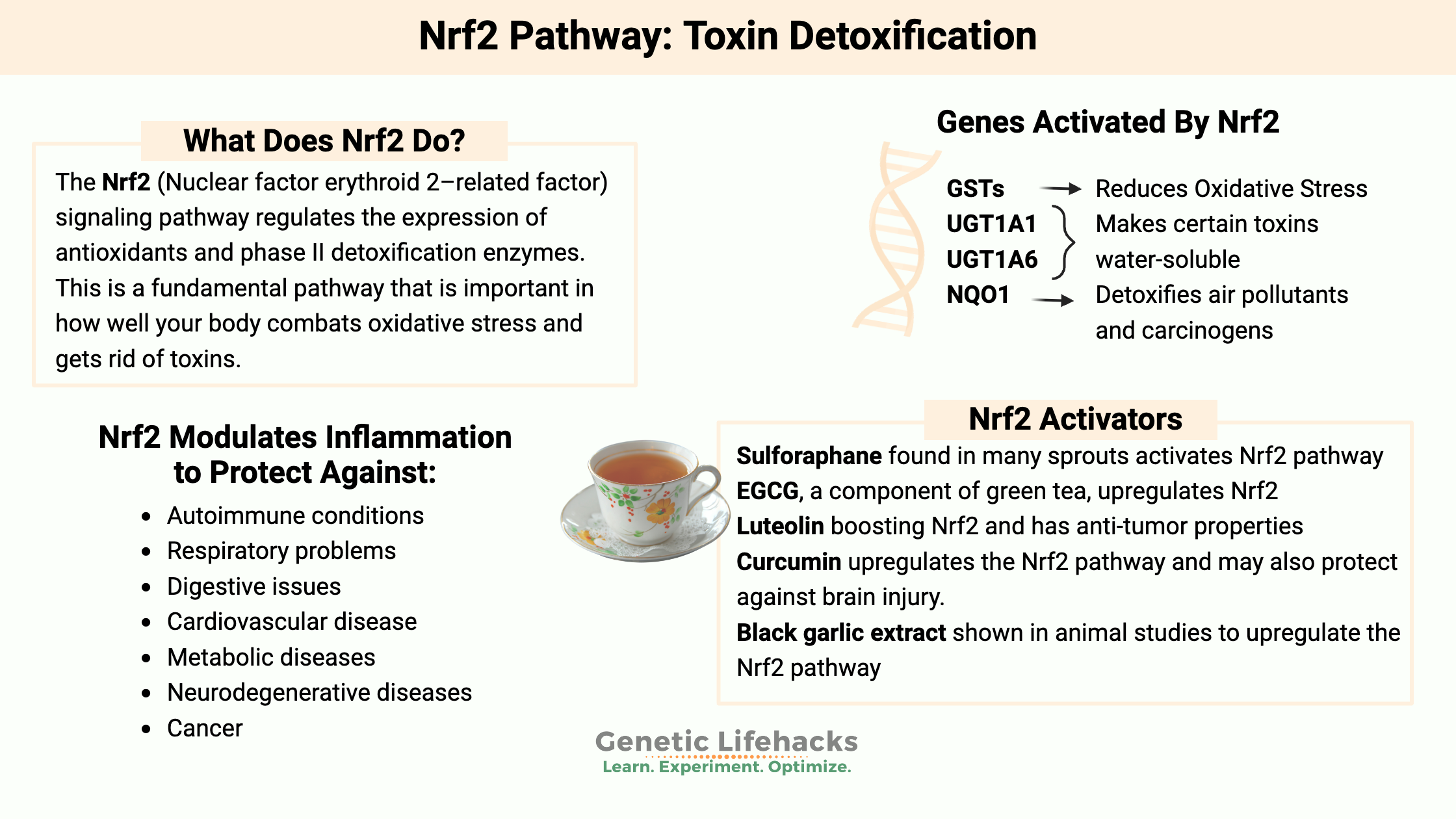
The Nrf2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor) signaling pathway regulates the expression of antioxidants and phase II detoxification enzymes. This is a fundamental pathway that is important in how well your body combats oxidative stress and gets rid of toxins.
I think of Nrf2 as flipping the switch that calls up the phase II enzymes to take out the trash produced in the first phase of detoxification. Nrf2 is also important in clearing out the free radicals produced in cells as part of their normal production of energy.
<b>Members</b> will see their genotype report below and the solutions in the Lifehacks section. <a href=”https://www.geneticlifehacks.com/membership/”>Consider joining today</a>.
Nrf2: Activating your body’s antioxidant defense
Nrf2 activates your body’s natural antioxidant defense system to reduce oxidative stress in the cell.
Specifically, the Nrf2 signaling pathway can increase the production of GSTs, NQO1, UGTs, and SULTs. These are the body’s natural antioxidant defense systems, important in every cell, all the time — but especially important when your body is under stress from an increased toxic burden.
Chronic oxidative stress is part of the root cause of chronic diseases; thus, activating the Nrf2 pathway is thought to reduce disease risk for quite a few chronic conditions.
The Nrf2 pathway is important for protecting against:[ref]
- autoimmune conditions
- respiratory problems
- digestive issues
- cardiovascular disease
- metabolic diseases
- neurodegenerative diseases
- cancer
How does Nrf2 work?
