Key takeaways:
~Dopamine is a powerful player in our cognitive function – impacting mood, movement, and motivation.
~ Excess dopamine – or – not having enough dopamine can cause mental and physical changes.
~Genetic variants in the dopamine receptors influence addiction, ADHD, neurological diseases, depression, psychosis, and aggression.
This article covers information on neurotransmitters related to psychiatric health. If you are under psychiatric care, talk with your doctor before making any changes.
Members will see their genotype report below, plus additional solutions in the Lifehacks section. Consider joining today.
Dopamine: Neurotransmitter for motion and emotion
Dopamine acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, transmitting a signal from one neuron to the next. It is a monoamine neurotransmitter, classified as a catecholamine. A monoamine just means that it contains a single amine group – and this is important in the way that it is regulated in the brain.
Dopamine is derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is converted to L-dopa and then to dopamine.
Dopamine is involved in:
- Movement
- Reward
- Memory
- Lactation
- Attention
- Sleep regulation
The dopamine molecule acts on dopamine receptors to cause motion and emotion.
Motion:
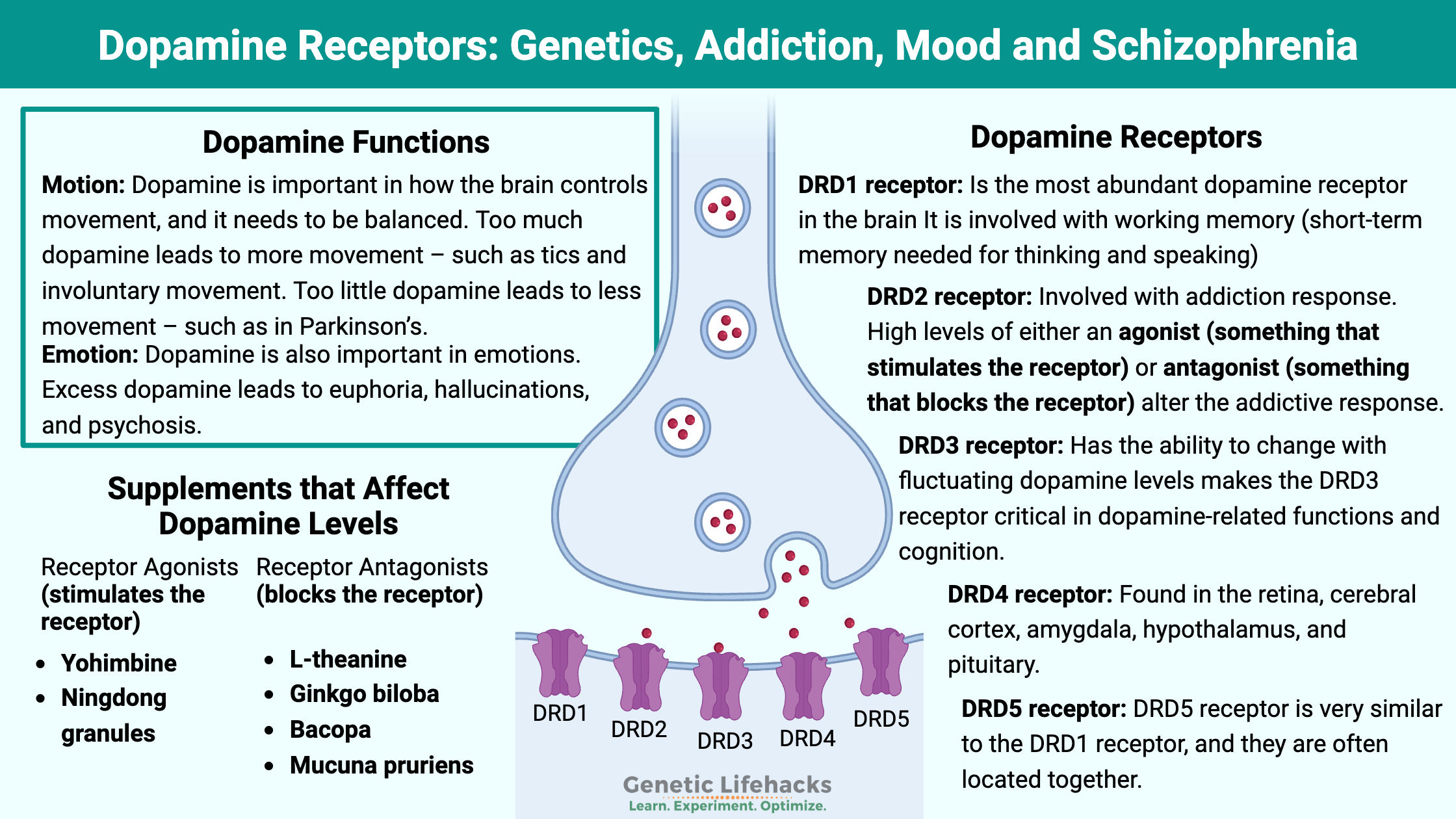
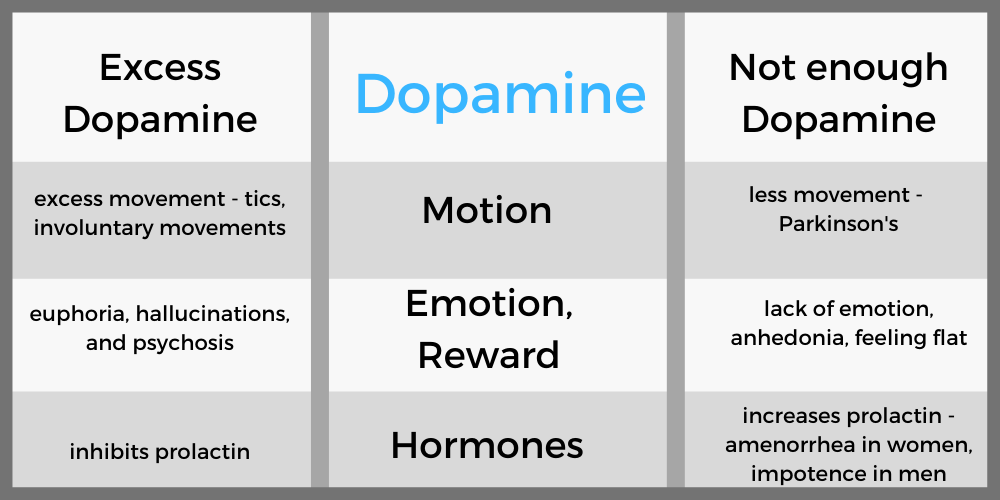
Dopamine is important in how the brain controls movement, and it needs to be balanced. Too much dopamine leads to more movement – such as tics and involuntary movement. Too little dopamine leads to less movement – such as in Parkinson’s.
Emotion:
Dopamine is also important in emotions. Excess dopamine leads to euphoria, hallucinations, and psychosis. Dopamine causes conditioning – for example, learning either not to do something (via punishment) or learning to do something through reward. Not enough dopamine leads to anhedonia – that feeling of not caring about anything.
Prolactin:
Dopamine also functions within the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to affect hormones. Specifically, dopamine inhibits prolactin. Without enough dopamine, it can lead to amenorrhea (lack of periods) in women and impotence and gynecomastia (moobs) in males.
Where is dopamine made?
There are two small regions deep in the brain where dopamine is made:
- the substantia nigra
- the ventral tegmental area
From there, it travels via tracts to other areas of the brain.
Dopamine Receptors: Understanding the different effects of dopamine
Dopamine doesn’t do anything by itself – it needs to bind with a receptor to cause an action. There are five different dopamine receptors in humans, coded for by the DRD1 through DRD5 genes. These G-protein coupled receptors receptors are responsible for the slightly different effects of dopamine in various brain regions as well as different tissues throughout the body.
