Key takeaways:
~ Gingivitis is caused by inflammation in your gum tissue.
~ Bacteria in the mouth causes the inflammation in the gums. Brushing and not smoking help to decrease inflammation.
~ Gum disease and oral health are linked to overall health, including heart disease and neurodegenerative diseases.
~ Genetic variants play a big role in how much inflammatory response you will have in the mouth. Targeting the right genes may help with gum disease.
What is Gingivitis?
Have you ever gone to the dentist, expecting a good report, only to be fussed at by the hygienist for bleeding gums? You brushed, flossed, and stayed away from candy for the past six months — so why on earth do you still have inflamed gums?
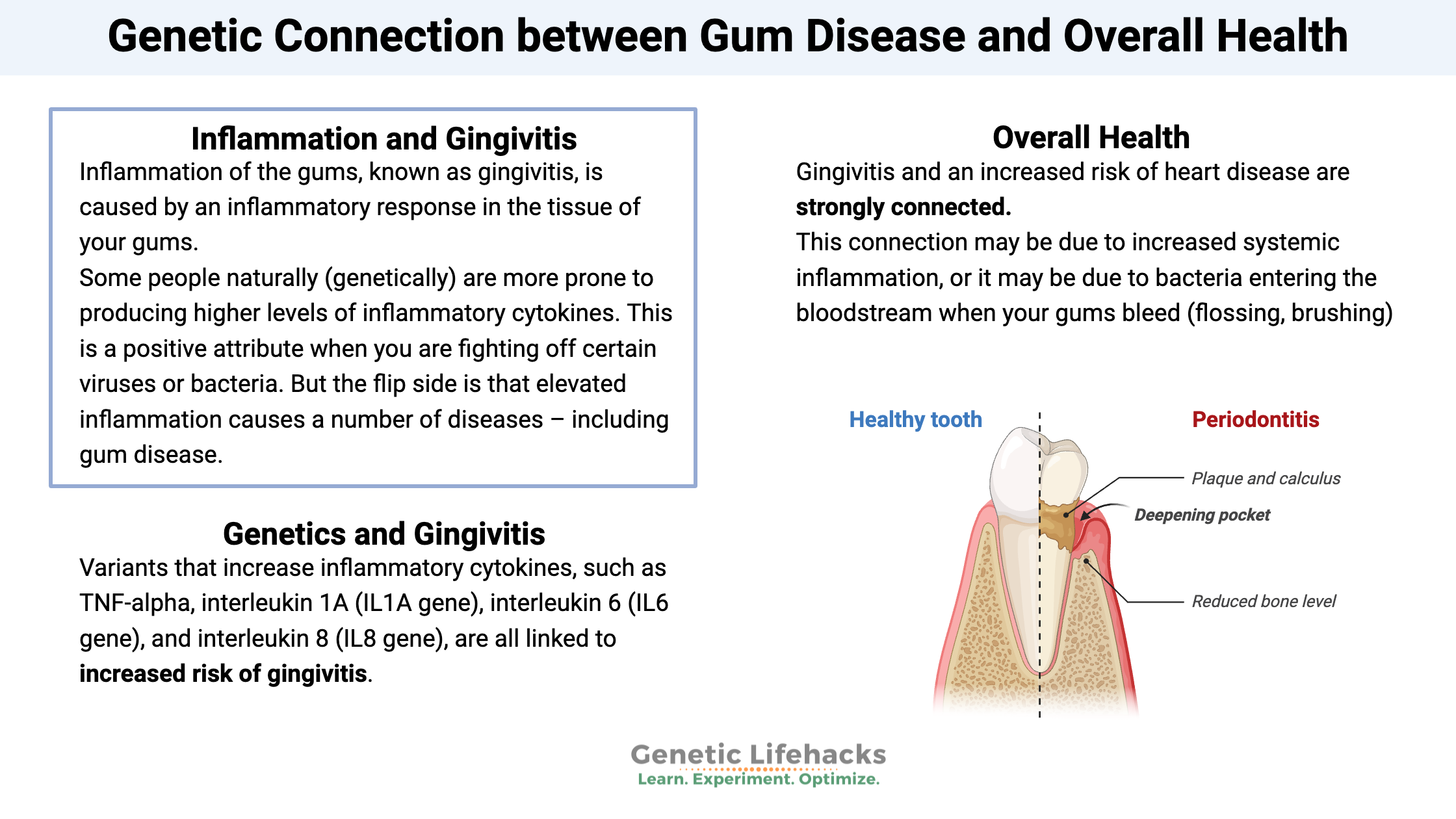
Inflammation of the gums, known as gingivitis, is caused by an inflammatory response in the tissue of your gums. Periodontal disease is another term you may have heard mentioned by your hygienist (as she stabs your gums with the sharp poking tool). Periodontal disease is a term that includes gingivitis and then the next step – inflammation of the jaw bone and loose teeth.[ref]
So what causes gingivitis? Lack of brushing and flossing… maybe. Smoking, for sure.
But what if you regularly brush and floss? And what about those people (you know who you are) who don’t brush and floss but have healthy gums?
