Key takeaways:
~ Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a hereditary component.
~ IBS can be caused by not digesting certain foods, by too much or too little serotonin, or from bile acid problems.
~ Understanding which genetic variants you have may help you target your underlying cause(s).
<b>Members</b> will see their genotype report below and the solutions in the Lifehacks section. <a href=”https://www.geneticlifehacks.com/membership/”>Consider joining today</a>.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Root Causes
We tend to take a gut health for granted — until something goes awry! For many people, a daily battle seems to be waged in their intestines. Pain, discomfort, bloating, diarrhea, and/or constipation… a.k.a. IBS or irritable bowel syndrome.
There are multiple causes of IBS. Pinpointing your root cause can help you figure out your solution for treating IBS. This article explains the research on the root causes of IBS, hereditary links to the genes that cause susceptibility, and solutions that fit your genes.
IBS is defined as a functional GI disorder with the following subtypes:
- Abdominal pain, bloating, gas
- Diarrhea (IBS-D)
- Constipation (IBS-C)
- OR – a mix of diarrhea and constipation (IBS-M)
Obtaining an IBS diagnosis often means eliminating other conditions — such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis).
IBS affects more than 10% of the population in Westernized countries[ref]
The causes of IBS are often a mystery — both to the person who has it and to their doctor. The use of the word ‘idiopathic‘ shows up frequently. Idiopathic simply means that the doctor doesn’t know the cause.
According to the NIH (National Institute of Health):[ref]
“Doctors aren’t sure what causes IBS.”
Not something that you want to hear from your doctor when dealing with the pain and discomfort of IBS! Often people will go through a series of dietary changes, trying to figure out which foods (if any) lead to their problems.
There may be a quicker way to get to the right solution…
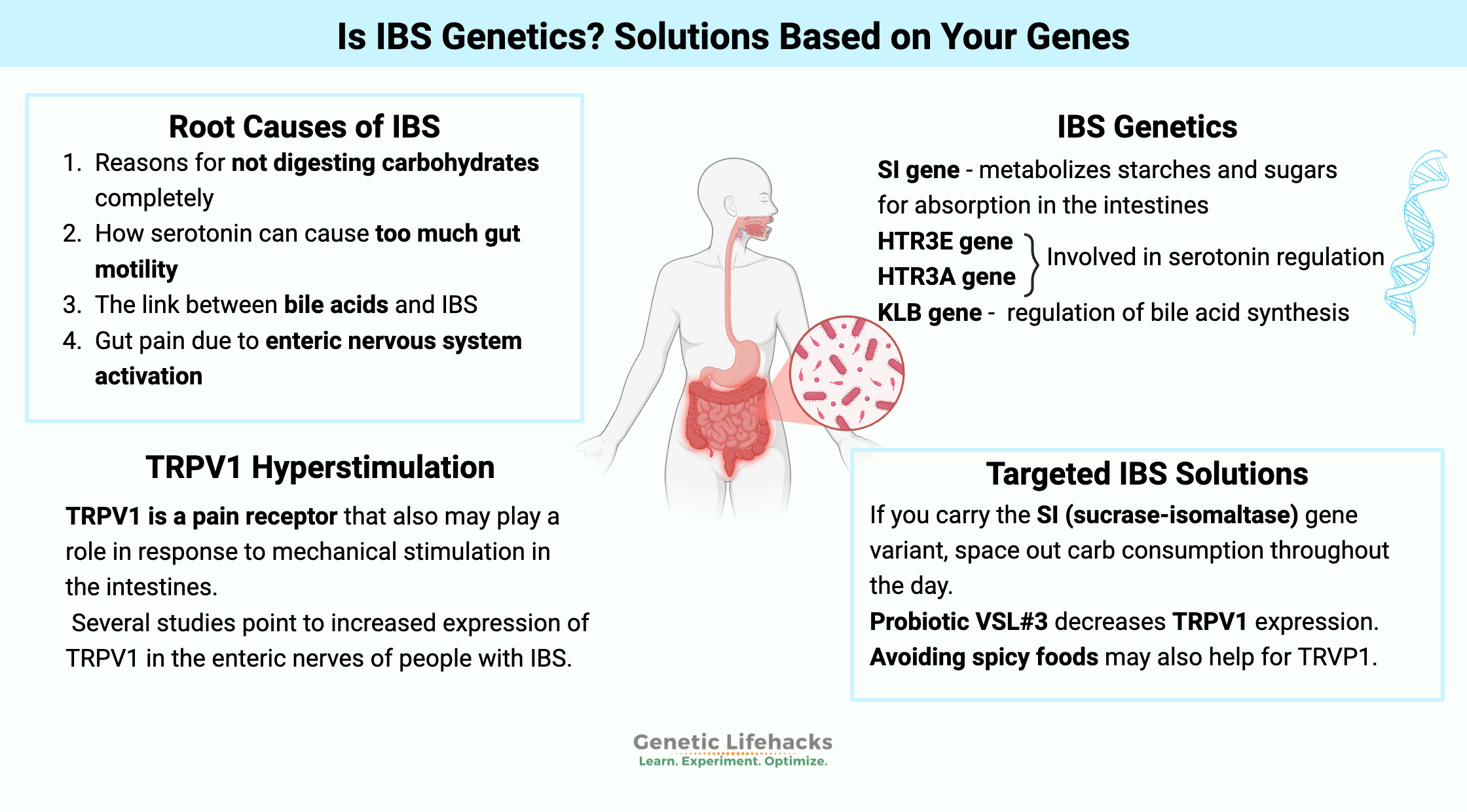
I will explain what researchers theorize about irritable bowel syndrome and then show how they link up to genetic risk factors. We will look at:
- Reasons for not digesting carbohydrates completely
- How serotonin can cause too much gut motility
- The link between bile acids and IBS
- Gut pain due to enteric nervous system activation
You can check your genetic data (below) and use that info to figure out the IBS solutions that may work best for you.