DRD1 receptor:
The most abundant dopamine receptor in the brain is DRD1. It is found in several regions of the brain, including the neostriatum, basolateral amygdala, cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
The DRD1 receptor is linked to the effects of alcohol consumption. Blocking the DRD1 gene decreases alcohol-seeking behavior in animal studies. It also decreases heroin and cocaine-seeking behavior.[ref]
Working memory – short-term memory needed for thinking and speaking – depends on the DRD1 receptors in the prefrontal cortex. Interestingly, working memory is considered to have a strong genetic component based on the DRD1 gene variants.[ref]
DRD2 receptor:
The DRD2 receptor is less abundant in the cerebral cortex than the DRD1 receptors, but it is abundant in other areas of the brain with dopaminergic neurons.
Both agonists and antagonists of the DRD2 receptor have been shown in animal studies to decrease alcohol and opiate consumption. The studies show that higher levels of either an agonist (something that stimulates the receptor) or antagonist (something that blocks the receptor) alter the addictive response.[ref]
DRD3 receptor:
The DRD3 receptor is found in the ventral striatum and other limbic areas in the brain. In humans, there are low amounts of DRD3 receptors found in the cortical regions. This differs from other species and is a good reminder that animal studies may not be totally applicable to humans.[ref]
The DRD3 receptor has a higher affinity for dopamine (>20-fold higher than DRD2 receptors). This means that dopamine is more likely to bind with the DRD3 receptors, and high levels of dopamine will prompt the brain to make more DRD3 receptors. The ability to change with fluctuating dopamine levels makes the DRD3 receptor critical in dopamine-related functions and cognition.[ref]
DRD4 receptor:
This dopamine receptor is found at lower levels than DRD1 through DRD3. It is found in the retina, cerebral cortex, amygdala, hypothalamus, and pituitary. The DRD4 receptor likely doesn’t play a role in alcohol, opiate, or cocaine addiction.[ref]
DRD5 receptor:
The DRD5 receptor is very similar to the DRD1 receptor, and they are often located together. There seems to be a lot more research on DRD1, but often substances that bind to DRD1 also bind to DRD5.[ref]
Dopamine and Addiction:
Addiction to drugs causes compulsive drug-seeking behavior. The dopamine system is involved in the rewarding effects of drugs, and a lot of addictive drugs increase dopamine levels in certain regions of the brain. In fact, it has been known since the 1990s that blocking dopamine transmission takes away the reward effects of some addictive substances, such as cocaine and amphetamines.[ref]
There are three theories on how dopamine is related to addiction. First, the extra dopamine produced by addictive substances trains the brain through the reward system. It is the idea that the brain learns to like the drug, or makes it a habit. The second theory is that addictive substances change the brain’s circuits, making them hypersensitive. Third, researchers theorize that there is an imbalance between dopamine and other neurotransmitters. [ref]
Mental disorders associated with abnormal dopamine levels:
Several diseases are associated with altered dopamine.
- Tics / Tourettes – excess striatal dopamine due to GABAergic network dysfunction[ref]
- Psychosis – excess dopamine
- Schizophrenia – excess dopamine in some areas of the brain (causes hallucinations) and not enough in others[ref][ref]
- Addiction – caused in part by repeated surges in dopamine (reward) and increased dopamine receptors
- ADHD -associated with low dopamine function in certain areas of the brain[ref]
- Bipolar affective disorder – high dopamine during mania which elevated DRD2 and DRD3 receptors, coupled with reduced dopamine during depression[ref]
- Anorexia – decreased reward (dopamine) for food along with other neurotransmitter imbalances (such as histamine)[ref]
- Depression – low dopamine is seen in people with inflammation-associated depression.[ref]
Additionally, Parkinson’s disease is caused by not enough dopamine due to degradation of the dopamine-producing area of the brain (substantia nigra).
Related article: ADHD Genes
Connections between dopamine levels and inflammation:
Neuroinflammation in dopaminergic neurons causes cell death and a reduction in dopamine. This is thought to be the cause of Parkinson’s disease.[ref]
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is needed for the synthesis of dopamine. Pro-inflammatory cytokines reduce the production of BH4, thus potentially reducing dopamine levels in situations of systemic inflammation.[ref]
” Dopaminergic neurotransmission is very sensitive to inflammation. At the periphery, the production of neopterin and nitric oxide during inflammation consumes tetrahydrobiopterin to the detriment of the hydroxylase enzymes that use this compound as a cofactor”.[ref]
Dopamine Receptor Genotype Report:
Members: Log in to see your data below.
