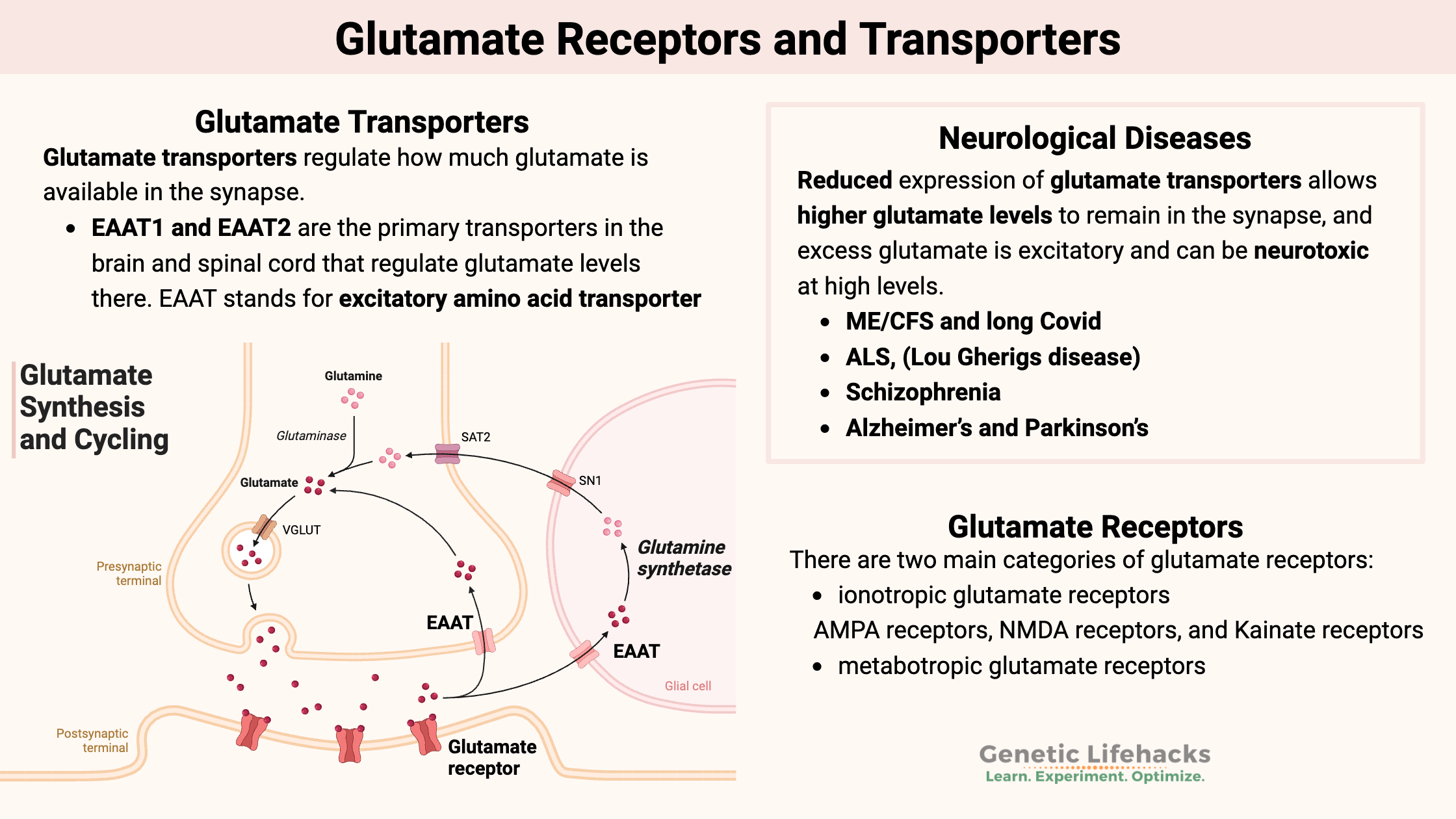
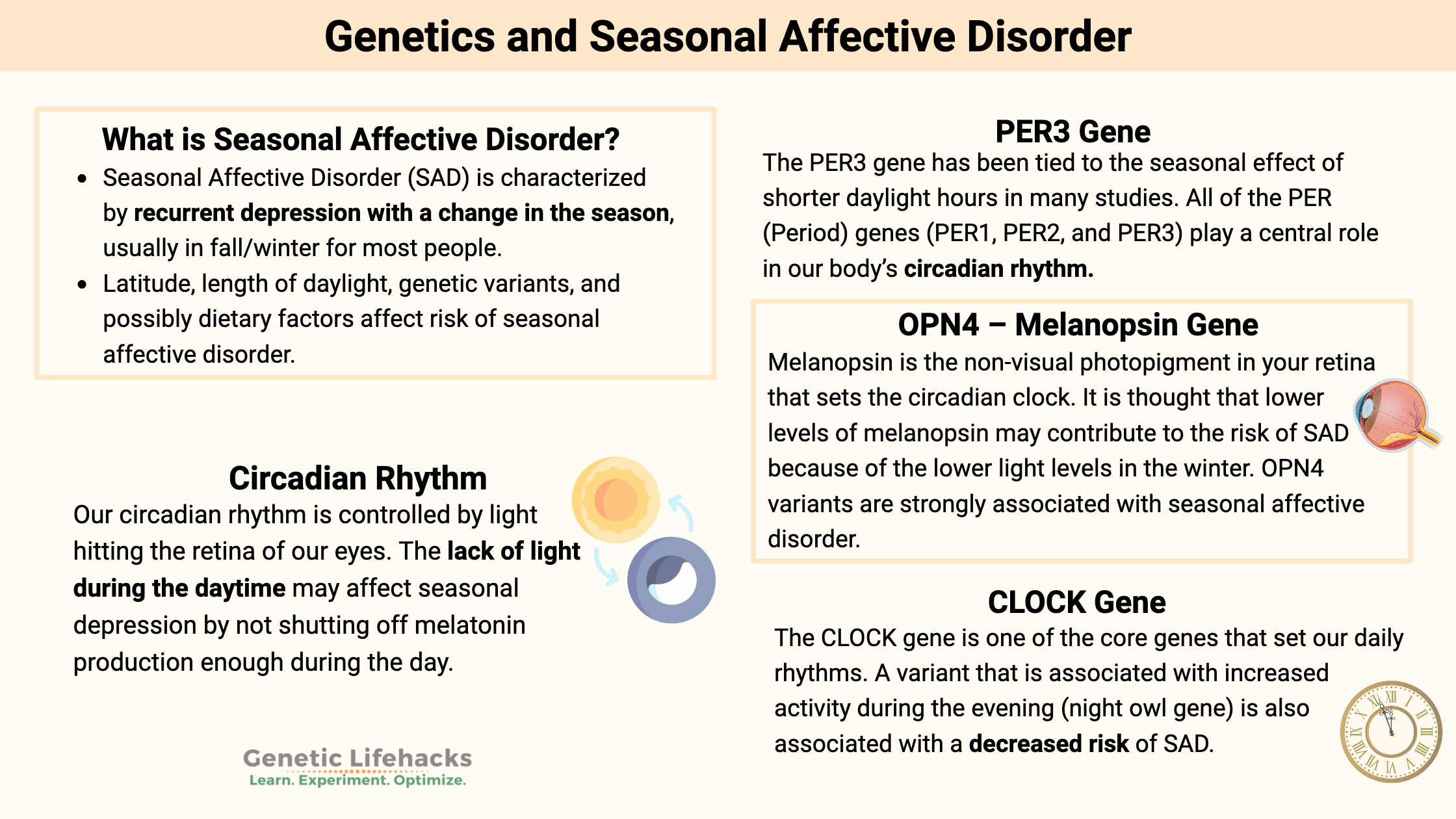
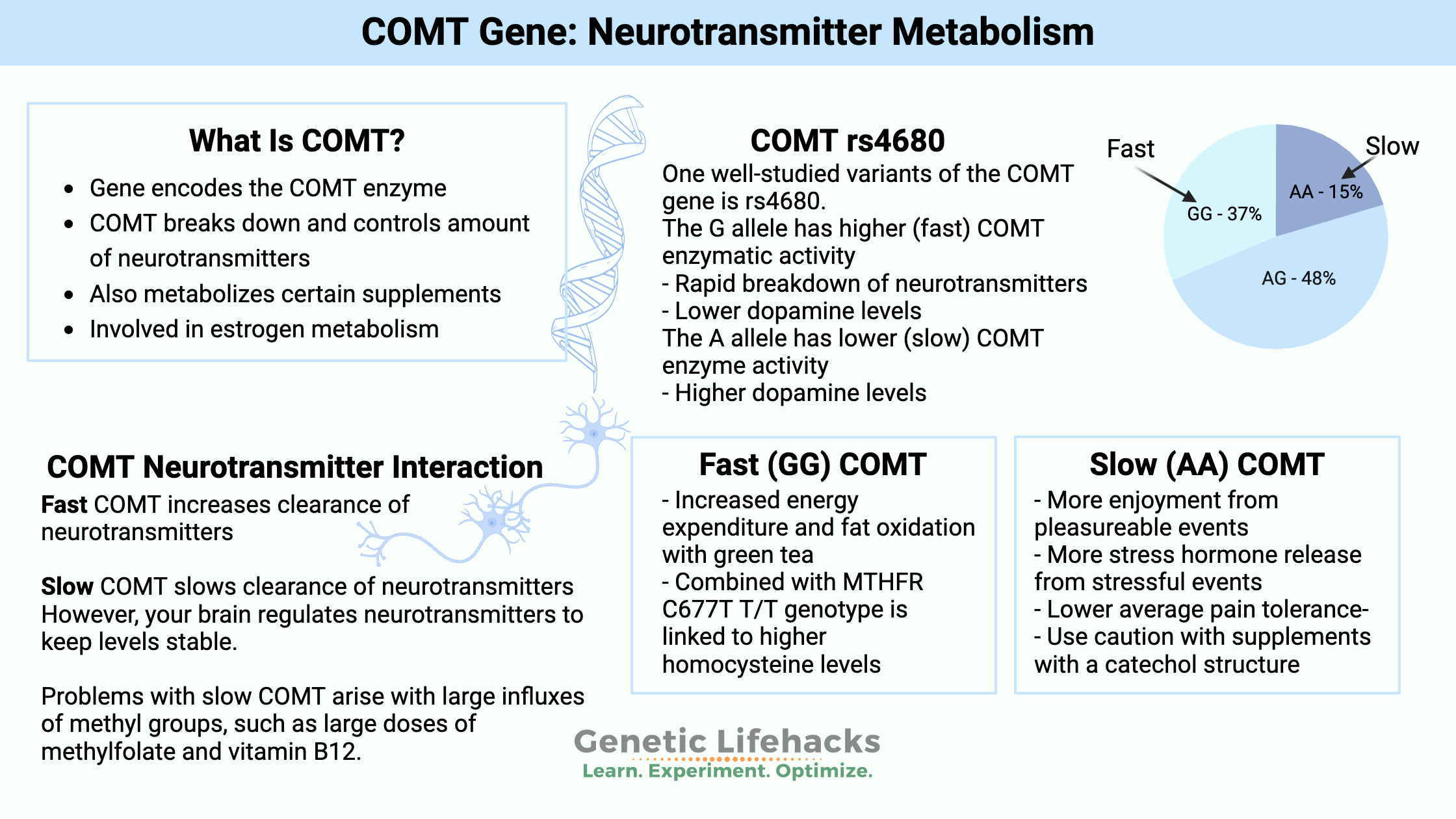
