Key takeaways:
~ CYP2E1 is a phase I metabolism gene that encodes an enzyme that breaks down toxins in the liver.
~ Genetic variants impact the way that the CYP2E1 enzyme works, leading to an increased risk of negative effects of certain toxins.
Members will see their genotype report below, plus additional solutions in the Lifehacks section. Join today.
What does the CYP2E1 gene do?
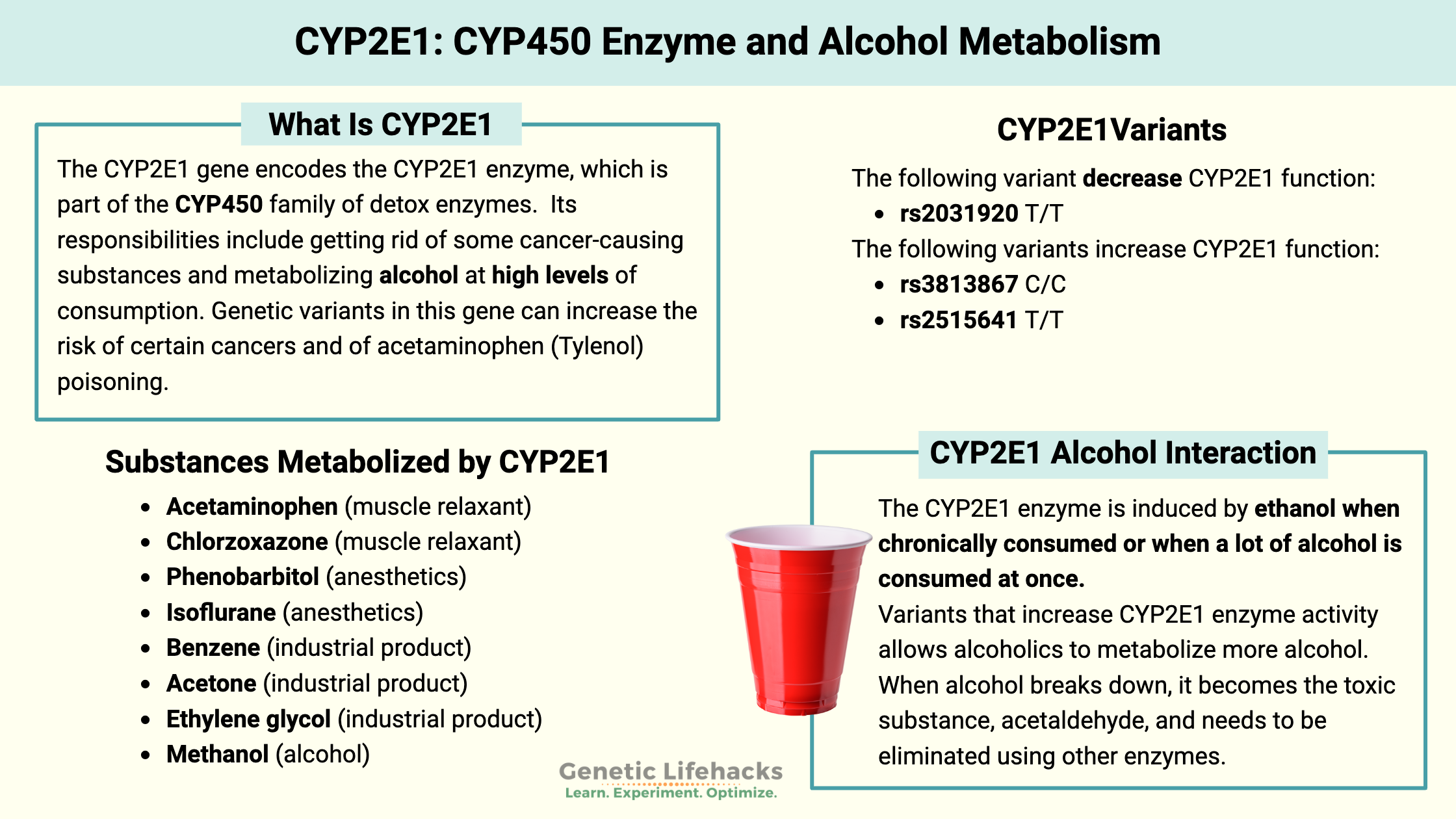
The CYP2E1 enzyme is part of the phase I detoxification system. Its responsibilities include getting rid of some cancer-causing substances and metabolizing alcohol at high levels of consumption. Genetic variants in this gene can increase the risk of certain cancers and of acetaminophen (Tylenol) poisoning.
The CYP2E1 gene encodes the CYP2E1 enzyme, which is part of the CYP450 family of detox enzymes. CYP2E1 is one of the more abundant enzymes, making up about 20% of the CYP proteins in the liver.