Not a member? Join here.
Why is this section is now only for members? Here’s why…
Lifehacks:
Again, let me caution that you don’t want to experiment with your neurotransmitters if you are under psychiatric care without talking with your doctor. Read the research and talk with your doctor or health care practitioner.
Increasing dopamine naturally:
Related Genes and Topics:
Serotonin Genes
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is important in depression, sleep, and many other aspects of health. Learn how genetic variants in the serotonin receptor genes impact their function.
COMT Gene
Wondering why your neurotransmitters are out of balance? It could be due to your COMT genetic variants. The COMT gene codes for the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase which breaks down (metabolizes) the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
References:
Aguiar, Sebastian, and Thomas Borowski. “Neuropharmacological Review of the Nootropic Herb Bacopa Monnieri.” Rejuvenation Research, vol. 16, no. 4, Aug. 2013, pp. 313–26. PubMed Central, doi:10.1089/rej.2013.1431.
Baetu, Irina, et al. “Commonly-Occurring Polymorphisms in the COMT, DRD1 and DRD2 Genes Influence Different Aspects of Motor Sequence Learning in Humans.” Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, vol. 125, Nov. 2015, pp. 176–88. ScienceDirect, doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2015.09.009.
—. “Commonly-Occurring Polymorphisms in the COMT, DRD1 and DRD2 Genes Influence Different Aspects of Motor Sequence Learning in Humans.” Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, vol. 125, Nov. 2015, pp. 176–88. ScienceDirect, doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2015.09.009.
Balestri, Martina, et al. “Genetic Modulation of Personality Traits: A Systematic Review of the Literature.” International Clinical Psychopharmacology, vol. 29, no. 1, Jan. 2014, pp. 1–15. PubMed, doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e328364590b.
Bolton, Jennifer L., et al. “Association between Polymorphisms of the Dopamine Receptor D2 and Catechol-o-Methyl Transferase Genes and Cognitive Function.” Behavior Genetics, vol. 40, no. 5, Sept. 2010, pp. 630–38. PubMed, doi:10.1007/s10519-010-9372-y.
Bombin, Igor, et al. “DRD3, but Not COMT or DRD2, Genotype Affects Executive Functions in Healthy and First-Episode Psychosis Adolescents.” American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, vol. 147B, no. 6, Sept. 2008, pp. 873–79. PubMed, doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30710.
Byrne, Kaileigh A., et al. “Dopaminergic Genetic Polymorphisms Predict Rule-Based Category Learning.” Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, vol. 28, no. 7, July 2016, pp. 959–70. PubMed Central, doi:10.1162/jocn_a_00942.
Can, Adem, et al. “Chronic Lithium Treatment Rectifies Maladaptive Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens.” Journal of Neurochemistry, vol. 139, no. 4, Nov. 2016, pp. 576–85. PubMed Central, doi:10.1111/jnc.13769.
—. “Chronic Lithium Treatment Rectifies Maladaptive Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens.” Journal of Neurochemistry, vol. 139, no. 4, Nov. 2016, pp. 576–85. PubMed Central, doi:10.1111/jnc.13769.
Carlson, Shaun W., and C. Edward Dixon. “Lithium Improves Dopamine Neurotransmission and Increases Dopaminergic Protein Abundance in the Striatum after Traumatic Brain Injury.” Journal of Neurotrauma, vol. 35, no. 23, 01 2018, pp. 2827–36. PubMed, doi:10.1089/neu.2017.5509.
Chang, Yun-Hsuan, et al. “Genetic Variants of the BDNF and DRD3 Genes in Bipolar Disorder Comorbid with Anxiety Disorder.” Journal of Affective Disorders, vol. 151, no. 3, Dec. 2013, pp. 967–72. ScienceDirect, doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.08.017.
