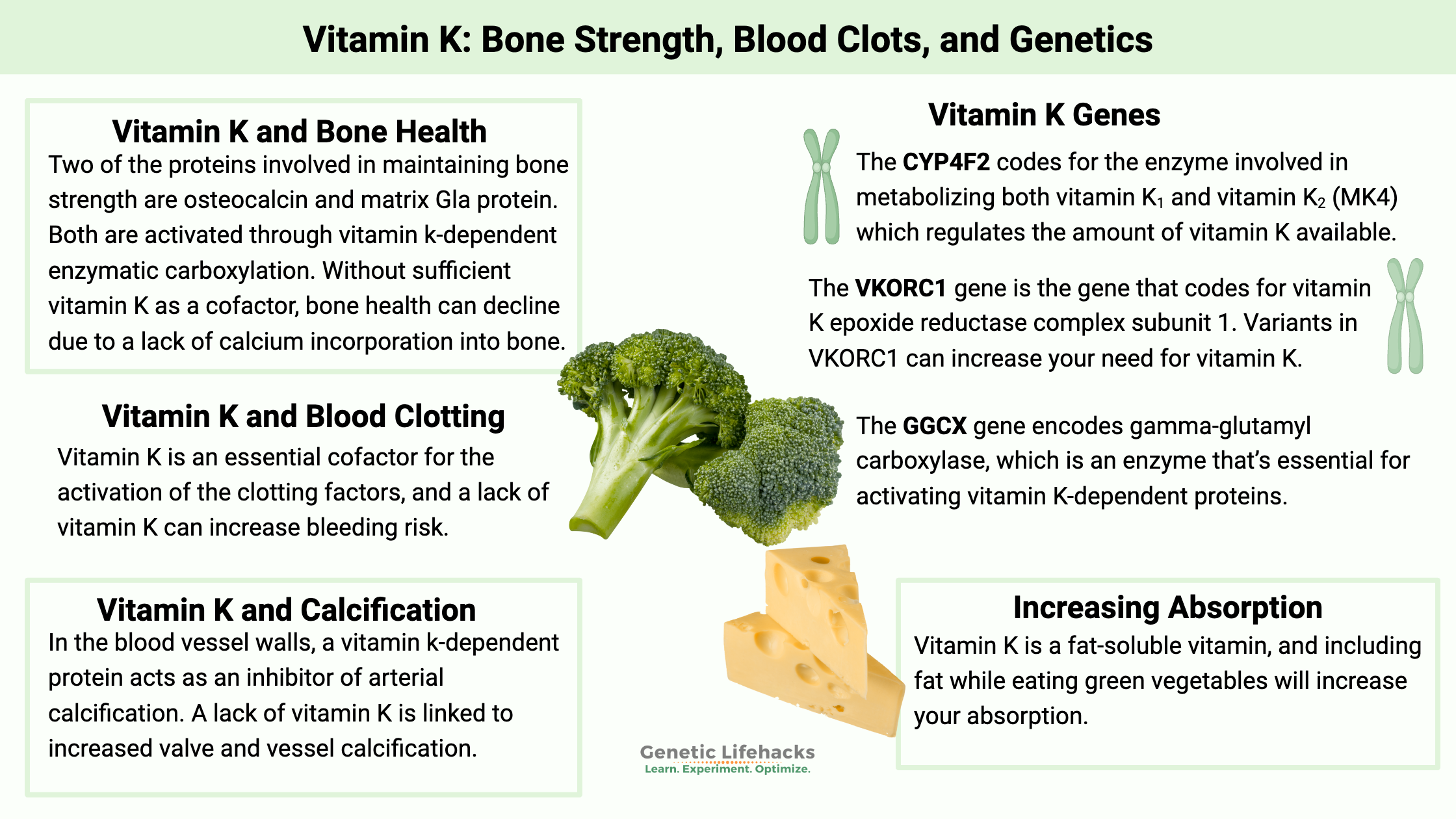
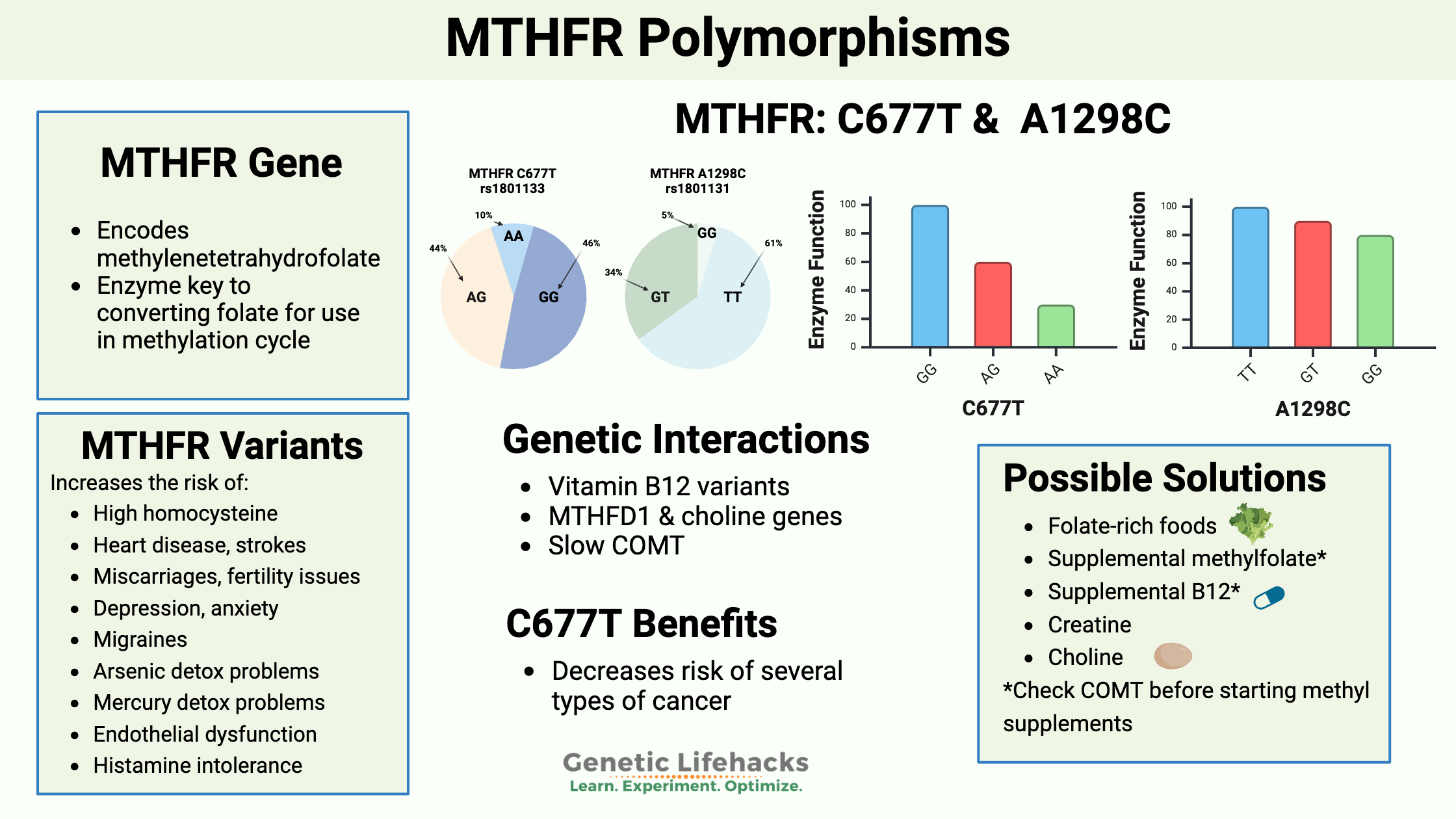
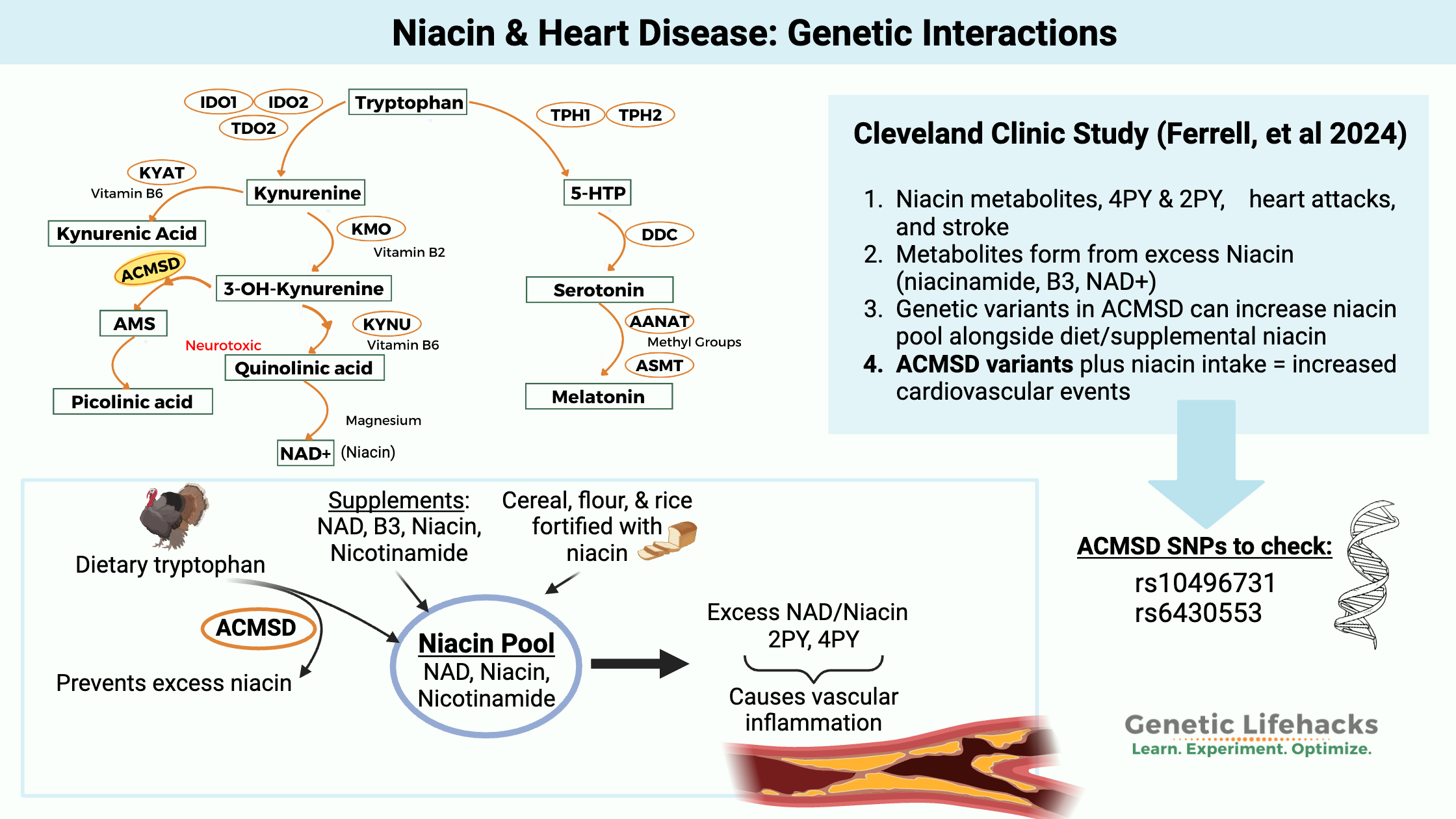