The key here is the body’s response to the bacteria and biofilm on the teeth. The mouth is teeming with bacteria, and your immune system is on high alert to keep those bacteria from crossing into the bloodstream.
Inflammation, gingivitis, and genetics:
Some people naturally (genetically) are more prone to producing higher levels of inflammatory cytokines. This is a positive attribute when you are fighting off certain viruses or bacteria. But the flip side is that elevated inflammation causes a number of diseases – including gum disease.
Frequently, people with gingivitis have higher CRP levels on average than people without gingivitis. And people with periodontitis had even higher CRP levels.[ref]
Genetic studies reveal a lot about the underlying causes of diseases, including gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Variants that increase inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha, interleukin 1A (IL1A gene), interleukin 6 (IL6 gene), and interleukin 8 (IL8 gene), are all linked to increased risk of gingivitis.
Your body also has ways to mitigate inflammatory cytokine production. Interleukin 10 is one such mechanism for moderating the inflammatory response. Genetic variants that decrease IL-10 are thus linked to increased inflammation and an increased risk of periodontal disease.
An increased inflammatory response to bacteria causes inflammation in the gums – gingivitis or periodontal disease. And targeting the right genetic variants may help you stop the bleeding and receding gums.
Heart disease and Gingivitis:
This article isn’t just about a little bleeding when you brush or floss. Gingivitis and an increased risk of heart disease are strongly connected.
This connection may be due to increased systemic inflammation, or it may be due to bacteria entering the bloodstream when your gums bleed (flossing, brushing).[ref]
Resolving inflammation:
The resolution of inflammation – the shutting off of inflammatory cytokine production – is actually an active process. Certain lipid-based molecules called pro-resolving mediators are produced to both stop inflammatory cytokine production and also promote the healing process (stem cells, etc.). These lipid-based pro-resolving mediators are produced from DHA and EPA, which are found in marine oils.
This is a huge and really important topic that I encourage you to read all about: Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators: Getting Rid of Chronic Inflammation.
Gingivitis Genotype Report:
Lifehacks for reducing gum disease:
Here are some natural options to explore for reducing inflammation in your gums:
Good oral hygiene:
It almost goes without saying (but I’m saying it anyway) that good oral hygiene measures, such as brushing your teeth and using a water flosser, are important in oral health and gingivitis. This is the starting point.
Reducing fluoride to reduce inflammation?
Studies show fluoride increases inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6.[ref][ref][ref]
Does this mean that you should stop drinking fluoridated water and use toothpaste without fluoride? I’ll let you read through the research and decide for yourself.
Related article: Fluoride and genetic interactions
Swish with salt water:
Rinsing with salt water has some interesting research behind it for decreasing gingivitis. The study on saline shows that it increases type-I collagen and fibronectin in gingivitis cells.[ref]
Supplements for reducing inflammation in your gums:
Related Articles and Topics:
Dental Implants: Genetics & Reducing the Risk of Implant Failures
TNF-alpha: Inflammation, Chronic Diseases, and Genetic Susceptibility
TNF-alpha: Inflammation, Chronic Diseases, and Genetic Susceptibility
References:
Andia, Denise C., et al. “Interleukin-8 Gene Promoter Polymorphism (Rs4073) May Contribute to Chronic Periodontitis.” Journal of Periodontology, vol. 82, no. 6, June 2011, pp. 893–99. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2010.100513.
Andrade, Eric Francelino, et al. “Can Resveratrol Treatment Control the Progression of Induced Periodontal Disease? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies.” Nutrients, vol. 11, no. 5, Apr. 2019, p. E953. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11050953.
Balappanavar, Aswini Y., et al. “Comparison of the Effectiveness of 0.5% Tea, 2% Neem and 0.2% Chlorhexidine Mouthwashes on Oral Health: A Randomized Control Trial.” Indian Journal of Dental Research: Official Publication of Indian Society for Dental Research, vol. 24, no. 1, Feb. 2013, pp. 26–34. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-9290.114933.
Cavalla, Franco, et al. “CCR5Δ32 (Rs333) Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Risk of Chronic and Aggressive Periodontitis: A Case-Control Analysis Based in Disease Resistance and Susceptibility Phenotypes.” Cytokine, vol. 103, Mar. 2018, pp. 142–49. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.022.
—. “CCR5Δ32 (Rs333) Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Risk of Chronic and Aggressive Periodontitis: A Case-Control Analysis Based in Disease Resistance and Susceptibility Phenotypes.” Cytokine, vol. 103, Mar. 2018, pp. 142–49. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.022.
Chen, Xing, et al. “Quantitative Assessment of the Associations between Interleukin-8 Polymorphisms and Periodontitis Susceptibility.” Journal of Periodontology, vol. 86, no. 2, Feb. 2015, pp. 292–300. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2014.140450.
Corrêa, M. G., et al. “Systemic Treatment with Resveratrol and/or Curcumin Reduces the Progression of Experimental Periodontitis in Rats.” Journal of Periodontal Research, vol. 52, no. 2, Apr. 2017, pp. 201–09. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12382.