Chen, Dingyan, et al. “Association between Polymorphisms of DRD2 and DRD4 and Opioid Dependence: Evidence from the Current Studies.” American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, vol. 156B, no. 6, Sept. 2011, pp. 661–70. PubMed, doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31208.
—. “Association between Polymorphisms of DRD2 and DRD4 and Opioid Dependence: Evidence from the Current Studies.” American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, vol. 156B, no. 6, Sept. 2011, pp. 661–70. PubMed, doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31208.
Chen, Jingshan, et al. “Functional Analysis of Genetic Variation in Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT): Effects on MRNA, Protein, and Enzyme Activity in Postmortem Human Brain.” American Journal of Human Genetics, vol. 75, no. 5, Nov. 2004, pp. 807–21. PubMed, doi:10.1086/425589.
Coull, Jennifer T., et al. “Dopamine Precursor Depletion Impairs Timing in Healthy Volunteers by Attenuating Activity in Putamen and Supplementary Motor Area.” The Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 32, no. 47, Nov. 2012, pp. 16704–15. PubMed Central, doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1258-12.2012.
Dahlin, Maria, et al. “CSF Levels of Dopamine and Serotonin, but Not Norepinephrine, Metabolites Are Influenced by the Ketogenic Diet in Children with Epilepsy.” Epilepsy Research, vol. 99, no. 1–2, Mar. 2012, pp. 132–38. PubMed, doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.11.003.
Firouzabadi, Negar, et al. “DRD3 Ser9Gly Polymorphism and Its Influence on Risperidone Response in Autistic Children.” Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences: A Publication of the Canadian Society for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Societe Canadienne Des Sciences Pharmaceutiques, vol. 20, no. 1, 2017, pp. 445–52. PubMed, doi:10.18433/J3H63T.
Genis-Mendoza, Alma Delia, et al. “Association between Polymorphisms of the DRD2 and ANKK1 Genes and Suicide Attempt: A Preliminary Case-Control Study in a Mexican Population.” Neuropsychobiology, vol. 76, no. 4, 2017, pp. 193–98. PubMed, doi:10.1159/000490071.
He, Hairong, et al. “Associations between Dopamine D2 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia Risk: A PRISMA Compliant Meta-Analysis.” Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, vol. 12, Dec. 2016, pp. 3129–44. PubMed Central, doi:10.2147/NDT.S118614.
—. “Associations between Dopamine D2 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia Risk: A PRISMA Compliant Meta-Analysis.” Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, vol. 12, Dec. 2016, pp. 3129–44. PubMed Central, doi:10.2147/NDT.S118614.
Hildebrand, Patricia, et al. “Effects of Dietary Tryptophan and Phenylalanine-Tyrosine Depletion on Phasic Alertness in Healthy Adults – A Pilot Study.” Food & Nutrition Research, vol. 59, 2015, p. 26407. PubMed, doi:10.3402/fnr.v59.26407.
Howes, Oliver D., et al. “The Role of Genes, Stress, and Dopamine in the Development of Schizophrenia.” Biological Psychiatry, vol. 81, no. 1, Jan. 2017, pp. 9–20. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.07.014.
James, Morgan H., et al. “Cued Reinstatement of Cocaine but Not Sucrose Seeking Is Dependent on Dopamine Signaling in Prelimbic Cortex and Is Associated with Recruitment of Prelimbic Neurons That Project to Contralateral Nucleus Accumbens Core.” International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 21, no. 1, Nov. 2017, pp. 89–94. PubMed Central, doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyx107.
Kang, Seung-Gul, et al. “DRD3 Gene Rs6280 Polymorphism May Be Associated with Alcohol Dependence Overall and with Lesch Type I Alcohol Dependence in Koreans.” Neuropsychobiology, vol. 69, no. 3, 2014, pp. 140–46. PubMed, doi:10.1159/000358062.
Kehr, J., et al. “Ginkgo Biloba Leaf Extract (EGb 761®) and Its Specific Acylated Flavonol Constituents Increase Dopamine and Acetylcholine Levels in the Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex: Possible Implications for the Cognitive Enhancing Properties of EGb 761®.” International Psychogeriatrics, vol. 24 Suppl 1, Aug. 2012, pp. S25-34. PubMed, doi:10.1017/S1041610212000567.
