Histamine Intolerance: Genetic Report, Supplements, and Real Solutions
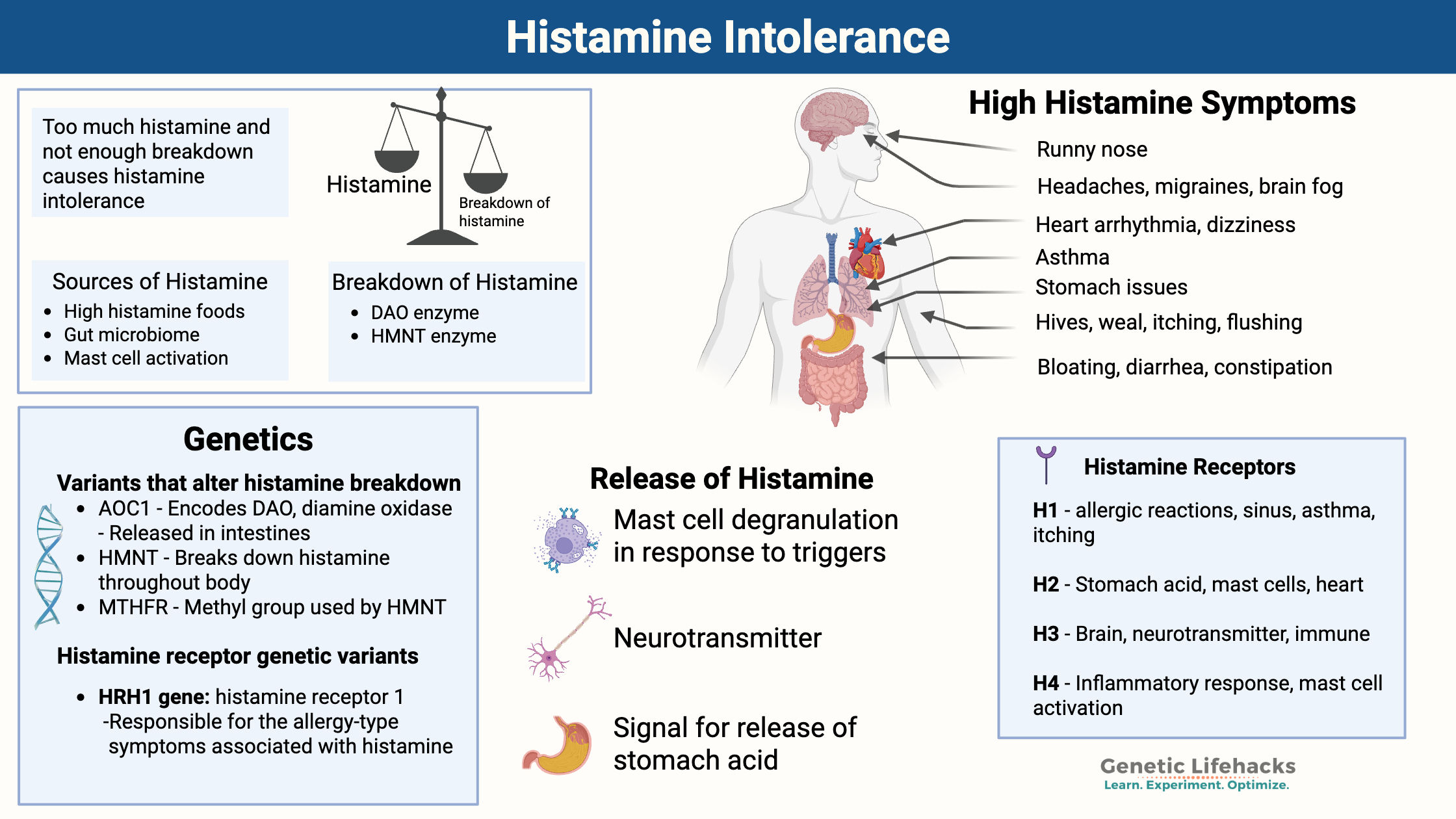