CYP2E1 metabolism must work in conjunction with the phase II metabolism processes. Some of the metabolites created by CYP2E1, such as formaldehyde from methanol, are toxic and need to be eliminated quickly. The key is balance – you don’t want too much CYP2E1 metabolism to overwhelm your body’s phase II detox pathways, but you also need enough CYP2E1 metabolism so that you can eliminate alcohol, methanol, and other substances from your body.
Breaking down toxins (including alcohol):
Let’s dig into the research on some of the toxic substances that the CYP2E1 enzyme helps to metabolize.
The CYP2E1 enzyme helps in the metabolism of alcohol in the liver, especially in certain situations. When you drink alcohol, it is mostly metabolized by the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme, but CYP2E1 helps out a little bit. The CYP2E1 enzyme is induced by ethanol when chronically consumed or when a lot of alcohol is consumed at once. Essentially, the CYP2E1 enzyme remains upregulated in people with alcohol use disorder who drink regularly, and it is induced if someone who is an occasional drinker imbibes a lot of alcohol at once.[ref]
Research shows that it is the increase in the CYP2E1 enzyme that allows alcoholics to metabolize more alcohol. When alcohol breaks down, it becomes the toxic substance, acetaldehyde, and needs to be eliminated using other enzymes.
Related article: Alcohol and acetaldehyde metabolism genes
CYP2E1 is also involved in the metabolism of acrylamide, which is produced through the Maillard reaction when food is cooked. Examples of acrylamide formation in food would be in toast, french fries, potato chips, cookies, and toasted breakfast cereal. Acrylamide can be carcinogenic (cancer-causing), so it is important to metabolize and get rid of it quickly.
Medications metabolized by CYP2E1:
When it comes to breaking down drugs, the CYP2E1 enzyme is important in metabolizing acetaminophen and chlorzoxazone (muscle relaxant). CYP2E1 also helps with the breakdown or activation of several anesthetics (phenobarbitol, isoflurane), as well as several industrial products including benzene, acetone, and ethylene glycol. [ref]
In the metabolism of acetaminophen, the conversion process utilizes CYP2E1 and forms a toxic metabolite, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), which can lead to liver toxicity in high doses. Again, high CYP2E1 production with a slower elimination of the toxic metabolite can lead to negative consequences, such as liver damage.[ref]
Finally, the CYP2E1 enzyme is also involved in the metabolism of methanol, a toxic alcohol. CYP2E1 catalyzes the reaction of methanol into formaldehyde, which then gets converted to formic acid.
We are exposed to methanol in multiple ways:[ref]
- Methanol is found in most alcoholic beverages
- Fresh orange juice contains about 20–40 mg/l of methanol.
- Fruits, such as bananas and apples, contain methanol (up to 18.27 mg/kg)
- The gut microbiome produces methanol when digesting plant fiber
- Aspartame is broken down in the intestines and forms a little methanol (10%)
Endogenous substances metabolized by CYP2E1:
The CYP2E1 enzyme doesn’t just hang out in the body waiting for you to take acetaminophen or drink a bunch of alcohol. We have the CYP2E1 gene because it is responsible for the biotransformation of substances that are made in the body:[ref][ref][ref]
- acetone (ketone body)
- saturated C12 to C18 fatty acids
- glycerol
CYP2E1 and liver disease:
Most CYP2E1 detoxification activity takes place in the liver, and CYP2E1 activity is linked to the risk of liver diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and also alcohol-related liver diseases. Studies show that CYP2E1 is expressed in both the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum in the liver. When CYP2E1 is involved in detoxification reactions, it produces a lot of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and can damage mitochondria in the liver cells.
CYP2E1 in the brain:
Nicotine also induces the CYP2E1 enzyme in the brain. CYP2E1 catalyzes about 20% of alcohol metabolism in the brain. This may explain why smokers who also drink a lot can have a higher rate of alcohol metabolism. Additionally, smokers with alcohol use disorder consume twice the amount of alcohol as non-smokers.[ref][ref]
Obesity and CYP2E1:
Similar to what is seen in increased alcohol consumption, people who are obese have an increased amount of CYP2E1 enzyme. This can be important for the correct dosages of medications that are metabolized with CYP2E1.[ref]
CYP2E1 Genotype Report:
Members: Log in to see your data below.
Not a member? Join here.
Why is this section is now only for members? Here’s why…
Lifehacks:
Cooking methods to reduce cancer risk:
If you carry the genetic variants linked to slower CYP2E1 function, avoiding high levels of acrylamide may help in cancer prevention. Acrylamide is produced when foods are cooked over high heat or flames. Changing your cooking methods to use low, slow heating and avoiding frying or grilling over high heat can reduce acrylamide formation.
Related Articles and Topics:
Alcohol Addiction: Exploring the Genetic and Environmental Factors