Le-Niculescu, H., et al. “Convergent Functional Genomics of Anxiety Disorders: Translational Identification of Genes, Biomarkers, Pathways and Mechanisms.” Translational Psychiatry, vol. 1, no. 5, May 2011, p. e9. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/tp.2011.9.
Levran, Orna, et al. “Overlapping Dopaminergic Pathway Genetic Susceptibility for Heroin and Cocaine Addictions in African Americans.” Annals of Human Genetics, vol. 79, no. 3, May 2015, pp. 188–98. PubMed Central, doi:10.1111/ahg.12104.
Li, Lizhuo, et al. “The Association Between Genetic Variants in the Dopaminergic System and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Meta-Analysis.” Medicine, vol. 95, no. 11, Mar. 2016, p. e3074. PubMed, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000003074.
Ling, Daijun, et al. “Association between Polymorphism of the Dopamine Transporter Gene and Early Smoking Onset: An Interaction Risk on Nicotine Dependence.” Journal of Human Genetics, vol. 49, no. 1, 2004, pp. 35–39. PubMed, doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0104-5.
Mang, Cameron S., et al. “Exploring Genetic Influences Underlying Acute Aerobic Exercise Effects on Motor Learning.” Scientific Reports, vol. 7, no. 1, 21 2017, p. 12123. PubMed, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12422-3.
Martinez, Luis A., et al. “A Ketogenic Diet Diminishes Behavioral Responses to Cocaine in Young Adult Male and Female Rats.” Neuropharmacology, vol. 149, 01 2019, pp. 27–34. PubMed, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.02.001.
Mohammadi, Hiwa, et al. “Relationship between Serum Homovanillic Acid, DRD2 C957T (Rs6277), and HDAT A559V (Rs28364997) Polymorphisms and Developmental Stuttering.” Journal of Communication Disorders, vol. 76, Dec. 2018, pp. 37–46. PubMed, doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2018.08.003.
Naß, Janine, and Thomas Efferth. “Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacotherapy of Military Personnel Suffering from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder.” Current Neuropharmacology, vol. 15, no. 6, Aug. 2017, pp. 831–60. PubMed Central, doi:10.2174/1570159X15666161111113514.
Nyman, Emma S., et al. “Sex-Specific Influence of DRD2 on ADHD-Type Temperament in a Large Population-Based Birth Cohort.” Psychiatric Genetics, vol. 22, no. 4, Aug. 2012, p. 197. journals.lww.com, doi:10.1097/YPG.0b013e32834c0cc8.
Nymberg, Charlotte, et al. “DRD2/ANKK1 Polymorphism Modulates the Effect of Ventral Striatal Activation on Working Memory Performance.” Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 39, no. 10, Sept. 2014, pp. 2357–65. PubMed, doi:10.1038/npp.2014.83.
—. “DRD2/ANKK1 Polymorphism Modulates the Effect of Ventral Striatal Activation on Working Memory Performance.” Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 39, no. 10, Sept. 2014, pp. 2357–65. PubMed, doi:10.1038/npp.2014.83.
Ota, Vanessa Kiyomi, et al. “DRD1 Rs4532 Polymorphism: A Potential Pharmacogenomic Marker for Treatment Response to Antipsychotic Drugs.” Schizophrenia Research, vol. 142, no. 1–3, Dec. 2012, pp. 206–08. PubMed, doi:10.1016/j.schres.2012.08.003.
Pan, Yuqing, et al. “Association of Dopamine D1 Receptor Gene Polymorphism with Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis.” Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, vol. 10, June 2014, pp. 1133–39. PubMed Central, doi:10.2147/NDT.S63776.
Pinsonneault, Julia K., et al. “Dopamine Transporter Gene Variant Affecting Expression in Human Brain Is Associated with Bipolar Disorder.” Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 36, no. 8, July 2011, pp. 1644–55. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/npp.2011.45.