Digesting Carbs: Enzymes and Gut motility
Carbohydrates should be digested, broken down, and absorbed in the small intestine.
When that doesn’t happen — either due to a lack of enzymes to break them down or increased gut movement — the carbs end up in the colon.
Extra carbs in the colon feed the bacteria there, and they party all night, giving off gas.
While frank deficiencies of the enzymes that break down different carbohydrates are somewhat rare, researchers are now discovering that partial enzyme deficiencies could be causing IBS symptoms in some people.[ref]
Enzyme deficiencies can have a genetic cause (explained in detail in the genotype section below). Two genetic causes of enzyme deficiency linked to irritable bowel syndrome are:
- sucrase-isomaltase deficiency
- lactase deficiency
Sucrase-isomaltase (SI) deficiency is a lack of the enzyme that breaks down certain starches and sugars.
SI (sucrase-isomaltase) deficiency leads to the accumulation of unabsorbed carbs in the intestines. This leads to a change in the gut microbiome, increased short-chain fatty acids, increased gas, and often diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating.[ref]
Related article: Why the FODMAPs diet doesn’t work for you (SI gene)
Lactose is a sugar found in milk and dairy products, and lactase is the enzyme the body produces to break down lactose.
Most people of European descent have inherited a genetic variant that still allows for lactase production as an adult. But for people who don’t produce lactase as an adult (e.g., most Asians and 10% of Caucasians), drinking milk may aggravate irritable bowel syndrome symptoms.
Related article: Lactose intolerance genes
Serotonin: making things move
Most of the serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) your body produces is in the intestines. It acts as both a neurotransmitter and an immune system regulator.
Serotonin is the signaling molecule that regulates motility, secretion, and vasodilation. The stimulation of the intestinal tract produces more serotonin and serotonin receptors.[ref]
Genetic variants or environmental factors can alter serotonin levels.
Microbes in the gut can influence the amount of serotonin synthesized there.[ref] In essence, an overgrowth of certain bacteria could influence and increase serotonin synthesis.[ref]
Increased serotonin can increase motility, causing diarrhea.
There are several different serotonin receptors in the intestines. The overactivation of the 5-HT3R receptor has specific links to IBS with diarrhea. One study showed that people with IBS-D had double the number of 5-HT3R in the intestinal mucosa compared with a control group.[ref]
Bile acid synthesis and IBS
Your body produces bile acids for digesting fats as well as for getting rid of waste products, such as bilirubin. Adults produce between 400 and 800 ml of bile per day.
Typically, the gallbladder stores bile when you haven’t recently eaten. When stimulated, the gallbladder releases the bile into the upper part of the small intestines. The bile acids then break up or emulsify fats so they can be easily digested by lipases.[ref]
About 95% of the bile acids are reabsorbed when they reach the end of the small intestine. From there, recycling occurs through the liver for reuse.
If too much bile acid ends up in the colon, diarrhea will ensue… This can be either from too much being produced or from not enough being reabsorbed at the end of the small intestines (at the ileum).
When excess bile acid reaches the colon, it causes diarrhea by stimulating an increase in water in the stool.
Studies show that between 10 – 25% of patients with IBS-D had problems stemming from bile acids reaching the colon.[ref]
Enteric nervous system irritation: one genetic cause of IBS
The enteric nerves in the intestines cause peristalsis or movement. Several studies point to increased expression of TRPV1 in the enteric nerves of people with IBS. TRPV1 is a pain receptor that also may play a role in response to mechanical stimulation (i.e., foodstuff pressing on the intestines).
TRPV1 stands for transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1. It is also the receptor that capsaicin binds to, causing you to sense spicy heat.
A study that looked at the TRPV1 receptors in biopsies from IBS patients found that they had a 3.5-fold increase compared to normal people. Basically, it causes hypersensitivity to pain in the intestines (irritability!).[ref]
Another study points to histamine as a possible cause of sensitized TRPV1 channels in IBS.[ref] To tie this back to bile acids, a study points to bile acids causing mast cell activation (releasing histamine) and increasing TRPV1 expression.[ref]
Variants in the TRPM8 gene have also been linked in large, genome-wide studies to an increased risk of IBS-C. This transient receptor potential channel is also thought to be associated with bile acid secretion.[ref]
IBS Genotype Report:
Genetics plays a role in susceptibility to IBS. It is likely, for most people, IBS is caused by a combination of genetic susceptibility along with environmental (or diet) factors.[ref]
The key here is that knowing your genetic susceptibility can lead to the right solution for you.
Members: Log in to see your data below.
Not a member? Join here.
Why is this section is now only for members? Here’s why…
Lifehacks: Personalized, natural IBS solutions
The following are research-backed options that are organized by the genetic variant that they target.
Carbohydrates and Enzymes:
If you carry the SI (sucrase-isomaltase) gene variant that increases the risk of IBS-D, reducing the consumption of starches and sucrose is an obvious first step.
If you don’t want to eliminate carbs, try spacing out your starch/sugar consumption throughout the day. Don’t overwhelm your intestines with a big meal of starches and sugars. In particular, researchers found that limiting starches that are converted to maltose is important.[ref] Foods that commonly contain maltose include breads, breakfast cereals, crackers, barley, candies, honey molasses, peaches, pears, and cooked sweet potatoes. [ref]
Enzyme Supplements: There are digestive enzyme supplements readily available. Just be sure to check the label on the digestive enzymes to make sure that it contains sucrase and maltase.