Dashash, M., et al. “The Relationship between Interleukin-10 Gene Polymorphism at Position -1082 and Susceptibility to Gingivitis in Children.” Journal of Periodontology, vol. 76, no. 9, Sept. 2005, pp. 1455–62. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2005.76.9.1455.
Domínguez-Pérez, Rubén Abraham, et al. “Association of Cytokines Polymorphisms with Chronic Peridontitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Mexican Population.” Acta Odontologica Scandinavica, vol. 75, no. 4, May 2017, pp. 243–48. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2017.1280846.
Dominici, Roberto, et al. “Cloning and Functional Analysis of the Allelic Polymorphism in the Transcription Regulatory Region of Interleukin-1 Alpha.” Immunogenetics, vol. 54, no. 2, May 2002, pp. 82–86. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-002-0445-9.
Huynh, Nam Cong-Nhat, et al. “Rinsing with Saline Promotes Human Gingival Fibroblast Wound Healing In Vitro.” PLoS ONE, vol. 11, no. 7, July 2016, p. e0159843. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159843.
Jayaprakash, Deepika, et al. “Effect of Periodontal Therapy on C-Reactive Protein Levels in Gingival Crevicular Fluid of Patients with Gingivitis and Chronic Periodontitis: A Clinical and Biochemical Study.” Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology, vol. 18, no. 4, 2014, pp. 456–60. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-124X.138688.
Lang, N. P., et al. “Effect of Interleukin-1 Gene Polymorphisms on Gingival Inflammation Assessed by Bleeding on Probing in a Periodontal Maintenance Population.” Journal of Periodontal Research, vol. 35, no. 2, Apr. 2000, pp. 102–07. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0765.2000.035002102.x.
Lee, Jung-Hoo, et al. “The Association of Dietary Vitamin C Intake with Periodontitis among Korean Adults: Results from KNHANES Ⅳ.” PLoS ONE, vol. 12, no. 5, May 2017, p. e0177074. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177074.
Majumder, Poulami, et al. “Interleukin Gene Polymorphisms in Chronic Periodontitis: A Case-Control Study in the Indian Population.” Archives of Oral Biology, vol. 101, May 2019, pp. 156–64. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.03.015.
—. “Interleukin Gene Polymorphisms in Chronic Periodontitis: A Case-Control Study in the Indian Population.” Archives of Oral Biology, vol. 101, May 2019, pp. 156–64. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.03.015.
Moreira, P. R., et al. “Interleukin-6 Expression and Gene Polymorphism Are Associated with Severity of Periodontal Disease in a Sample of Brazilian Individuals.” Clinical and Experimental Immunology, vol. 148, no. 1, Apr. 2007, pp. 119–26. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03327.x.
Padayatty, Sebastian J., and Mark Levine. “Vitamin C Physiology: The Known and the Unknown And.” Oral Diseases, vol. 22, no. 6, Sept. 2016, pp. 463–93. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12446.
Reichert, S., et al. “Interleukin-2 -330 and 166 Gene Polymorphisms in Relation to Aggressive or Chronic Periodontitis and the Presence of Periodontopathic Bacteria.” Journal of Periodontal Research, vol. 44, no. 5, Oct. 2009, pp. 628–35. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.2008.01173.x.
Schenkein, Harvey A., and Bruno G. Loos. “Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Periodontal Diseases to Cardiovascular Diseases.” Journal of Clinical Periodontology, vol. 40, no. 0 14, Apr. 2013, pp. S51–69. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12060.
Schulz, Susanne, et al. “Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Interleukin-1gene Cluster and Subgingival Colonization with Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis.” Human Immunology, vol. 72, no. 10, Oct. 2011, pp. 940–46. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2011.05.009.
Spittler, Andreas, et al. “Immunomodulatory Effects of Glycine on LPS-Treated Monocytes: Reduced TNF-α Production and Accelerated IL-10 Expression.” The FASEB Journal, vol. 13, no. 3, 1999, pp. 563–71. Wiley Online Library, https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.13.3.563.
Tada, Akio, and Hiroko Miura. “The Relationship between Vitamin C and Periodontal Diseases: A Systematic Review.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 16, no. 14, July 2019, p. 2472. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142472.
Waugh, Declan Timothy. “Fluoride Exposure Induces Inhibition of Sodium/Iodide Symporter (NIS) Contributing to Impaired Iodine Absorption and Iodine Deficiency: Molecular Mechanisms of Inhibition and Implications for Public Health.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 16, no. 6, Mar. 2019, p. E1086. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061086.
“What Is Interleukin 6?” News-Medical.Net, 22 Feb. 2011, https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Interleukin-6.aspx.
Yan, Nan, et al. “Fluoride-Induced Neuron Apoptosis and Expressions of Inflammatory Factors by Activating Microglia in Rat Brain.” Molecular Neurobiology, vol. 53, no. 7, Sept. 2016, pp. 4449–60. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9380-2.
Zhao, Bo, and Ronghua Li. “The Association between Periodontitis and Interleukin-6 Genetic Polymorphism -174 G/C: A Meta-Analysis.” Archives of Oral Biology, vol. 96, Dec. 2018, pp. 13–20. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.08.007.