Rivera-Iñiguez, Ingrid, et al. “DRD2/ANKK1 TaqI A1 Polymorphism Associates with Overconsumption of Unhealthy Foods and Biochemical Abnormalities in a Mexican Population.” Eating and Weight Disorders: EWD, vol. 24, no. 5, Oct. 2019, pp. 835–44. PubMed, doi:10.1007/s40519-018-0596-9.
—. “DRD2/ANKK1 TaqI A1 Polymorphism Associates with Overconsumption of Unhealthy Foods and Biochemical Abnormalities in a Mexican Population.” Eating and Weight Disorders: EWD, vol. 24, no. 5, Oct. 2019, pp. 835–44. PubMed, doi:10.1007/s40519-018-0596-9.
Shafiei, Golia, et al. “Dopamine Signaling Modulates the Stability and Integration of Intrinsic Brain Networks.” Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.: 1991), vol. 29, no. 1, 01 2019, pp. 397–409. PubMed, doi:10.1093/cercor/bhy264.
Shnitko, Tatiana A., et al. “Acute Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Depletion of Phasic Dopamine in the Rat Brain.” Psychopharmacology, vol. 233, no. 11, 2016, pp. 2045–54. PubMed, doi:10.1007/s00213-016-4259-0.
Sun, Xue, et al. “DRD2: Bridging the Genome and Ingestive Behavior.” Trends in Cognitive Sciences, vol. 21, no. 5, May 2017, pp. 372–84. PubMed Central, doi:10.1016/j.tics.2017.03.004.
—. “DRD2: Bridging the Genome and Ingestive Behavior.” Trends in Cognitive Sciences, vol. 21, no. 5, May 2017, pp. 372–84. PubMed Central, doi:10.1016/j.tics.2017.03.004.
Tellez, Luis A., et al. “Separate Circuitries Encode the Hedonic and Nutritional Values of Sugar.” Nature Neuroscience, vol. 19, no. 3, Mar. 2016, pp. 465–70. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/nn.4224.
Tsang, Jonathan, et al. “The Relationship between Dopamine Receptor D1 and Cognitive Performance.” NPJ Schizophrenia, vol. 1, Mar. 2015, p. 14002. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/npjschz.2014.2.
—. “The Relationship between Dopamine Receptor D1 and Cognitive Performance.” NPJ Schizophrenia, vol. 1, Mar. 2015, p. 14002. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/npjschz.2014.2.
Vereczkei, Andrea, et al. “Multivariate Analysis of Dopaminergic Gene Variants as Risk Factors of Heroin Dependence.” PloS One, vol. 8, no. 6, 2013, p. e66592. PubMed, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066592.
Wang, Liang-Jen, et al. “A Potential Interaction between COMT and MTHFR Genetic Variants in Han Chinese Patients with Bipolar II Disorder.” Scientific Reports, vol. 5, Mar. 2015. PubMed Central, doi:10.1038/srep08813.
Xu, Haiyan, et al. “DRD2 C957T Polymorphism Interacts with the COMT Val158Met Polymorphism in Human Working Memory Ability.” Schizophrenia Research, vol. 90, no. 1–3, Feb. 2007, pp. 104–07. PubMed, doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.10.001.
Yao, Jun, et al. “Association between DRD2 (Rs1799732 and Rs1801028) and ANKK1 (Rs1800497) Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis.” American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, vol. 168B, no. 1, Jan. 2015, pp. 1–13. PubMed, doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32281.
Yoshitake, T., et al. “The Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761(R) and Its Main Constituent Flavonoids and Ginkgolides Increase Extracellular Dopamine Levels in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex.” British Journal of Pharmacology, vol. 159, no. 3, Feb. 2010, pp. 659–68. PubMed, doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00580.x.
Zhu, Feng, et al. “Dopamine D1 Receptor Gene Variation Modulates Opioid Dependence Risk by Affecting Transition to Addiction.” PLoS ONE, edited by Huiping Zhang, vol. 8, no. 8, Aug. 2013, p. e70805. DOI.org (Crossref), doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070805.