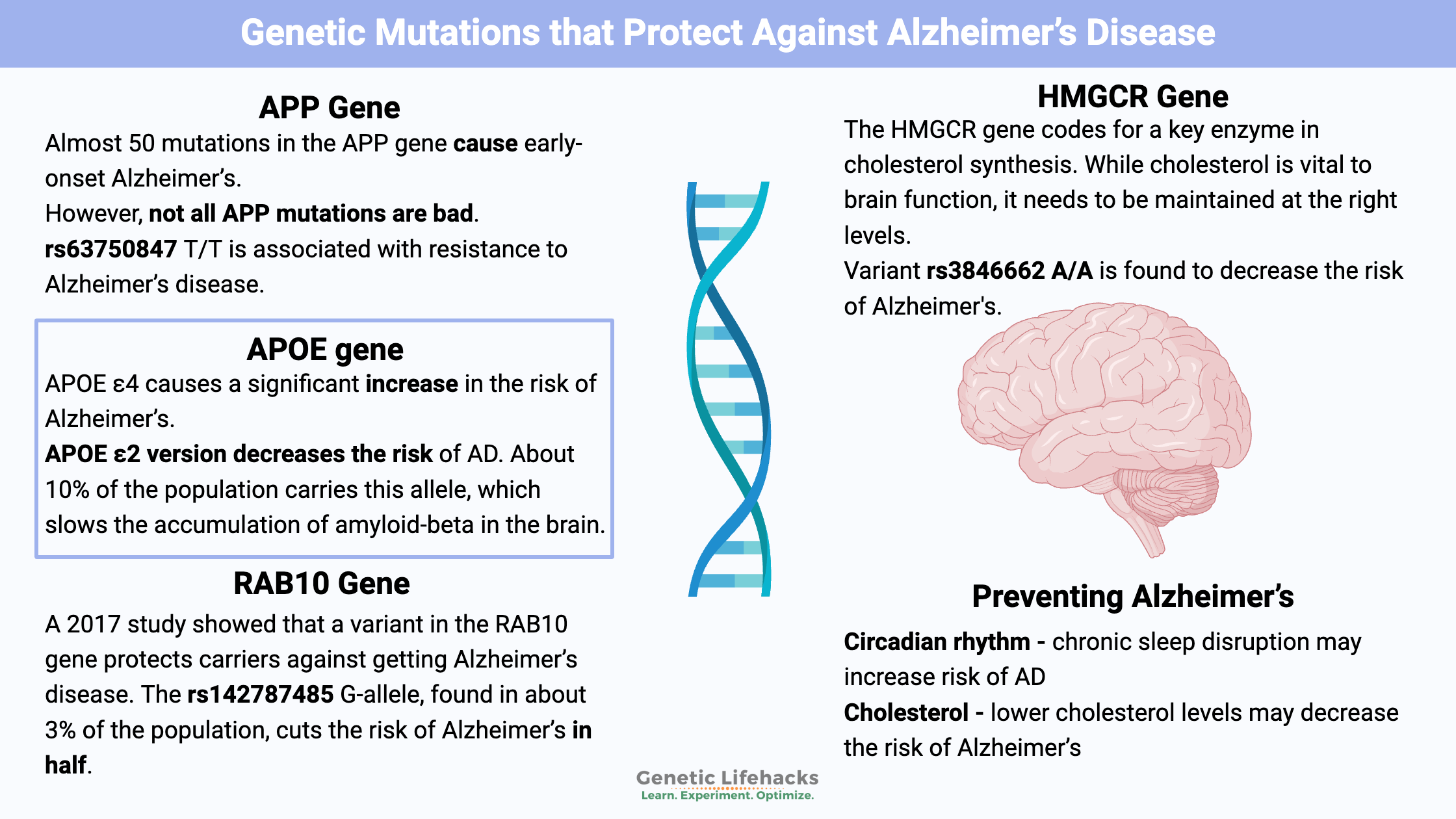
Genetic Mutations that Protect Against Alzheimer’s Disease
Just like there are genetic variants that increase the risk of Alzheimer’s, there are also variants that protect against this disease. Check your genetic data to get a better picture of your risk factors. (Member’s article)