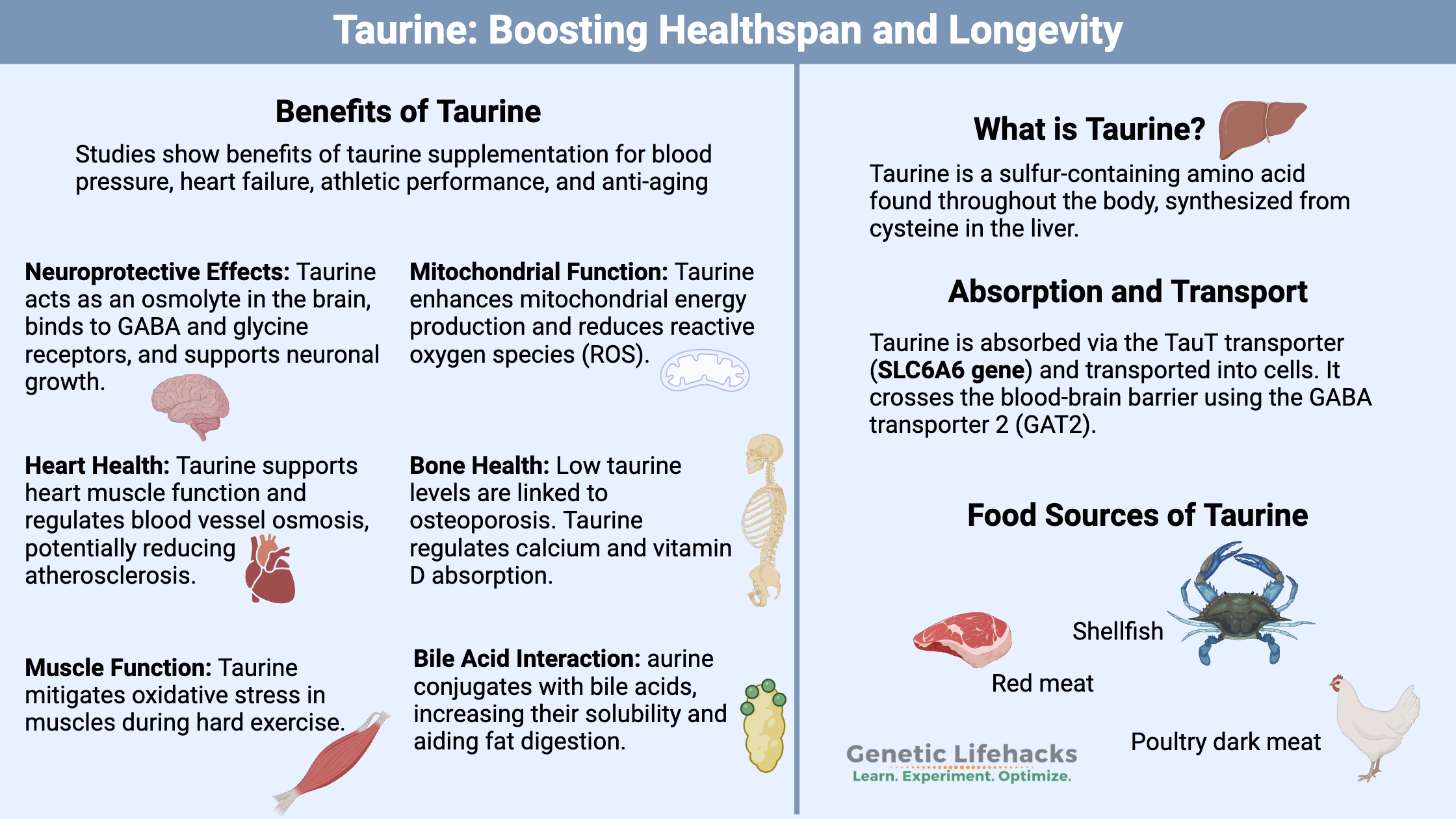
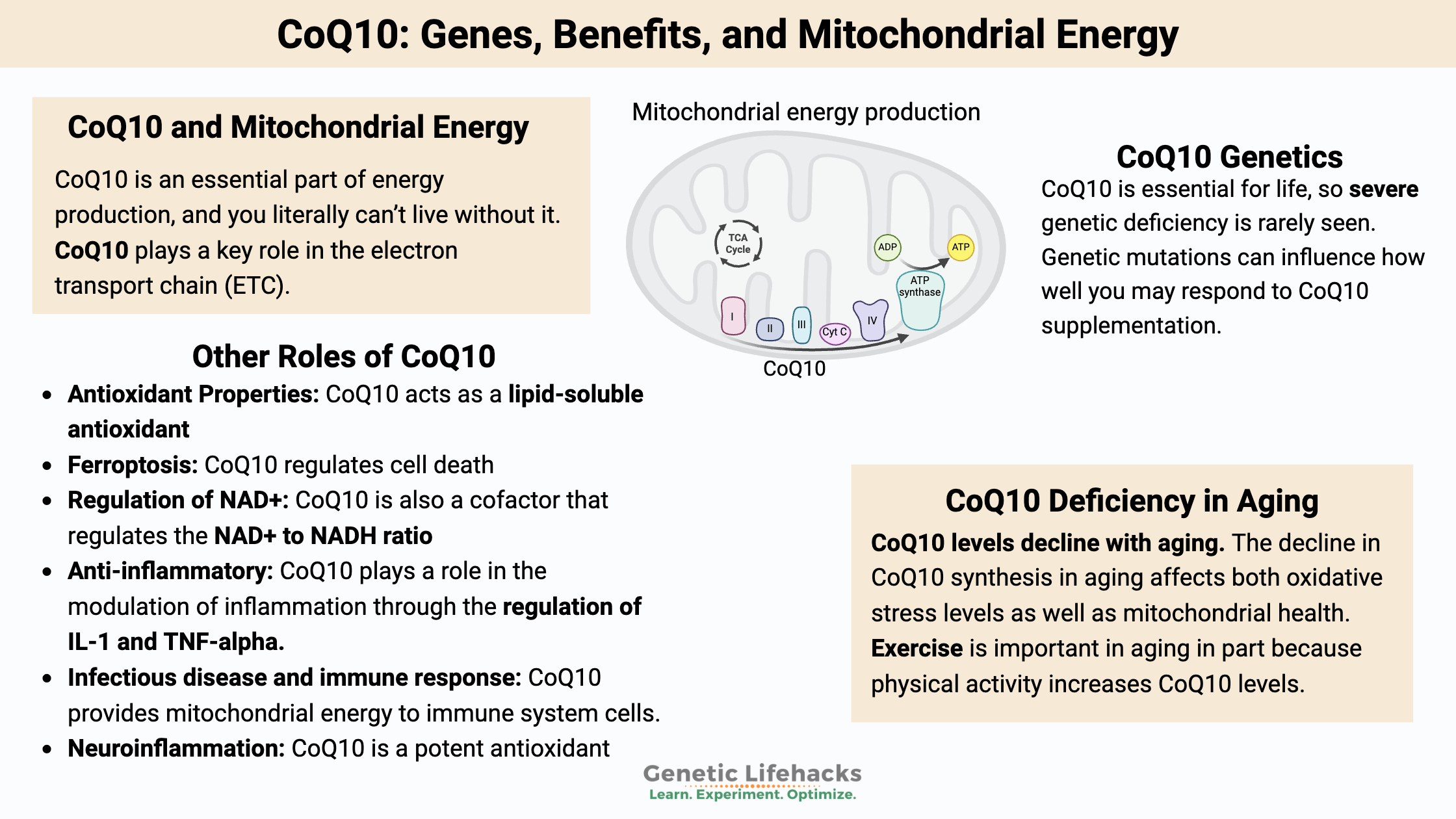
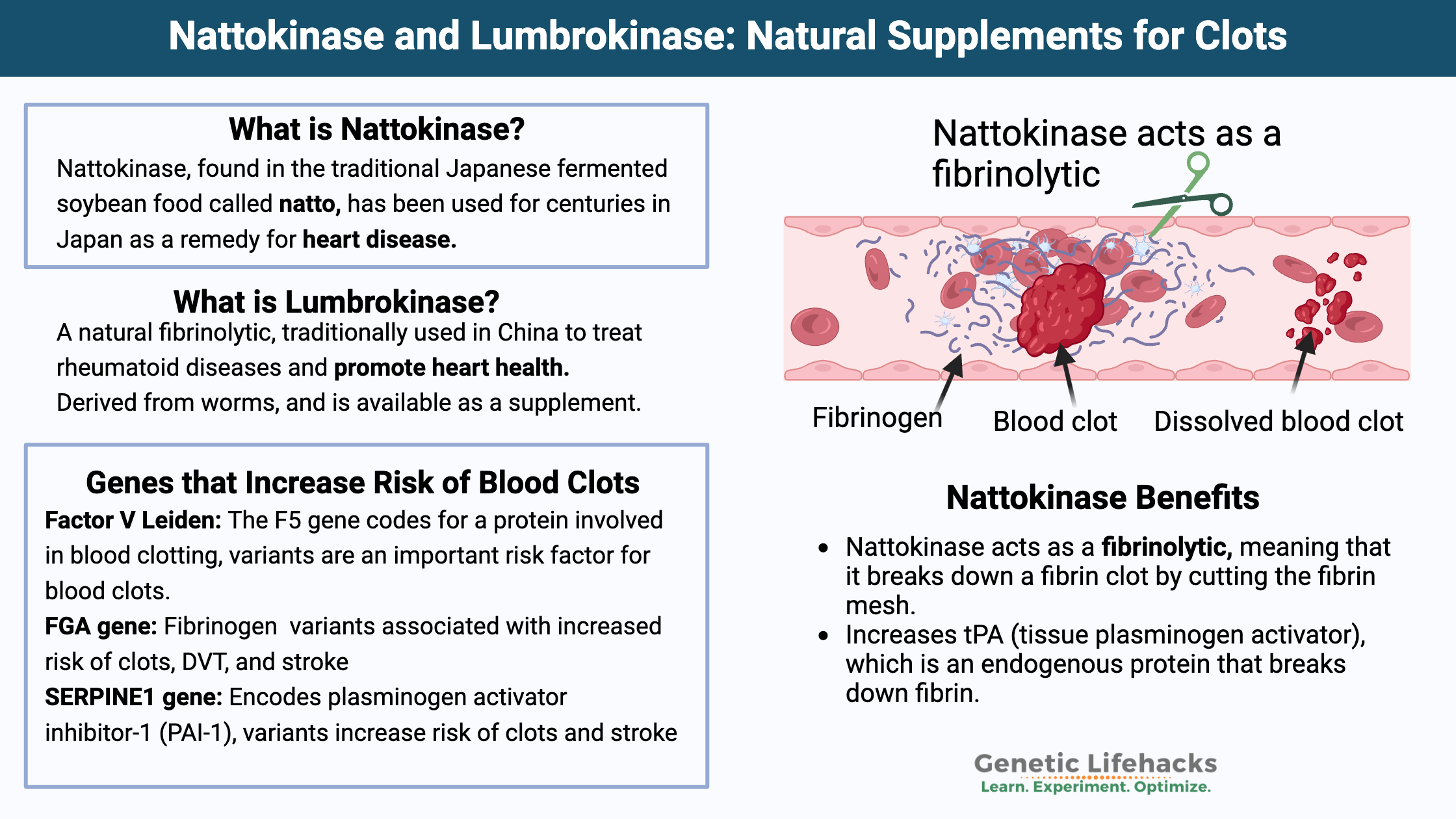
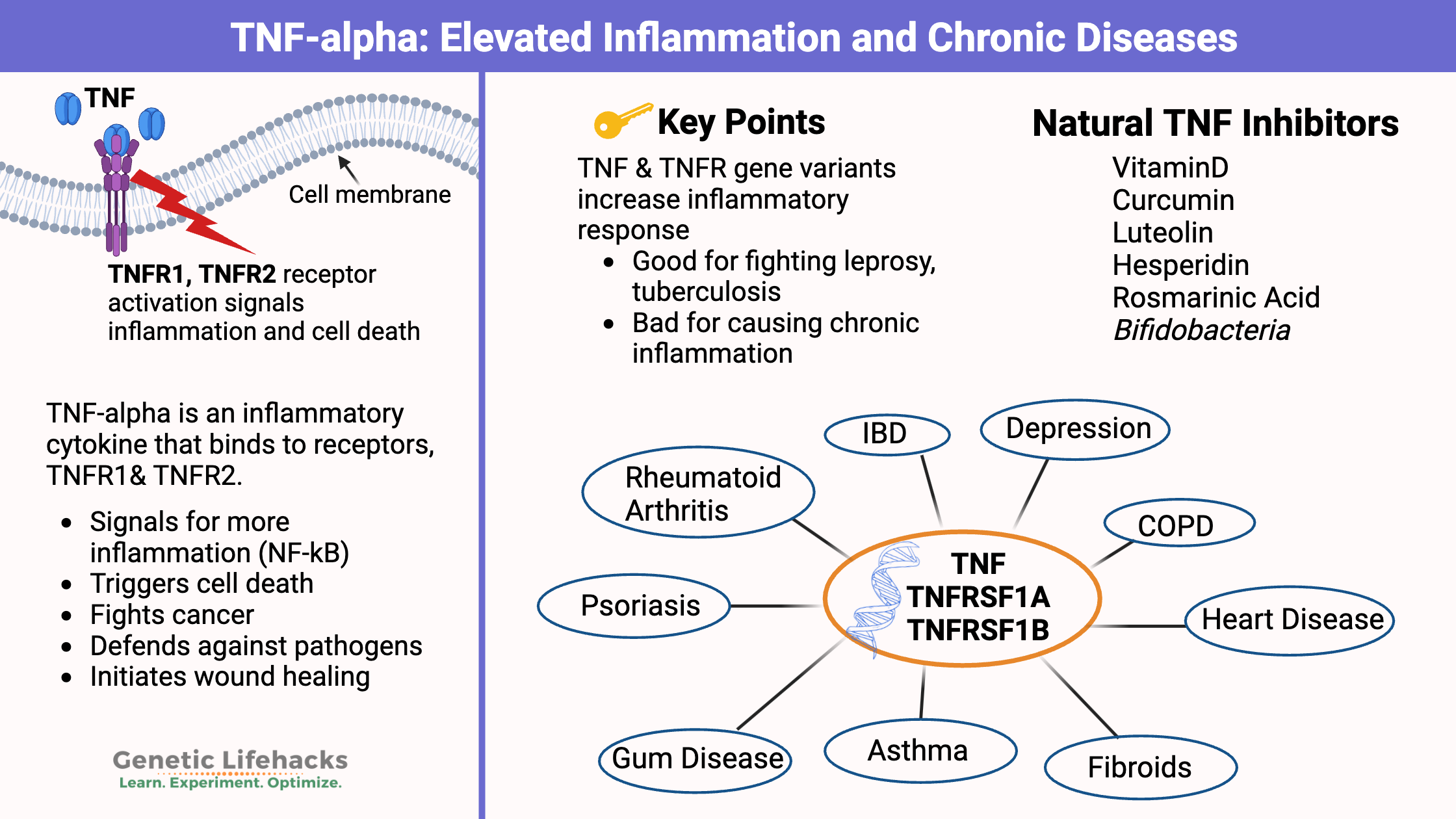
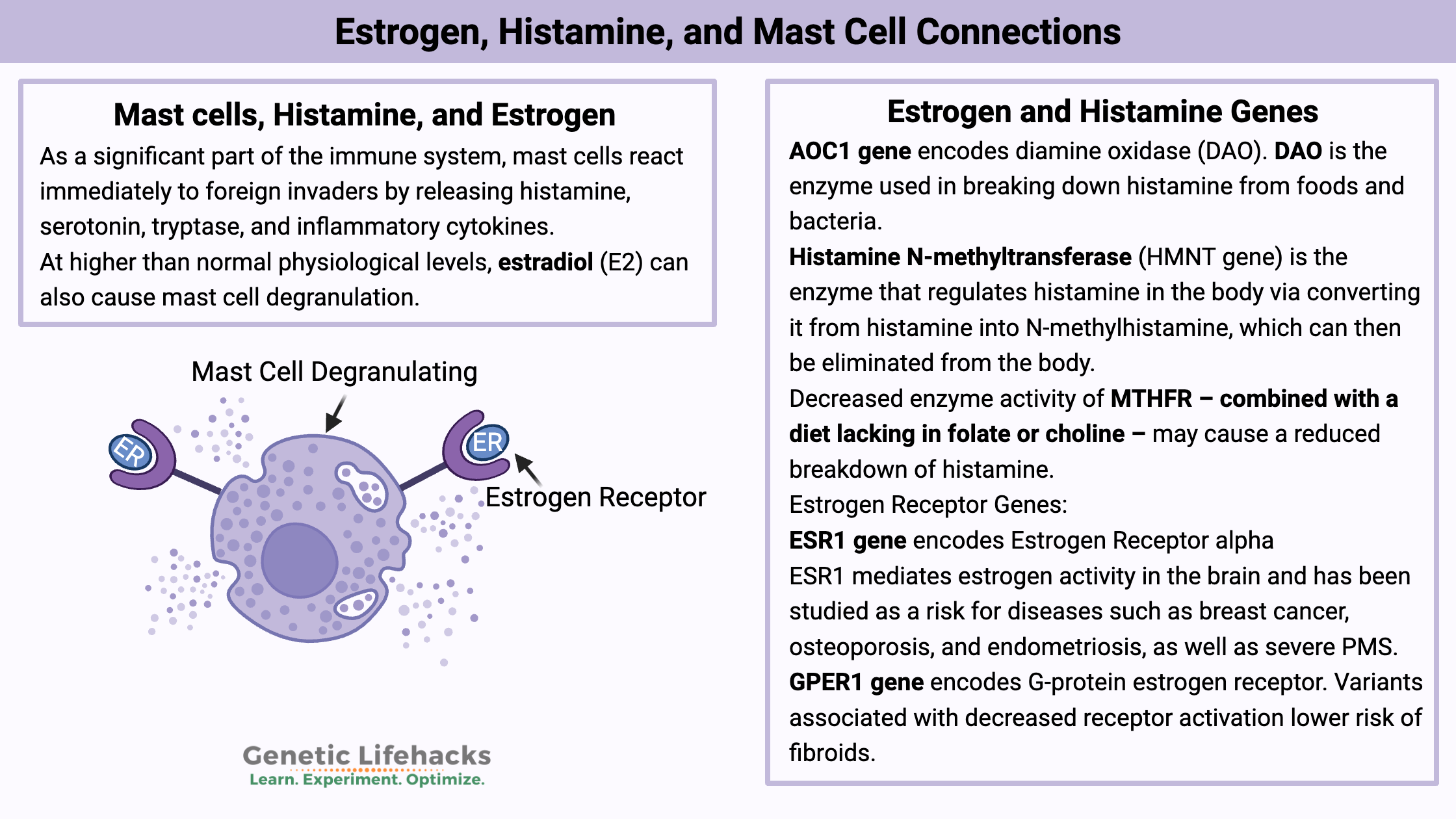
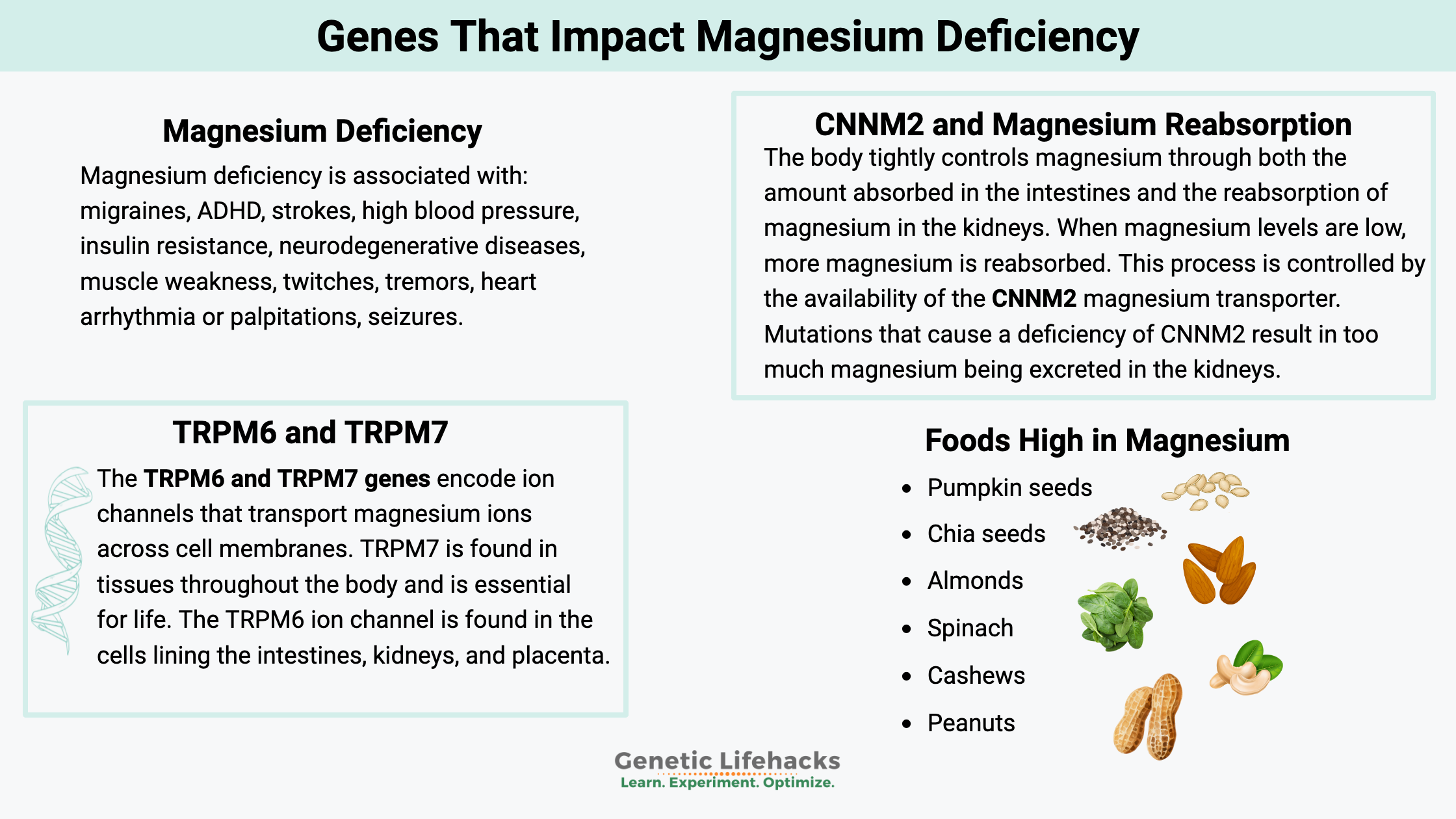
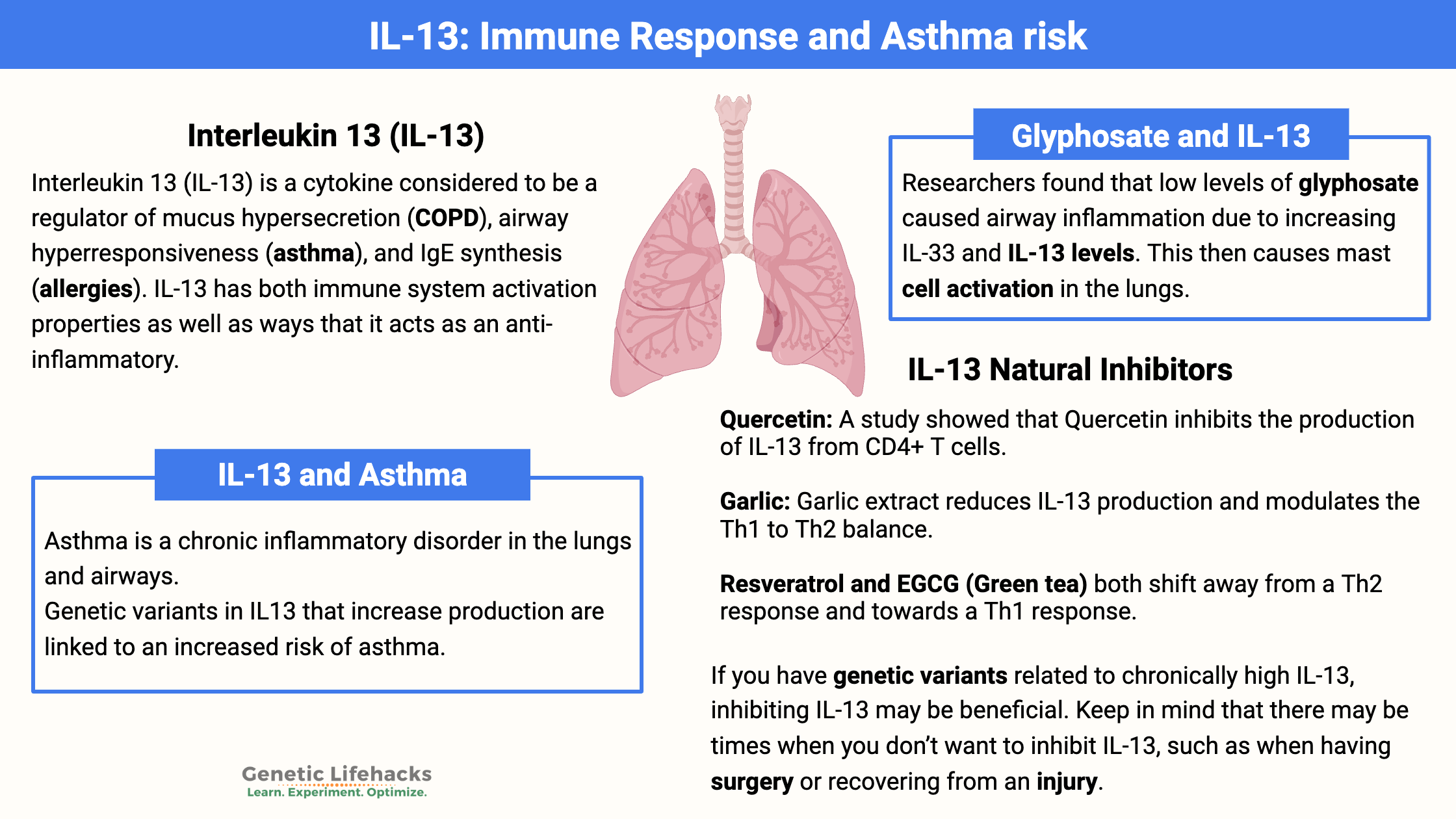
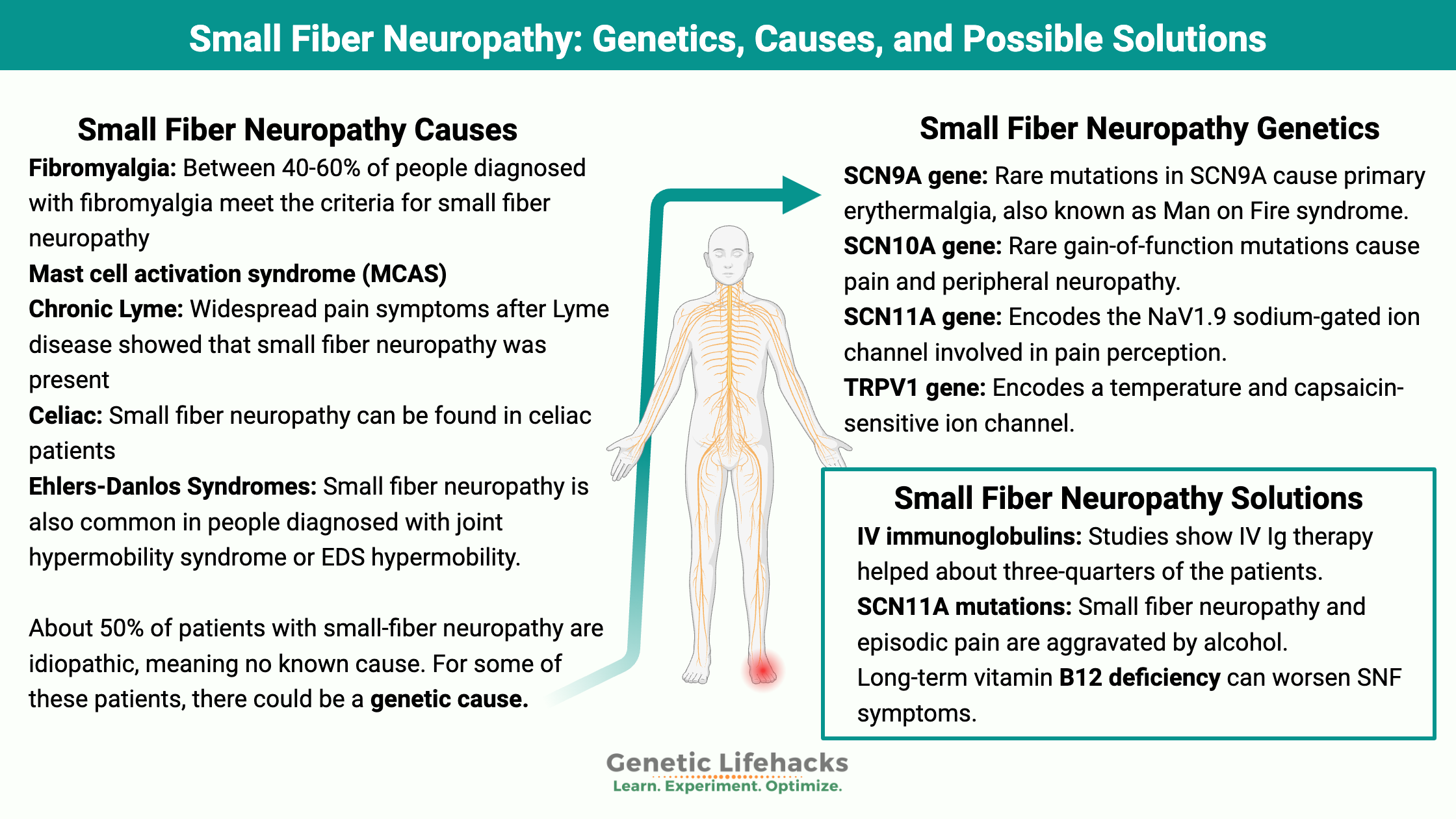
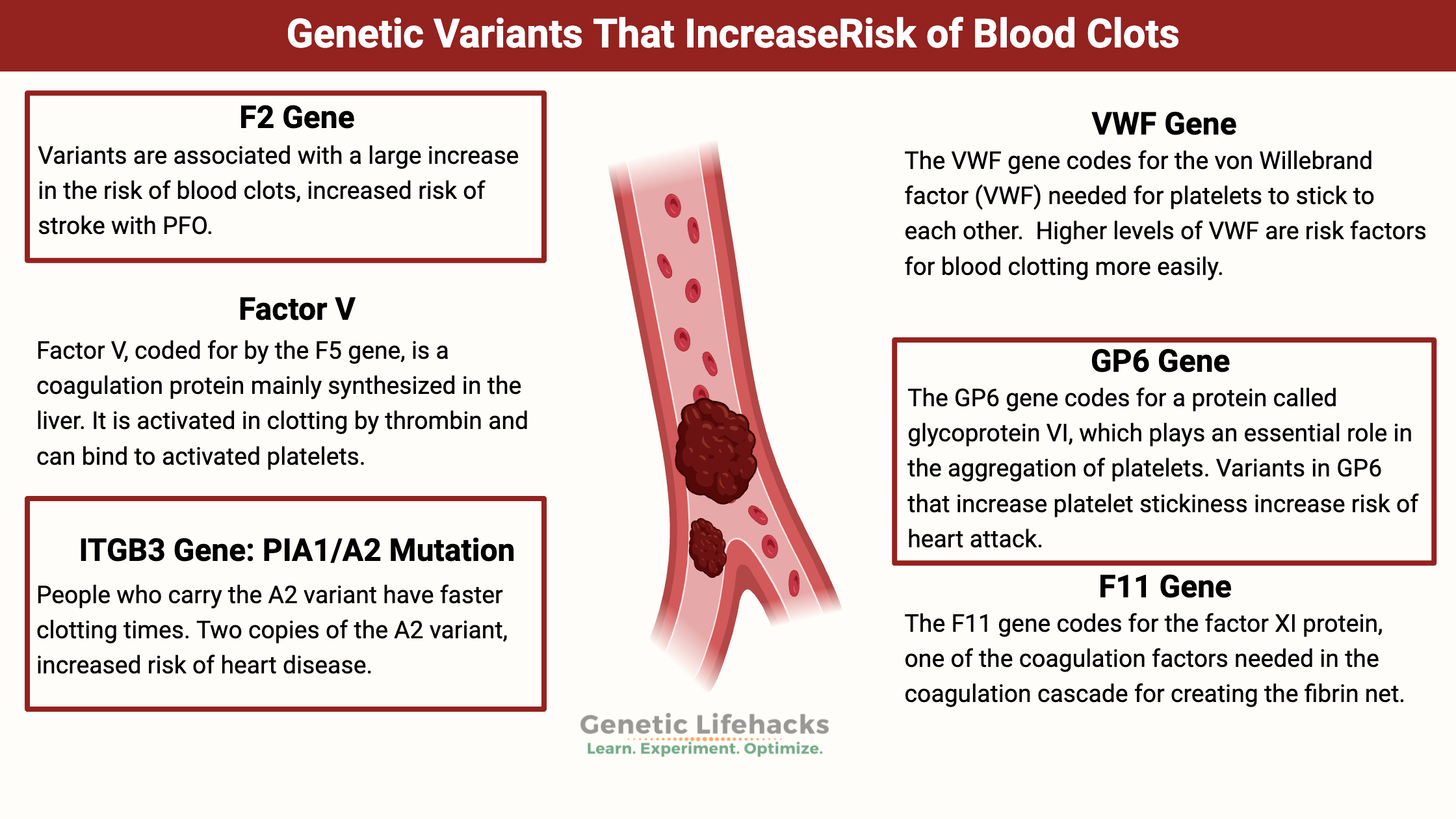
Vitamin K: Bone Strength, Blood Clots, Calcification, and Genetics
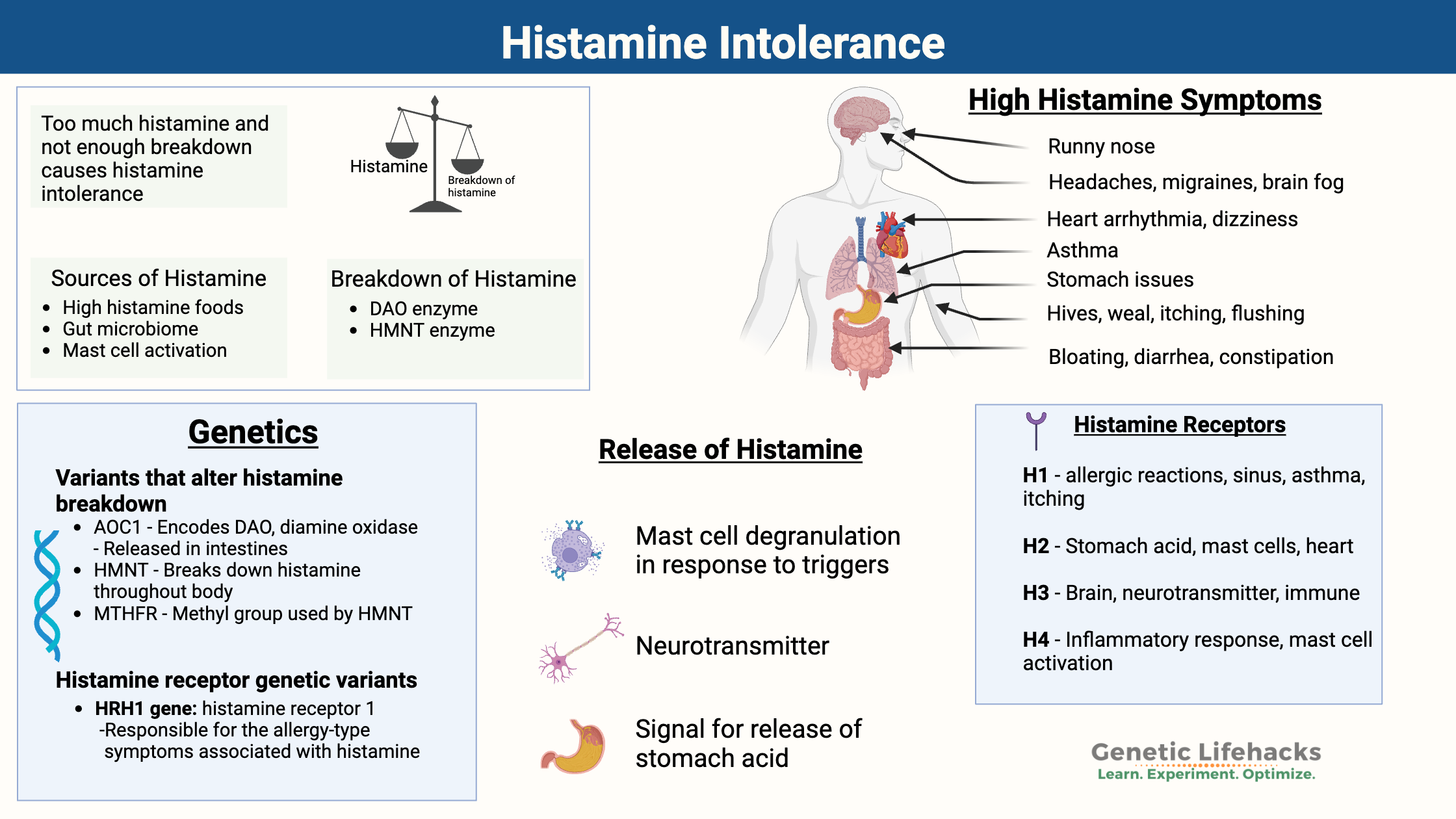
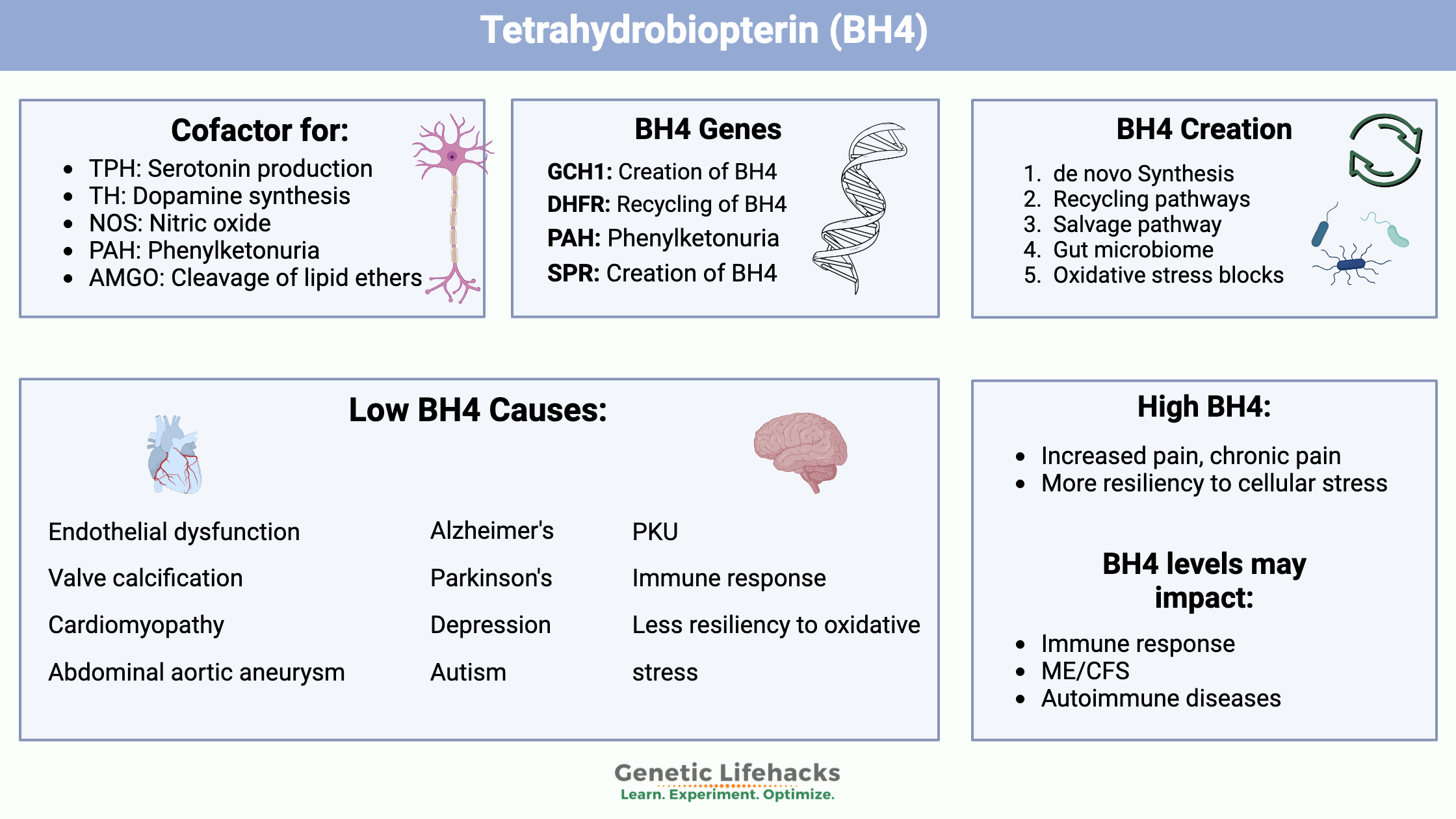
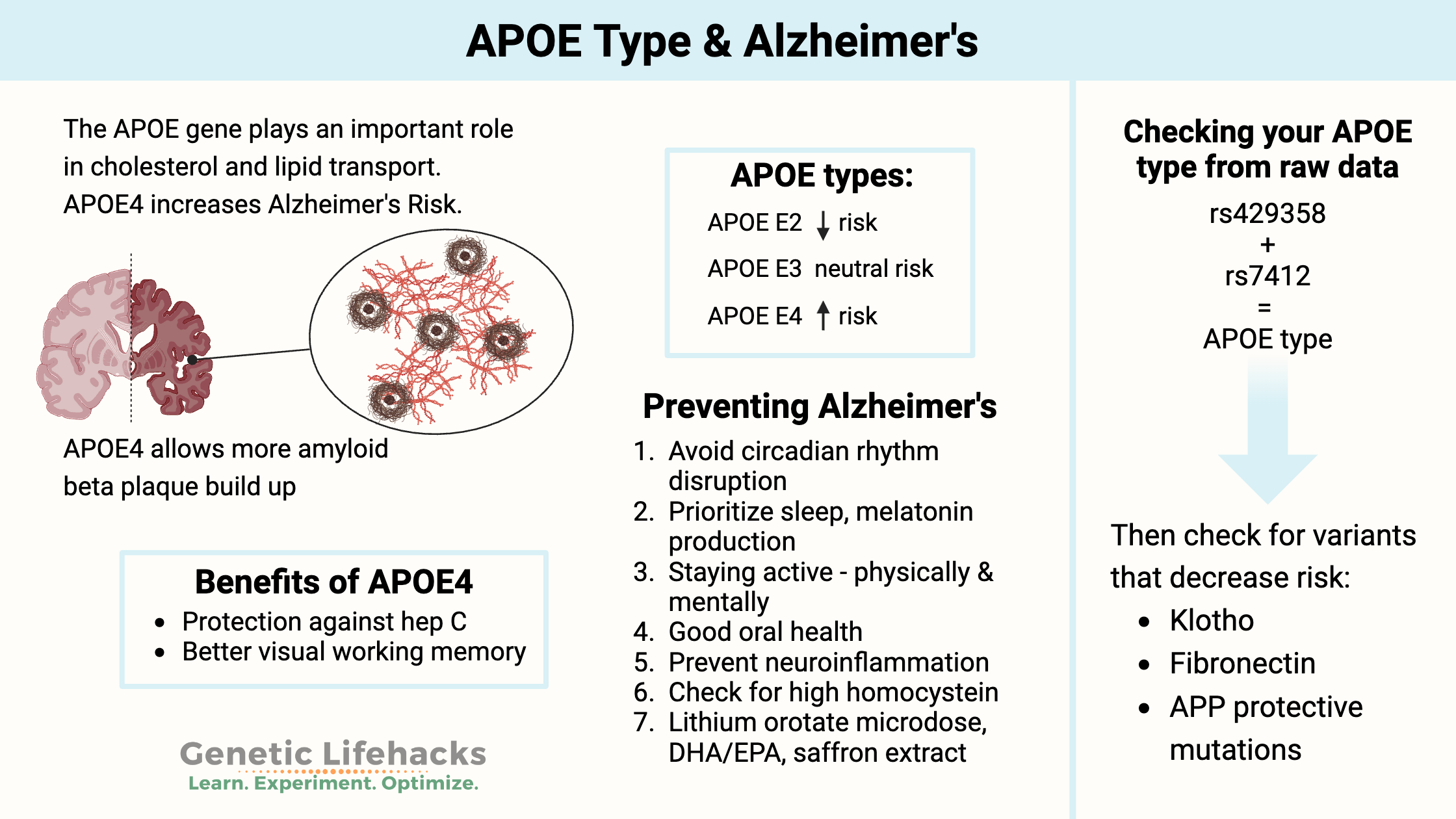
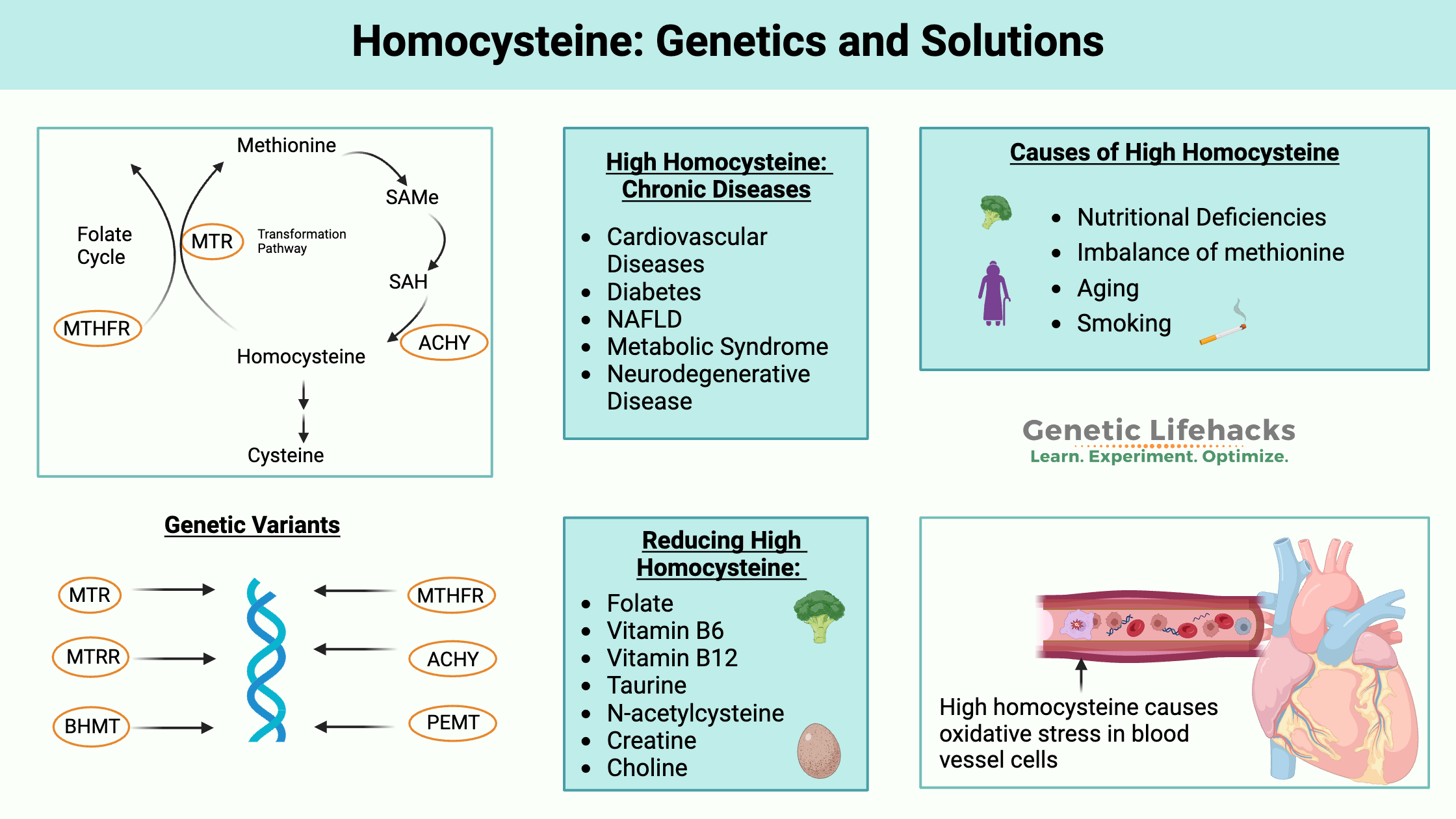
Genetic variations cause people to have higher or lower levels of vitamin K, which can affect blood clotting. Learn more about the genes that affect vitamin K and how it relates to your genetic raw data.