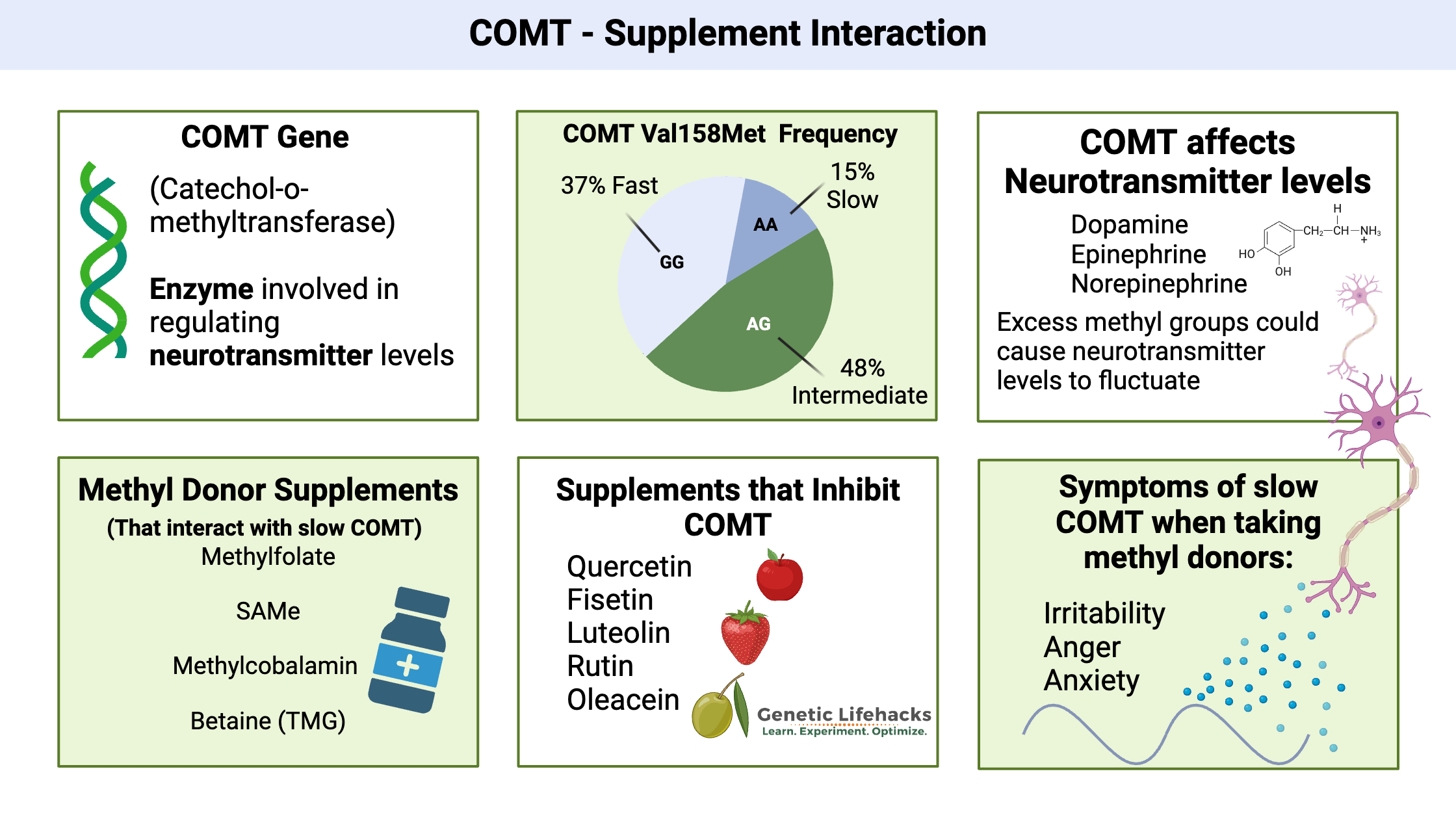
Dopamine Fasting: Addicted to the internet?
Genetics plays a role in susceptibility to addictive behavior, including internet and smartphone addiction. This article examines the latest fad of dopamine fasting along with genetic variants tied to internet use problems, smartphone usage disorder, and gaming disorders.