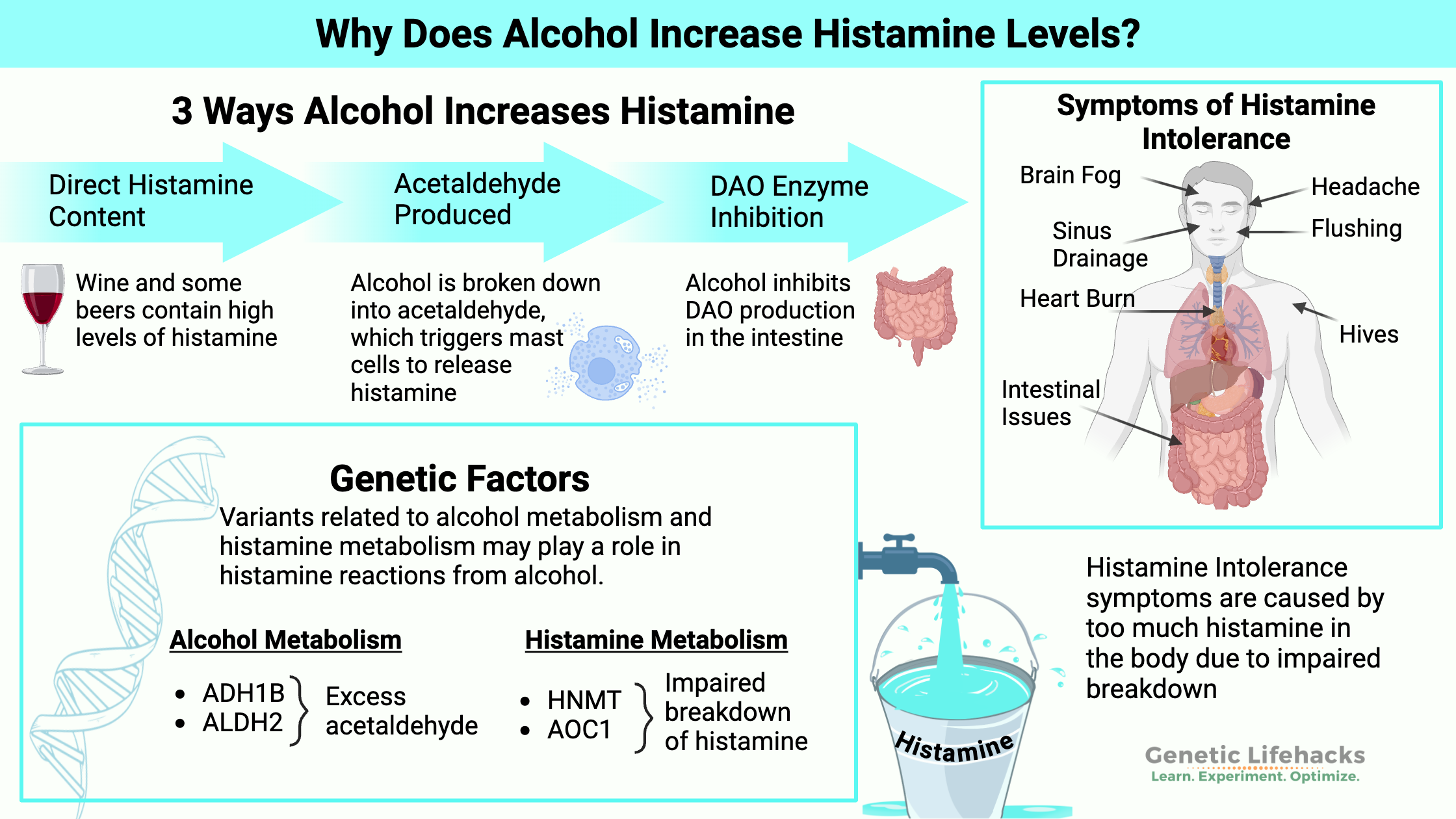
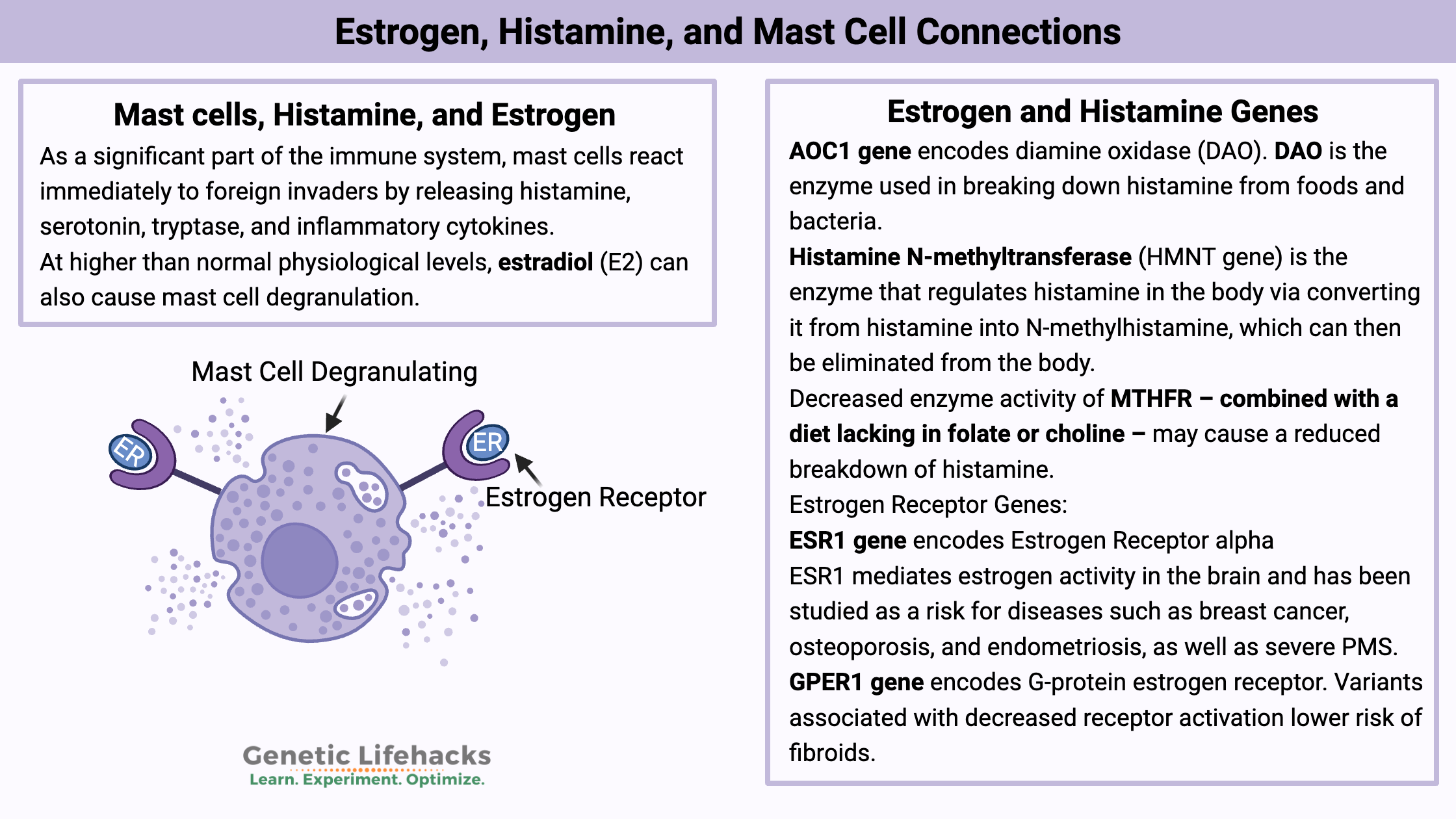
Genetics plays a big role in how well your body breaks down histamine. You can use your genetic data to figure out if your genes are part of the reason why you have histamine intolerance.