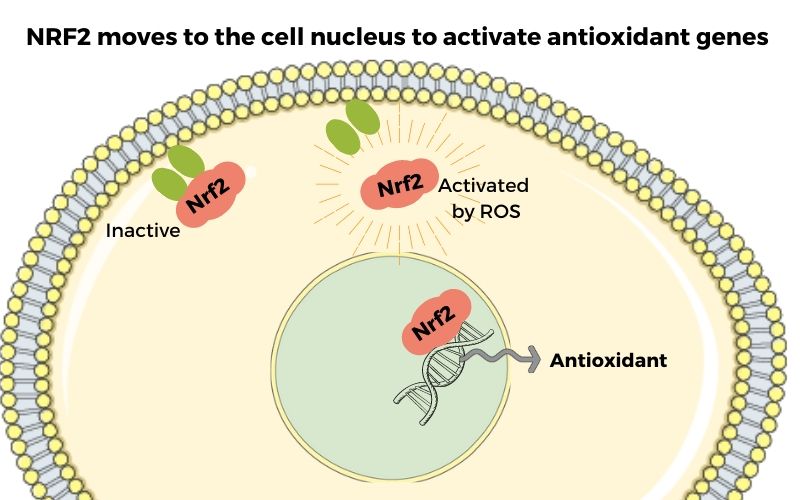
Normally, Nrf2 is located in the cytosol – the liquid inside the cell. It is hanging out, waiting to be needed.
When oxidative stress levels in a cell increase, Nrf2 moves into the cell nucleus, where the DNA is located. There it binds to certain areas of the DNA, triggering transcription of the cellular antioxidants needed to decrease the oxidative stress in the cell.[ref]
What is oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress in a cell is the imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the cell’s antioxidant capability.
Too much ROS puts the cell in a state of oxidative stress, which means that damage can occur due to the excess of free radicals. Excess ROS can damage proteins, oxidize lipids, or cause breaks and mutations in DNA.[ref]
Reactive oxygen species form in cells due to normal cellular processes, and your cells then balance this out with antioxidants. This is a normal, balanced process continually happening in cells — ROS forms and antioxidants neutralize it.
The problem comes when cells are exposed to environmental toxicants or other stressors that increase ROS beyond what is normal.
Sources of oxidative stress include:
- radiation
- environmental pollutants
- carcinogens
- cigarette smoke
- mold and mycotoxins
We are all exposed to environmental toxicants daily, from air pollution, food additives, microplastics, and personal care products.
Which genes does Nrf2 activate?
Normally, Nrf2 is present in the cytosol of cells and is kept there by another protein called Keap1. These two molecules hang out together while normal cellular processes take place.
When oxidative stress is high in cells, Nrf2 disassociates from Keap1 and moves to the nucleus. In the nucleus, Nrf2 turns on certain genes for transcription.
Nrf2 can activate the GST (glutathione S-transferase) genes in order to eliminate toxic compounds and reduce oxidative stress.[ref]
Related article: See your GST genetic variants
NRF2 can also induce UGT1A1 and UGT1A6, which are important for making certain toxins, such as acetaminophen, more water-soluble for excretion.
Related article: See your UGT genetic variants
Nrf2 also activates NQO1, which is important in detoxifying air pollutants, benzene, and several other carcinogens.
Related article: NQO1 genetic variants
Nrf2 modulates inflammation:
In addition to activating genes that counter oxidative stress, Nrf2 also keeps inflammatory molecules in check. NF-κB is an important regulator of the immune system. When NF-κB is not correctly regulated, the immune response can be overactive, such as in septic shock or autoimmune diseases.
Nrf2 acts to keep NF-κB in balance. Both molecules act in the nucleus to turn on other genes, and they interact to balance out proinflammatory and antioxidant responses.[ref]
The drawbacks of Nrf2 overactivation:
While Nrf2 activation can prevent oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and cancerous mutations, once cancer has taken hold, excessive Nrf2 activation may not be a good idea.[ref] For anyone with cancer or on chemotherapy, please be sure to talk with your doctor about whether activation of the Nrf2 pathway is right for you. Overactivation of Nrf2 can cause the activation of pro-growth genes in cancer cells.[ref]
Animal studies show that lower Nrf2 levels are protective against cardiomyopathy from iron overload.[ref] There are also tradeoffs for Nrf2 activation in chronic kidney disease, depending on the stage of the disease.[ref]
Nrf2: Genotype Report
Members: Log in to see your data below.
Not a member? Join here.
Why is this section is now only for members? Here’s why…
Lifehacks:
It isn’t as simple as everyone needs to boost Nrf2.
- If your genetic data shows that you have the variants linked to lower Nrf2, it may be important to boost Nrf2 if you are exposed to toxicants that cause oxidative stress.
- If your genetic data shows the variants linked to higher Nrf2, then boosting Nrf2 may not be all that important for you in most situations.
Age is likely also important to consider. Older adults are more likely to have higher ROS levels and thus may find boosting Nrf2 more beneficial.
The dark side: Prolonged activation of Nrf2 isn’t always beneficial. Studies show that excess activation of Nrf2 may cause tissue damage or promote cancer (in people who already have cancer).[ref]
Increase Nrf2 through lifestyle changes:
Regular exercise upregulates the Nrf2 pathway.[ref] Vitamin D also activates Nrf2, so consider exercising outside when possible.
Nrf2 Activators: 6 Natural Supplements that extend Nrf2
Related Articles and Topics: