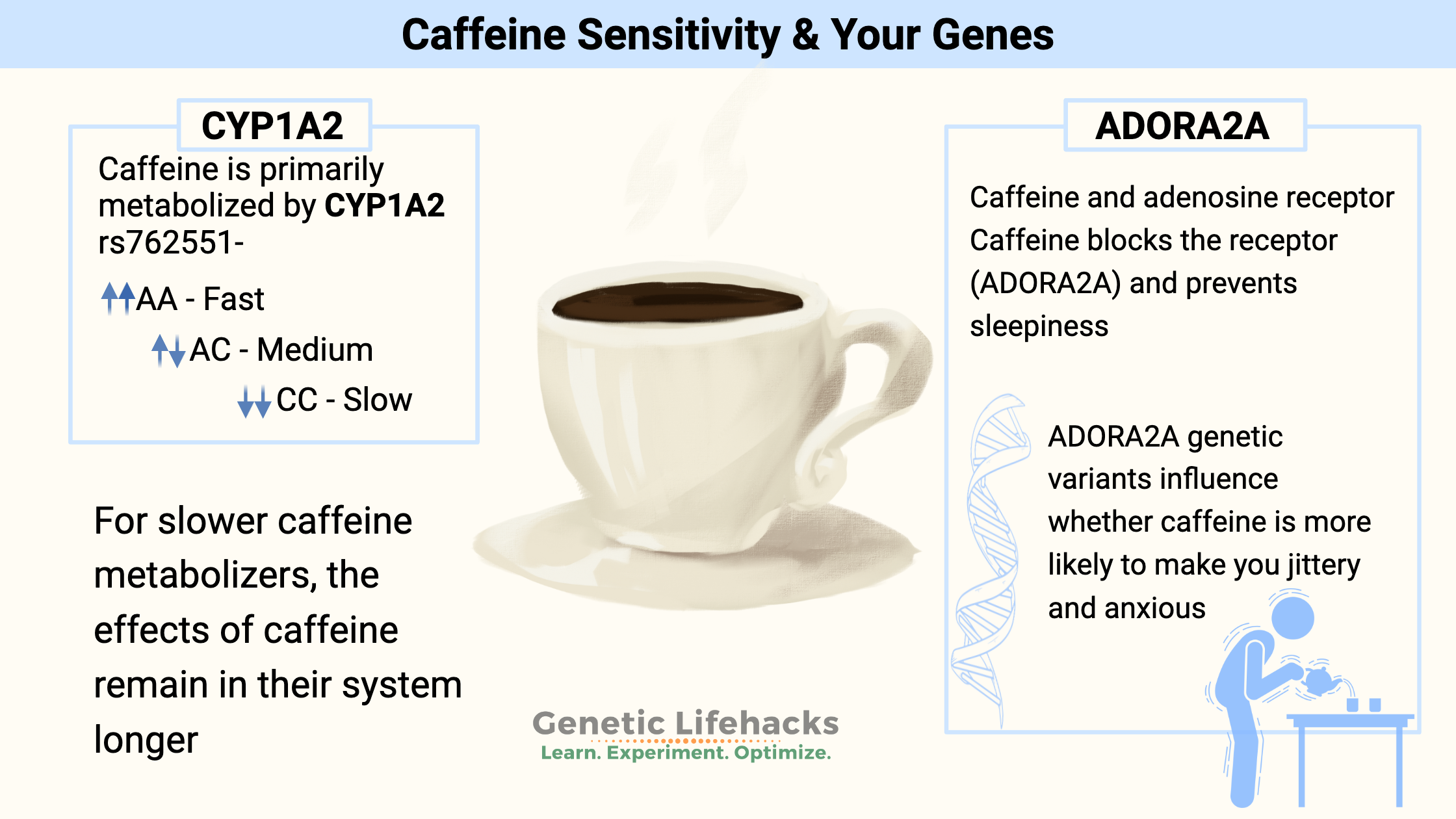
Key Takeaways:
~Caffeine is metabolized using the CYP1A2 enzyme.
~Genetic differences in CYP1A2 impact caffeine metabolism – whether you break down and eliminate caffeine slowly or quickly.
~The adenosine receptor (ADORA2A) is blocked by caffeine.
~Some people with ADORA2A variants get jittery or anxious with caffeine.
Members will see their genotype report below, plus additional solutions in the Lifehacks section. Join today.
Caffeine Metabolism and Adenosine Receptors:
Whether you start your morning with a cup of coffee or tea, caffeine remains the most popular ‘drug’ of choice for a large percentage of the population.
Caffeine wakes us up by blocking the adenosine receptor.
Adenosine builds up in the brain over the course of a day, causing us to feel sleepy. By blocking the adenosine receptor with caffeine, you no longer feel sleepy.
But… When the caffeine wears off, the adenosine is still there, causing the rebound effect of feeling even sleepier.
Caffeine Sensitivity Symptoms and Genes:
Changes to the adenosine A2A receptor gene (ADORA2A) also give rise to variations in how we respond to caffeine. Changes in the way the adenosine receptor functions due to genetic variants can alter a person’s response to caffeine.[ref]
Caffeine also acts as a central nervous system stimulant, increasing reaction time.
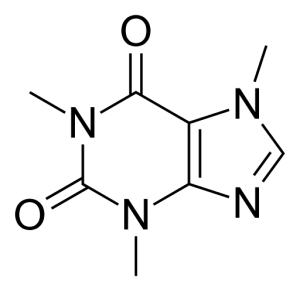
Animal studies show that the caffeine molecule binds to the adenosine 2A receptor (ADORA2A) in the hippocampus. In addition to increasing alertness and modulating anxiety, binding to the ADORA2A receptor in the brain is also how caffeine decreases memory. [ref]
CYP1A2 enzyme: How does caffeine affect you?
Have you ever thought that you may be immune to caffeine? That it just doesn’t seem to affect you?
Genes determine how quickly your body processes and eliminates caffeine and also whether it is likely to make you jittery or anxious.
The CYP1A2 gene encodes the enzyme that breaks down caffeine. Other drugs can also be broken down with the CYP1A2 gene (e.g., clozapine, olanzapine, theophylline), so be careful with drinking a lot of caffeine with certain medications.[ref]
People with genetic variants in the CYP1A2 gene usually break down caffeine more slowly, causing them to feel the effects of caffeine longer. Without the variants, you’ll break down caffeine quickly and may not notice the alerting effects as much or for as long.
Caffeine Sensitivity Genotype Report:
Lifehacks:
CYP1A2 Inhibitors: Slowing Down Caffeine Metabolism
Curcumin is an inhibitor of CYP1A2 in humans and in animals. A recent animal study found that curcumin prevented liver damage from aflatoxin B exposure.[ref] A potent carcinogen, aflatoxin B is a toxin produced by mold (Aspergillus) and is sometimes found in peanuts, corn, and other grains. Curcumin can be taken as a supplement and is also found in the spice, turmeric.
Other inhibitors of CYP1A2 include ciprofloxacin (antibiotic) and cimetidine.[ref] Keep in mind that caffeine metabolism may be altered when taking a CYP1A2 inhibitor.
In other words: If you are normally a fast metabolizer and drink coffee or tea with dinner, you may have problems sleeping if you couple that caffeine with a CYP1A2 inhibitor like cimetidine, curcumin, or ciprofloxacin.
Diet and Lifestyle:
Related Articles and Genes:
Metformin
A decades-old diabetes drug now holds promise for increasing healthspan. Research shows that metformin may reduce the risk of some of the diseases of aging, thus increasing the number of years someone is healthy.
ABCC11 gene: Ear wax and no body odor
The ABCC11 gene determines both the type of earwax a person has and whether they have no armpit or body odor.
Genetics of Double Eyelashes
Ever wonder why Elizabeth Taylor had such compelling eyes? It turns out that she probably carried a mutation for doubled eyelashes, also known as distichiasis.
References:
Arita, Reiko, et al. “Caffeine Increases Tear Volume Depending on Polymorphisms within the Adenosine A2a Receptor Gene and Cytochrome P450 1A2.” Ophthalmology, vol. 119, no. 5, May 2012, pp. 972–78. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.11.033.
Childs, Emma, et al. “Association between ADORA2A and DRD2 Polymorphisms and Caffeine-Induced Anxiety.” Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 33, no. 12, Nov. 2008, pp. 2791–800. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2008.17.
Healy, D. P., et al. “Interaction between Oral Ciprofloxacin and Caffeine in Normal Volunteers.” Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, vol. 33, no. 4, Apr. 1989, pp. 474–78. PubMed Central, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC172463/.
Hohoff, Christa, et al. “Association of Adenosine Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and in Vivo Adenosine A1 Receptor Binding in the Human Brain.” Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 39, no. 13, Dec. 2014, pp. 2989–99. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.150.
John R. Horn, PharmD, and PharmD Philip D. Hansten. “Get to Know an Enzyme: CYP1A2.” Pharmacy Times, vol. 0, Nov. 2007. www.pharmacytimes.com, https://www.pharmacytimes.com/view/2007-11-8279.
Koonrungsesomboon, Nut, et al. “The Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms on CYP1A2 Activity in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” The Pharmacogenomics Journal, vol. 18, no. 6, Dec. 2018, pp. 760–68. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41397-017-0011-3.
Kotsopoulos, Joanne, et al. “The CYP1A2 Genotype Modifies the Association between Coffee Consumption and Breast Cancer Risk among BRCA1 Mutation Carriers.” Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention: A Publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, Cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology, vol. 16, no. 5, May 2007, pp. 912–16. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-1074.
Lafranconi, Alessandra, et al. “Coffee Intake Decreases Risk of Postmenopausal Breast Cancer: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis on Prospective Cohort Studies.” Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 2, Jan. 2018, p. E112. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020112.
Lowcock, Elizabeth C., et al. “High Coffee Intake, but Not Caffeine, Is Associated with Reduced Estrogen Receptor Negative and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk with No Effect Modification by CYP1A2 Genotype.” Nutrition and Cancer, vol. 65, no. 3, 2013, pp. 398–409. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2013.768348.
Ran, Heng-Quan, et al. “Coffee Consumption and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: An Update Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies.” Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, vol. 32, no. 1, Feb. 2016, pp. 253–59. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.321.8761.
Renda, Giulia, et al. “Genetic Determinants of Cognitive Responses to Caffeine Drinking Identified from a Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial.” European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 25, no. 6, June 2015, pp. 798–807. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.03.001.
—. “Genetic Determinants of Cognitive Responses to Caffeine Drinking Identified from a Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial.” European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 25, no. 6, June 2015, pp. 798–807. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.03.001.
Rogers, Peter J., et al. “Association of the Anxiogenic and Alerting Effects of Caffeine with ADORA2A and ADORA1 Polymorphisms and Habitual Level of Caffeine Consumption.” Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 35, no. 9, Aug. 2010, pp. 1973–83. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.71.
Zhang, Ni-Ya, et al. “Curcumin Prevents Aflatoxin B₁ Hepatoxicity by Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Isozymes in Chick Liver.” Toxins, vol. 8, no. 11, Nov. 2016, p. E327. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8110327.