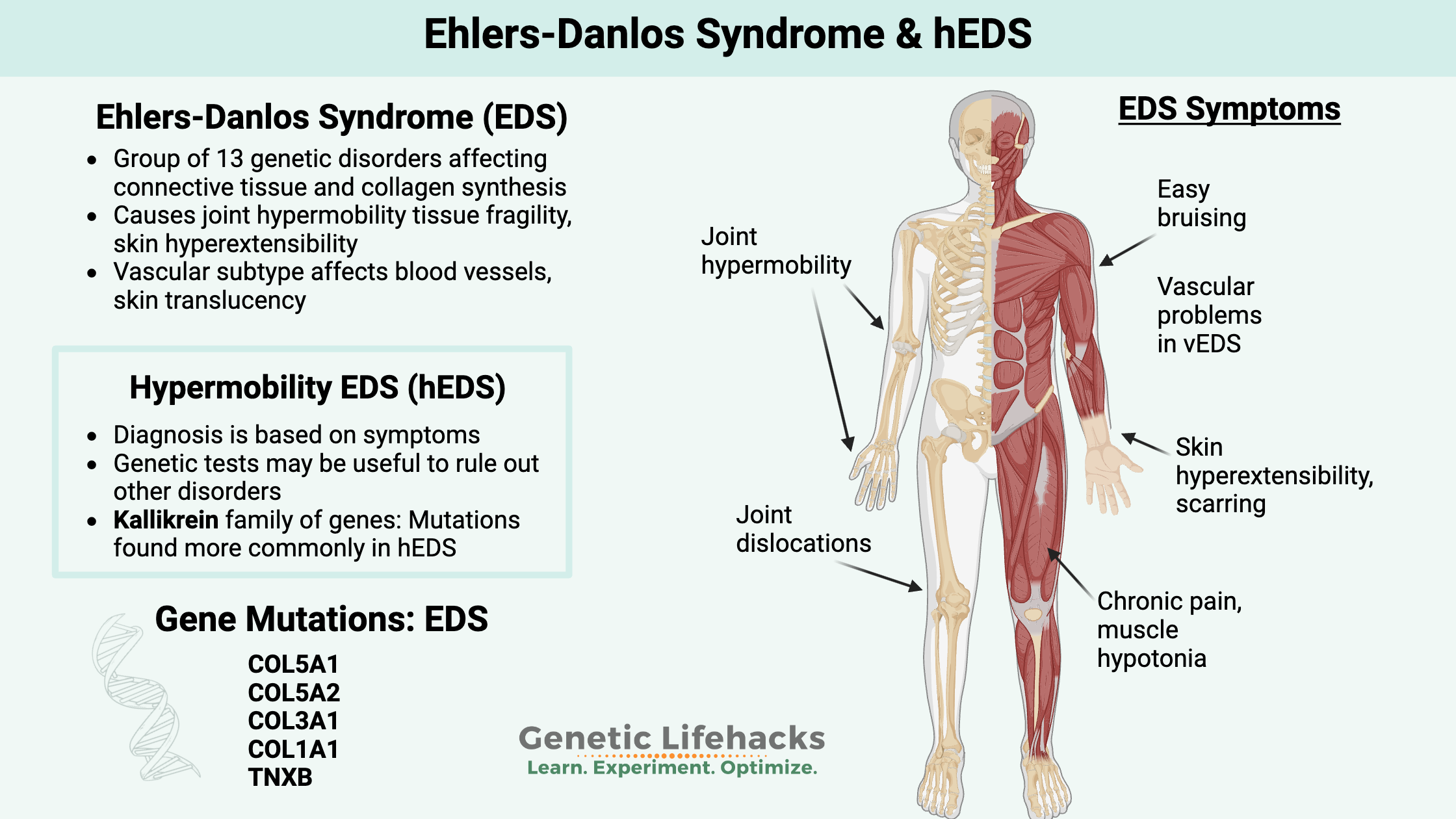
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiency – Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lactate Production
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase is central to cellular energy production. Learn about its role in energy production, genetic mutations, association with ME/CFS and Long Covid, and strategies to manage its deficiencies.